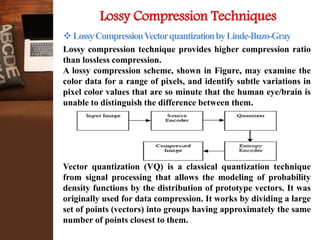
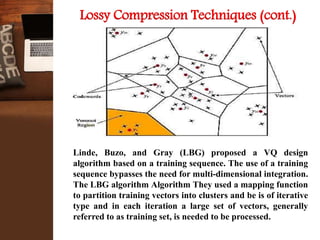
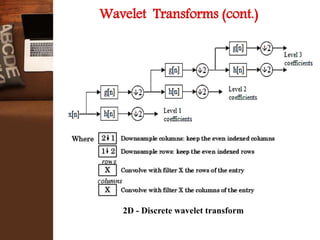
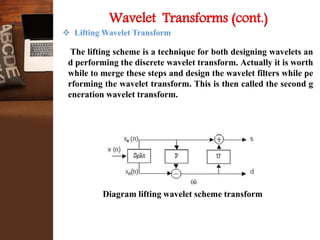
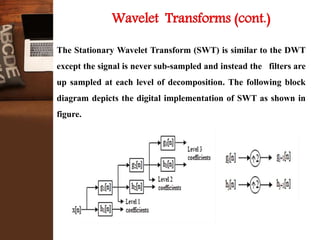
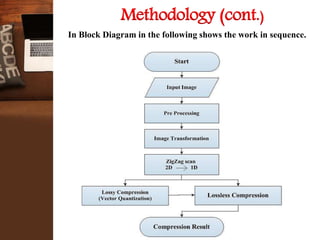
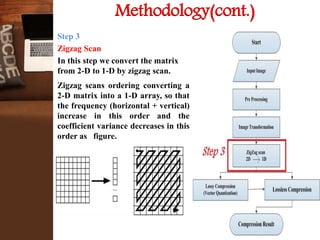
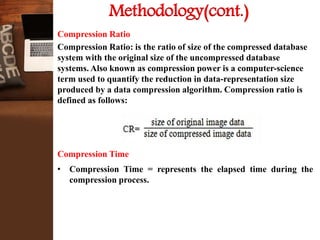
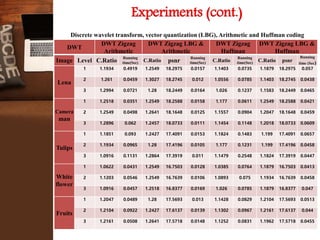
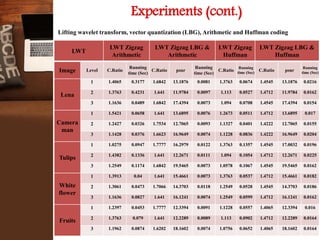
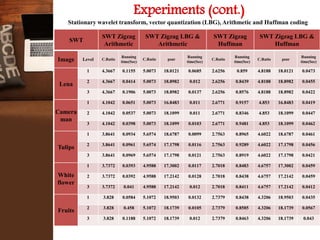
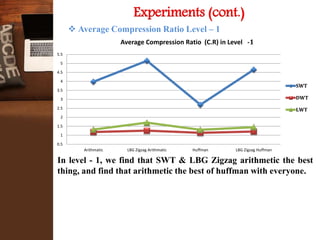
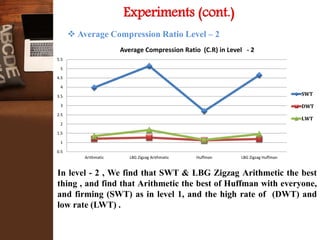
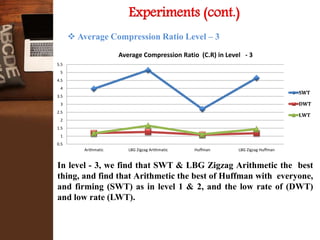
This document provides an overview of a research project on image compression. It discusses image compression techniques including lossy and lossless compression. It describes using discrete wavelet transform, lifting wavelet transform, and stationary wavelet transform for image transformation. Experiments were conducted to compare the compression ratio and processing time of different combinations of wavelet transforms, vector quantization, and Huffman/Arithmetic coding. The results were analyzed to evaluate the compression performance and efficiency of the different methods.