Embed presentation




![Applying the median filter>>I=imread('img.bmp'); >> I=I(:,:,1);>> imshow(I);>> L = medfilt2(I,[3 3]);>>figure, imshow(L)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlabimagerestorationtechniques-091213023552-phpapp01/85/Matlab-Image-Restoration-Techniques-5-320.jpg)


![Rectifying background illuminationStep 2: Use Morphological Opening to Estimate the Background>>background = imopen(I,strel('disk',15));>>figure, surf(double(background(1:8:end,1:8:end))),zlim([0 255]); set(gca,'ydir','reverse');Step 3: View the Background Approximation as a SurfaceRectifying background illuminationStep 2: Use Morphological Opening to Estimate the BackgroundStep 3: View the Background Approximation as a SurfaceRectifying background illuminationStep 4: Subtract the Background Image from the Original ImageI2 = I - background; imshow(I2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlabimagerestorationtechniques-091213023552-phpapp01/85/Matlab-Image-Restoration-Techniques-8-320.jpg)
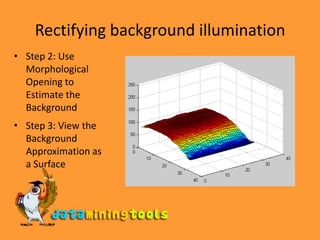



Linear filters like averaging and Gaussian filters can remove grain noise by averaging pixel values in a neighborhood. Median filters are better at removing outliers without reducing sharpness by setting a pixel to the median value in its neighborhood. The document demonstrates applying averaging and median filters in Matlab to remove noise, and using morphological opening to estimate and subtract a background illumination to rectify it.




![Applying the median filter>>I=imread('img.bmp'); >> I=I(:,:,1);>> imshow(I);>> L = medfilt2(I,[3 3]);>>figure, imshow(L)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlabimagerestorationtechniques-091213023552-phpapp01/85/Matlab-Image-Restoration-Techniques-5-320.jpg)


![Rectifying background illuminationStep 2: Use Morphological Opening to Estimate the Background>>background = imopen(I,strel('disk',15));>>figure, surf(double(background(1:8:end,1:8:end))),zlim([0 255]); set(gca,'ydir','reverse');Step 3: View the Background Approximation as a SurfaceRectifying background illuminationStep 2: Use Morphological Opening to Estimate the BackgroundStep 3: View the Background Approximation as a SurfaceRectifying background illuminationStep 4: Subtract the Background Image from the Original ImageI2 = I - background; imshow(I2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlabimagerestorationtechniques-091213023552-phpapp01/85/Matlab-Image-Restoration-Techniques-8-320.jpg)


