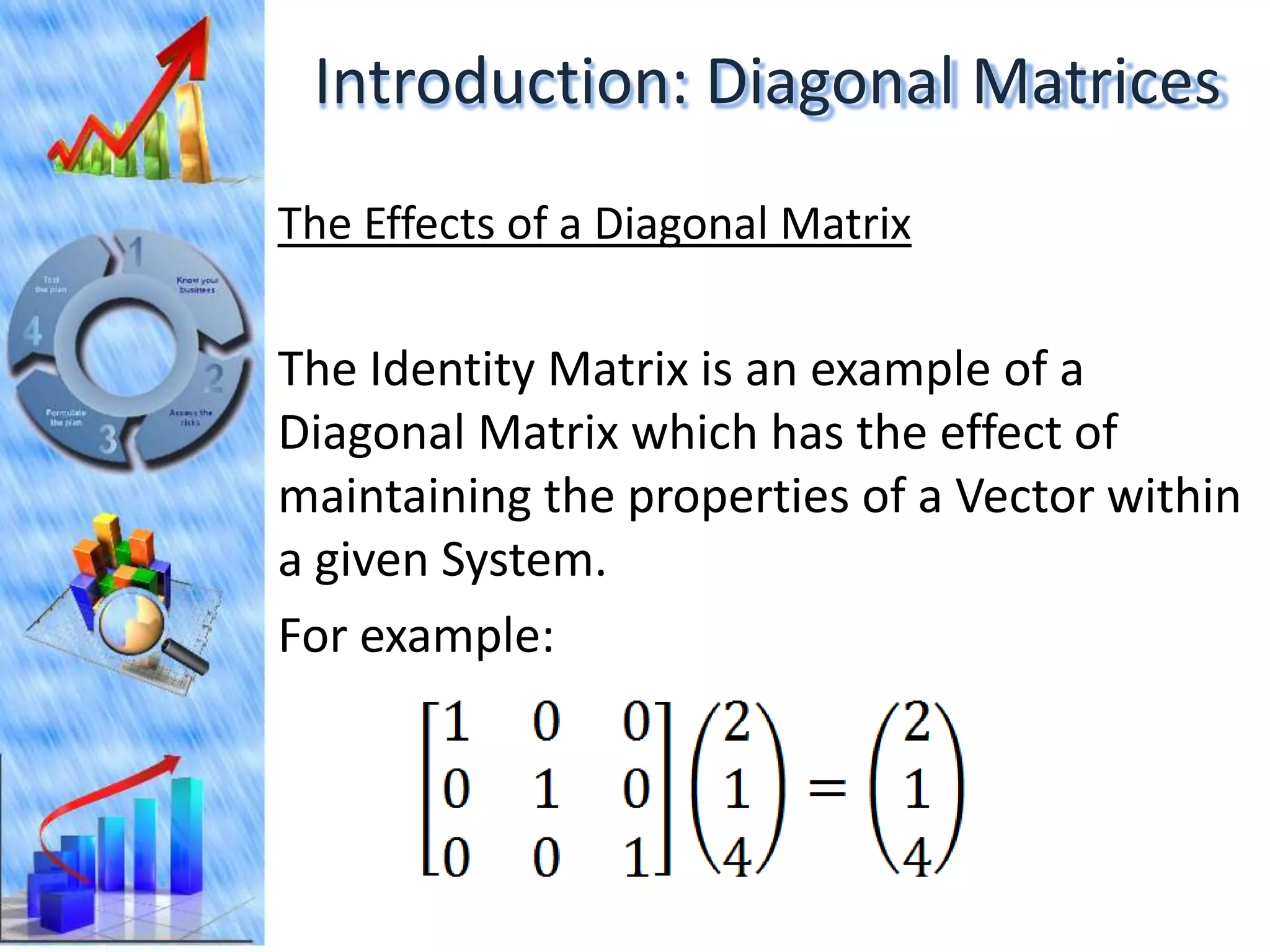
