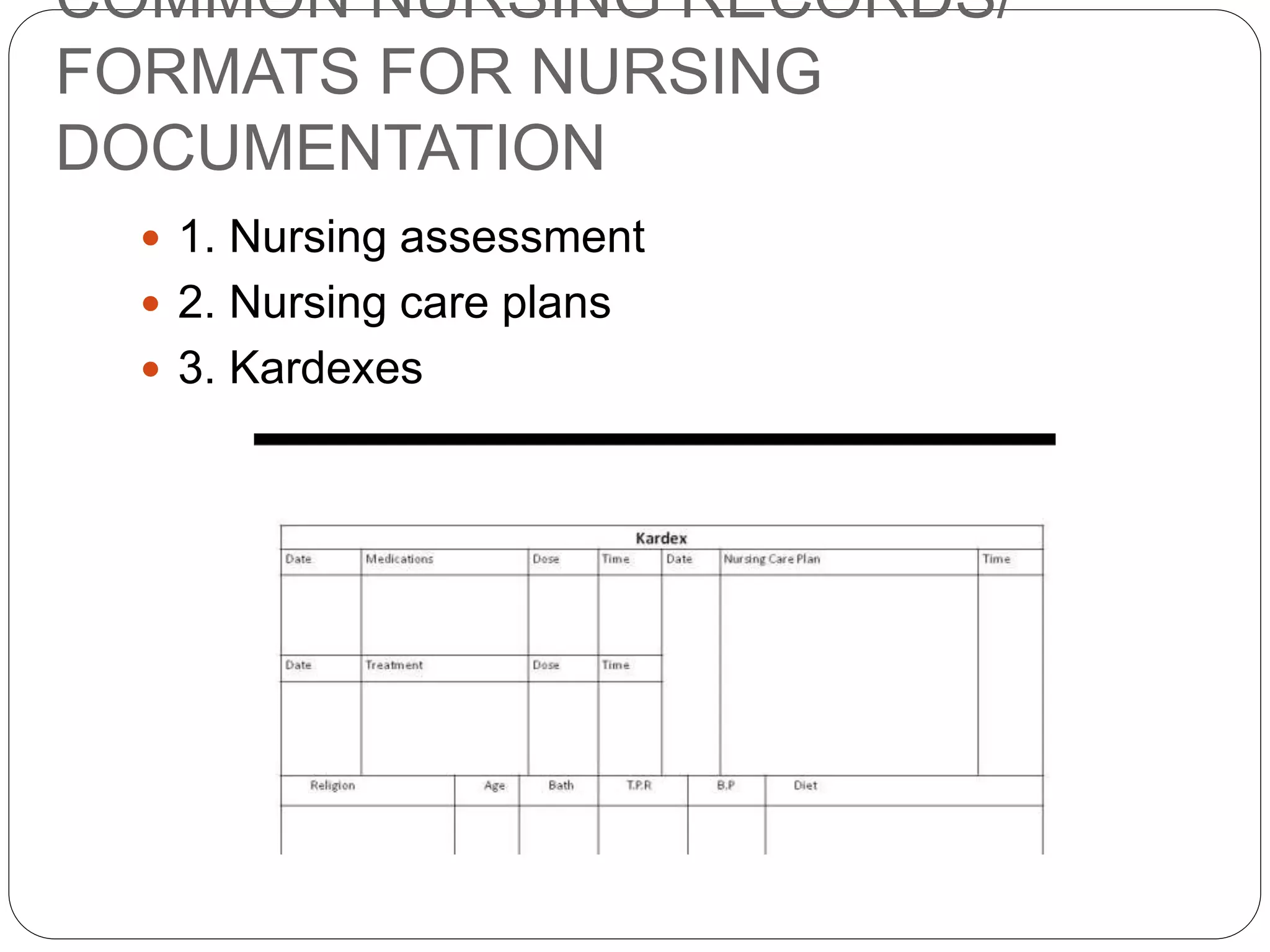
This document discusses documentation, recording, and reporting in healthcare. It defines documentation as written records of patient care and activities. Recording involves making entries in a patient's chart. Reports convey information orally or in writing. The purposes of reports and records include communication, planning care, legal documentation, research, education, auditing, reimbursement, and analysis. Key elements of legal and proper documentation include date, time, legibility, permanence, terminology, spelling, signature, accuracy, sequence, appropriateness, completeness, conciseness, and being factual. Guidelines for reporting emphasize being factual, accurate, complete, focused on current issues, and well-organized. Common types of reports include shift reports, transfer reports, telephone