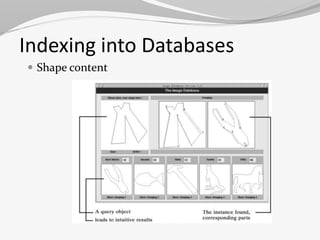
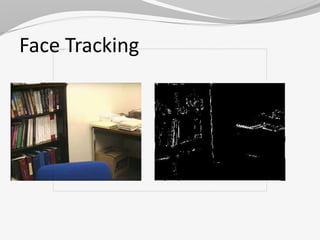
This document discusses image processing. It begins by defining image processing as the conversion of an image to digital form and performing operations to enhance the image or extract useful information. The main steps are importing, analyzing/manipulating, and outputting the image. Types of image processing include analog and digital. Applications include computer vision, medical imaging, and document processing. Advantages include manipulation and compact storage, while limitations include cost, time consumption, and lack of professionals. The document provides details on several image processing techniques and applications.