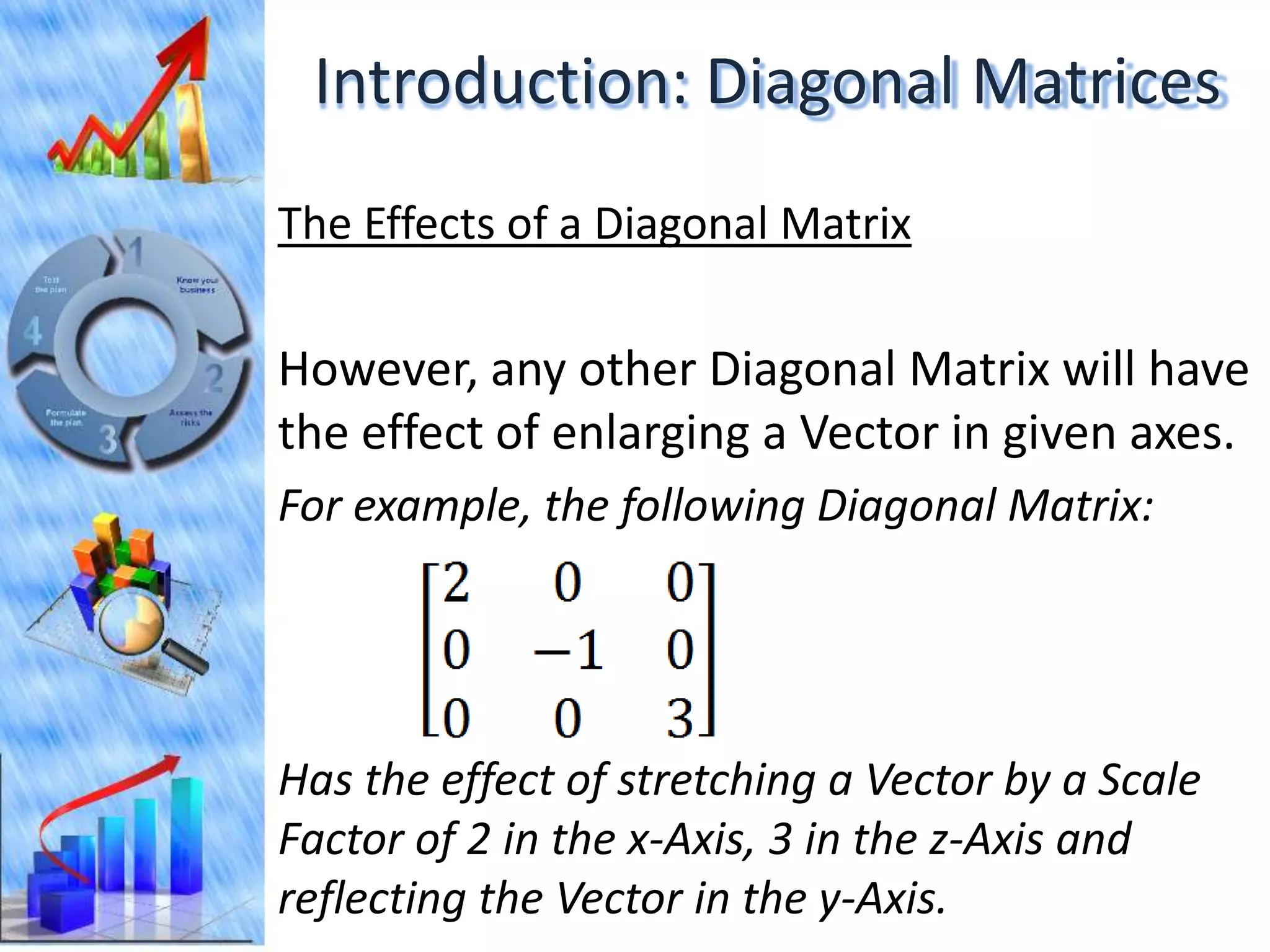
