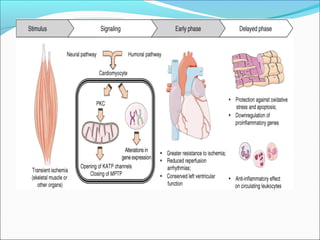
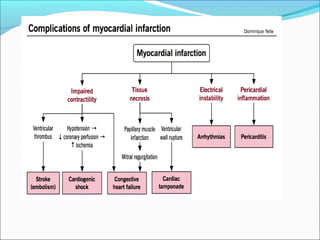
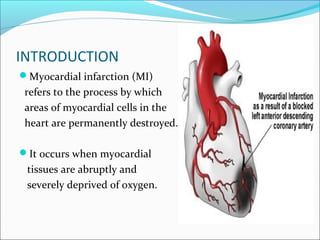
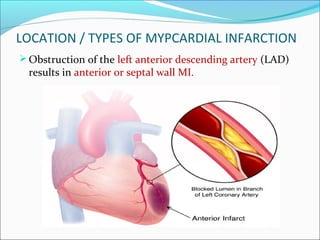
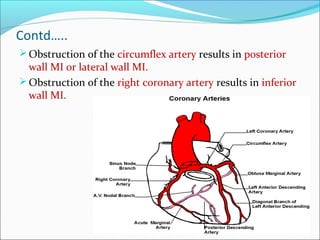
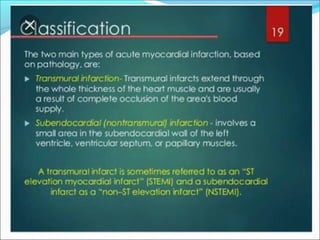
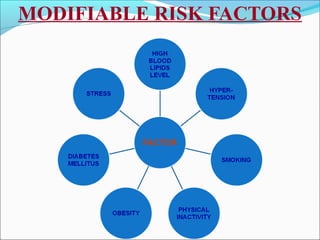
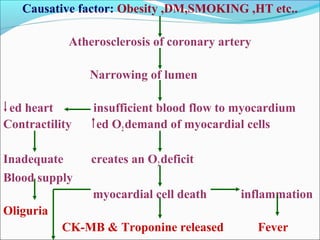
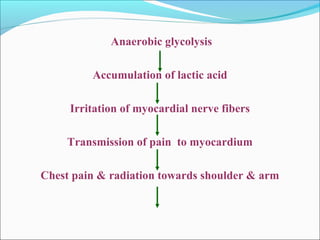
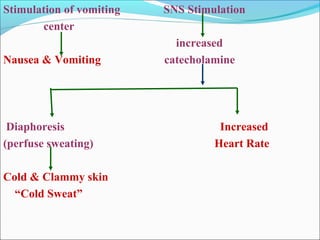
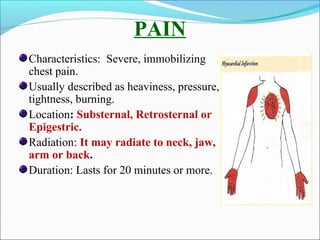
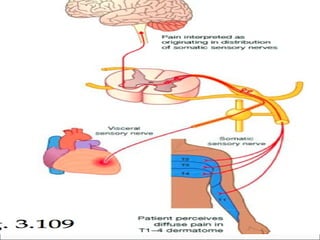
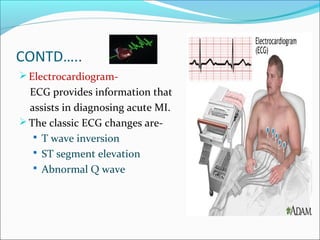
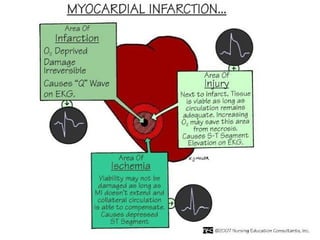
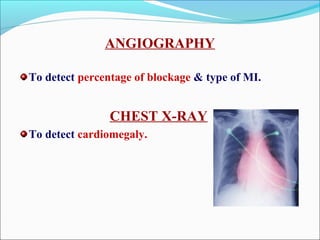
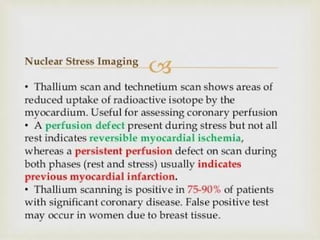
Myocardial infarction, also known as a heart attack, occurs when an area of heart muscle is damaged due to inadequate blood flow. It is usually caused by atherosclerosis leading to narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries. The left anterior descending artery supplies the anterior and septal walls of the heart, while the circumflex artery supplies the posterior and lateral walls. Obstruction of these arteries results in different types of MIs in the respective regions. Risk factors include age over 40, family history, male sex, obesity, diabetes, smoking, and hypertension. Symptoms include chest pain and potential radiation to the arm or shoulder. Diagnostic tests include electrocardiograms, cardiac enzymes, angiography, and imaging scans.










