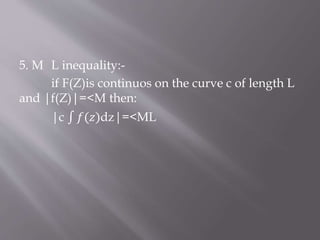Embed presentation
Downloaded 101 times





![1. Linearity:-
c [ 𝑘1𝑓(𝑧)+k2 G(z)]dz=k1 c 𝑓(𝑧) dz +k2 c 𝐺(𝑧)dz
For example:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maths-160502125523/85/Line-integral-ML-inequality-6-320.jpg)



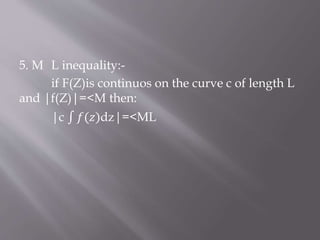


The document discusses line integrals of complex functions along curves. It defines a line integral as the integral of a continuous function f(z) along a curve c from point A to B, which is divided into n parts. It also provides the definition of a line integral in terms of a parameterization z(t) of the curve from a to b. Finally, it lists five properties of line integrals: linearity, sense reversal, partitioning of paths, integral inequality, and the Mean Value inequality.





![1. Linearity:-
c [ 𝑘1𝑓(𝑧)+k2 G(z)]dz=k1 c 𝑓(𝑧) dz +k2 c 𝐺(𝑧)dz
For example:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maths-160502125523/85/Line-integral-ML-inequality-6-320.jpg)