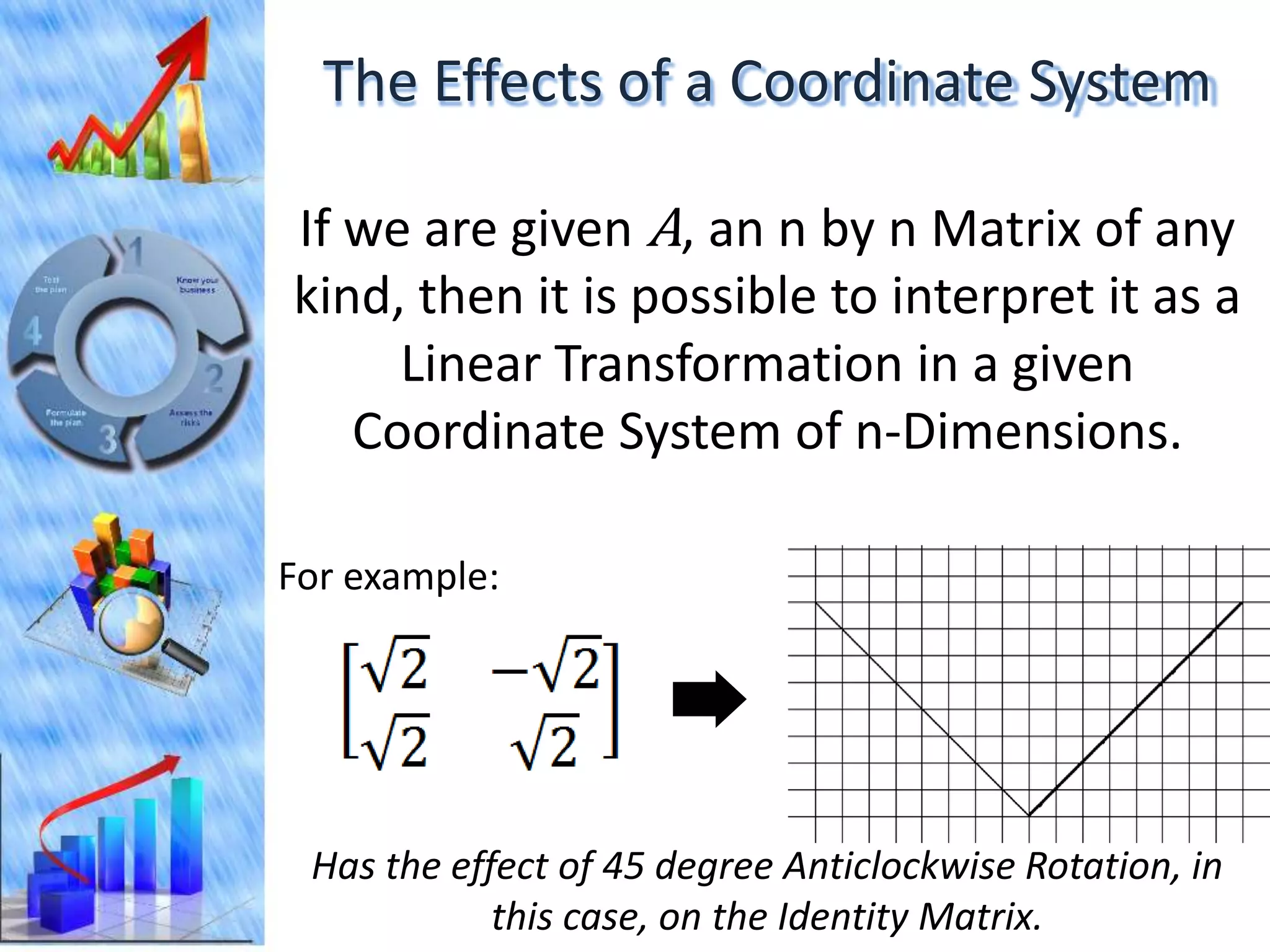