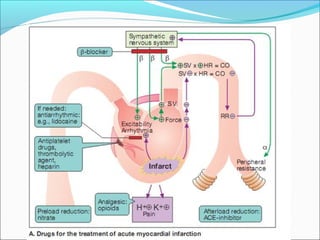
![1.To reduce pain anxiety and apprehension
1. After pain is not relieved by 3 doses of GTN given 5
min. apart , an opioid analgesic [morphine
/pethidine] or diazepam is administered parentally.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/myocardialinfractionramesh-170504133703/85/Myocardial-infarction-32-320.jpg)
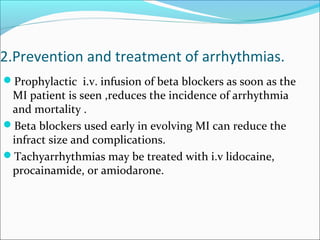

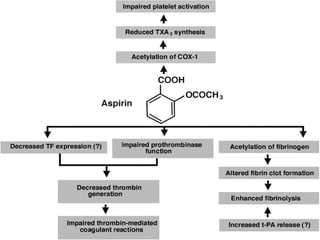
![4.Prevention of thrombus extension, embolism,
venous thrombosis-
1. Aspirin [162- 325 mg] as soon as MI is suspected. This is
continued at 80- 160 mg / day.
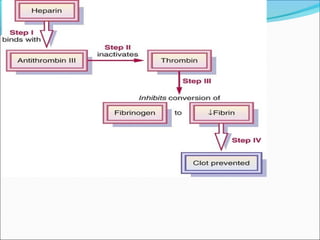
2. Anticoagulants [heparin followed by oral
anticoagulants ]are used to prevent deep vein thrombosis
and pulmonary or arterial embolism.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/myocardialinfractionramesh-170504133703/85/Myocardial-infarction-37-320.jpg)



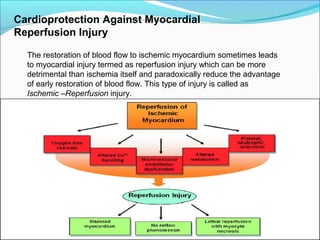
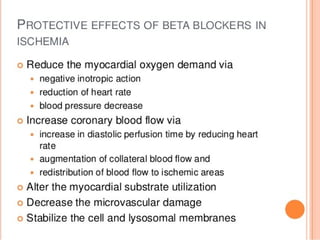
![a. The drugs which target these pathways are
cyclosporine, erythropoietin, glucagon-like peptide 1
and atrial nitriuretic peptides. The new strategies for protection
against reperfusion injury are Ischemic conditioning, targeting
the RISK [reperfusion injury salvage kinase]pathway, targeting
mitochondrial[phosphotyrosyl phosphatase activator] PTPa
b. The ischemic conditioning can be defined as preconditioning
when performed before reperfusion and post-conditioning . In clinical
practice the remote ischemic preconditioning is carried out with brief
occlusion of blood flow to either upper or lower limb by periodically inflating
and releasing the blood pressure cuff. The remote ischemic
preconditioning is believed to activate changes in intracellular
kinase and mitochondria that are cardio-protective..
c. The ischemic post-conditioning is carried out by transient
balloon occlusion of the infarct related artery. The remote
ischemic post-conditioning is carried out by transient occlusion
of other than the infarct related coronary artery.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/myocardialinfractionramesh-170504133703/85/Myocardial-infarction-52-320.jpg)