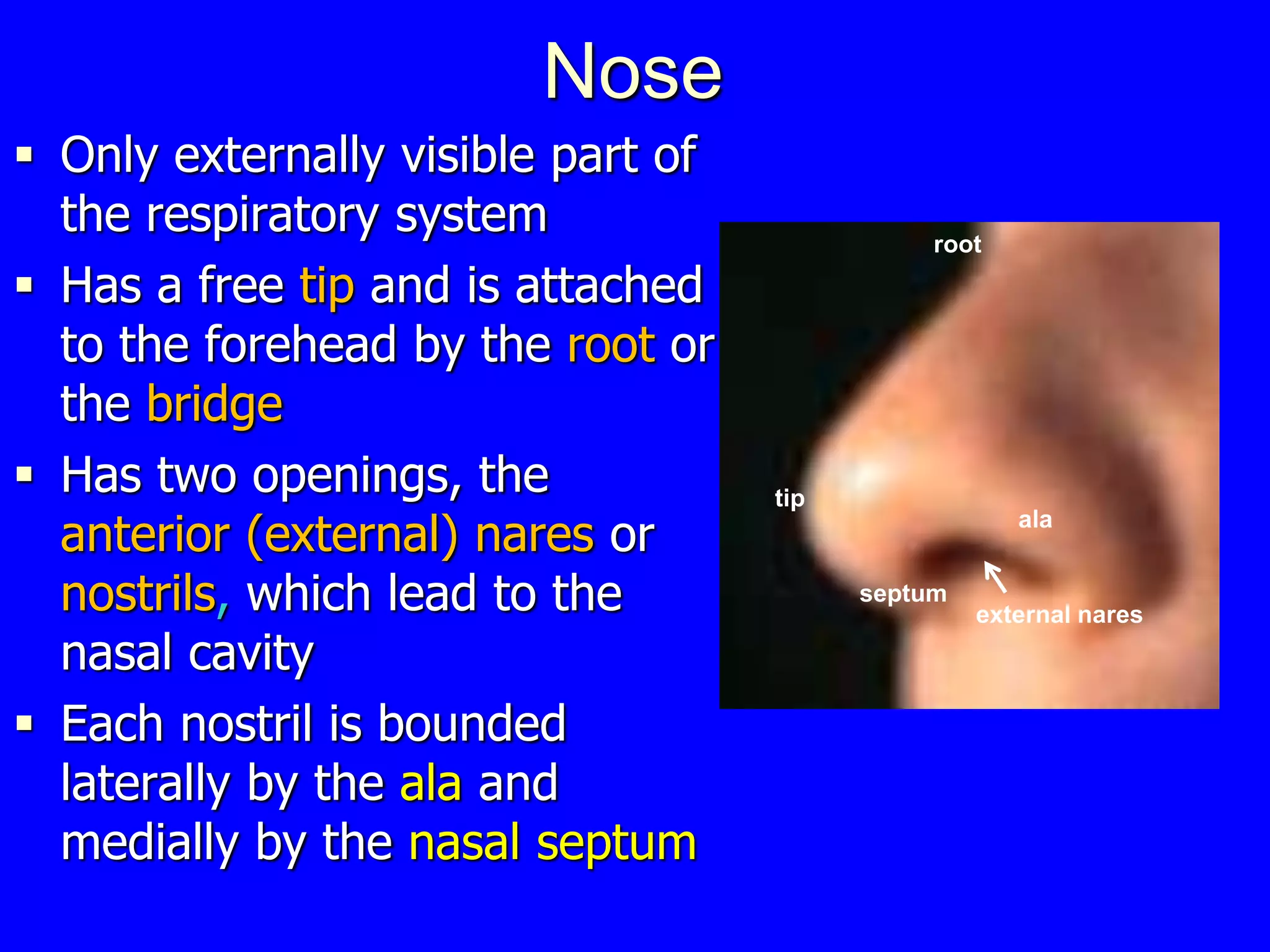
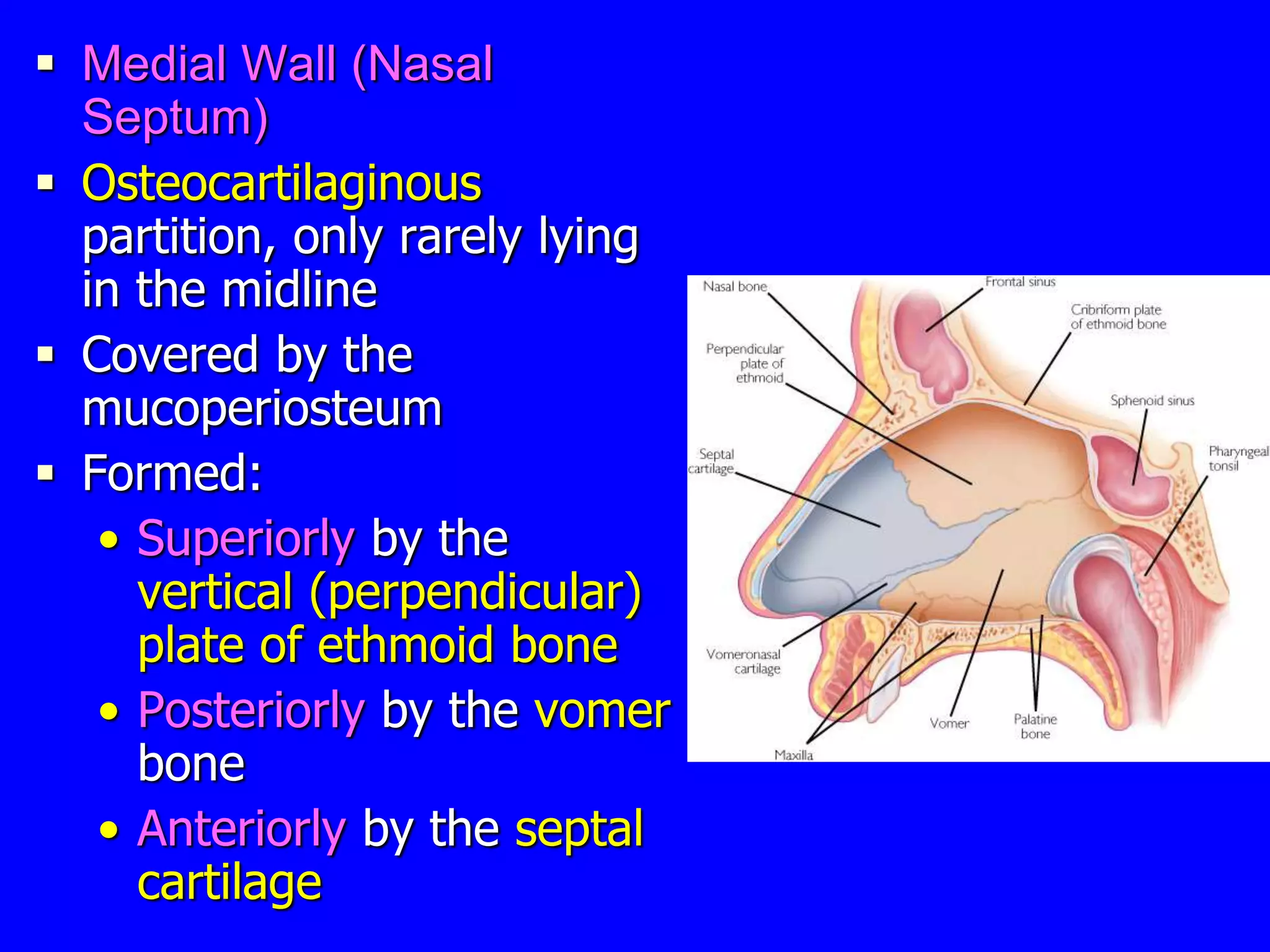
The nose and nasal cavity are responsible for warming, humidifying, and filtering inhaled air. The nasal cavity contains turbinates which increase its surface area and contain olfactory receptors. It connects to the paranasal sinuses, air-filled cavities in bones around the nose that help lighten the skull. The nose and sinuses are lined by respiratory mucosa and olfactory mucosa in some areas. They are supplied by nerves and blood vessels. Common conditions include rhinitis, sinusitis, and epistaxis.