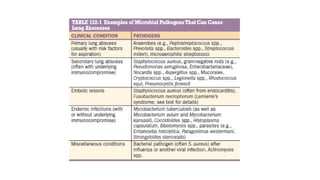
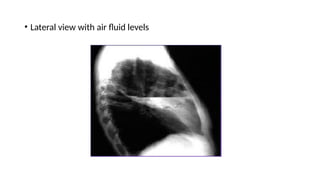
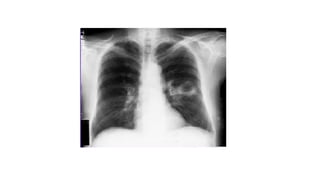
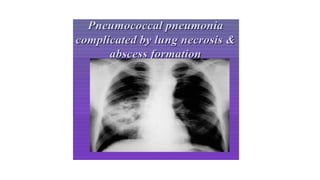
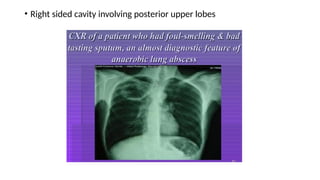
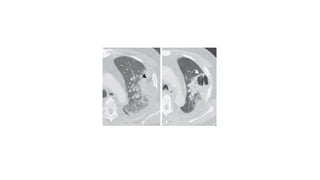
Lung abscesses are areas of necrosis and cavitation in the lungs, often due to microbial infection, primarily occurring from aspiration of anaerobic bacteria. They can be classified as primary or secondary, with varying risk factors, epidemiology, and clinical manifestation, and are diagnosed through imaging and microbiological studies. Treatment typically involves antibiotics and may require surgical intervention depending on the abscess's size and underlying causes.