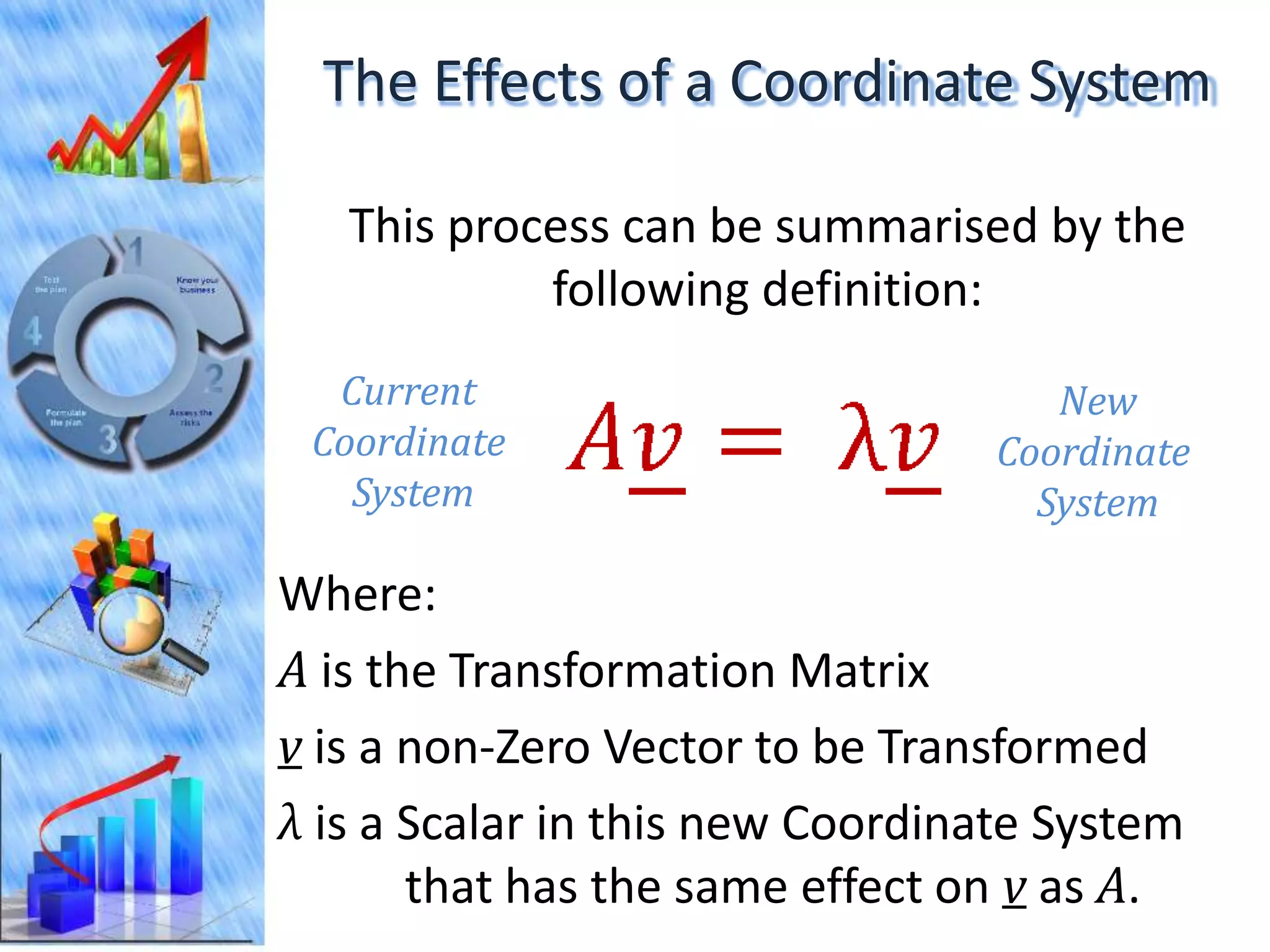
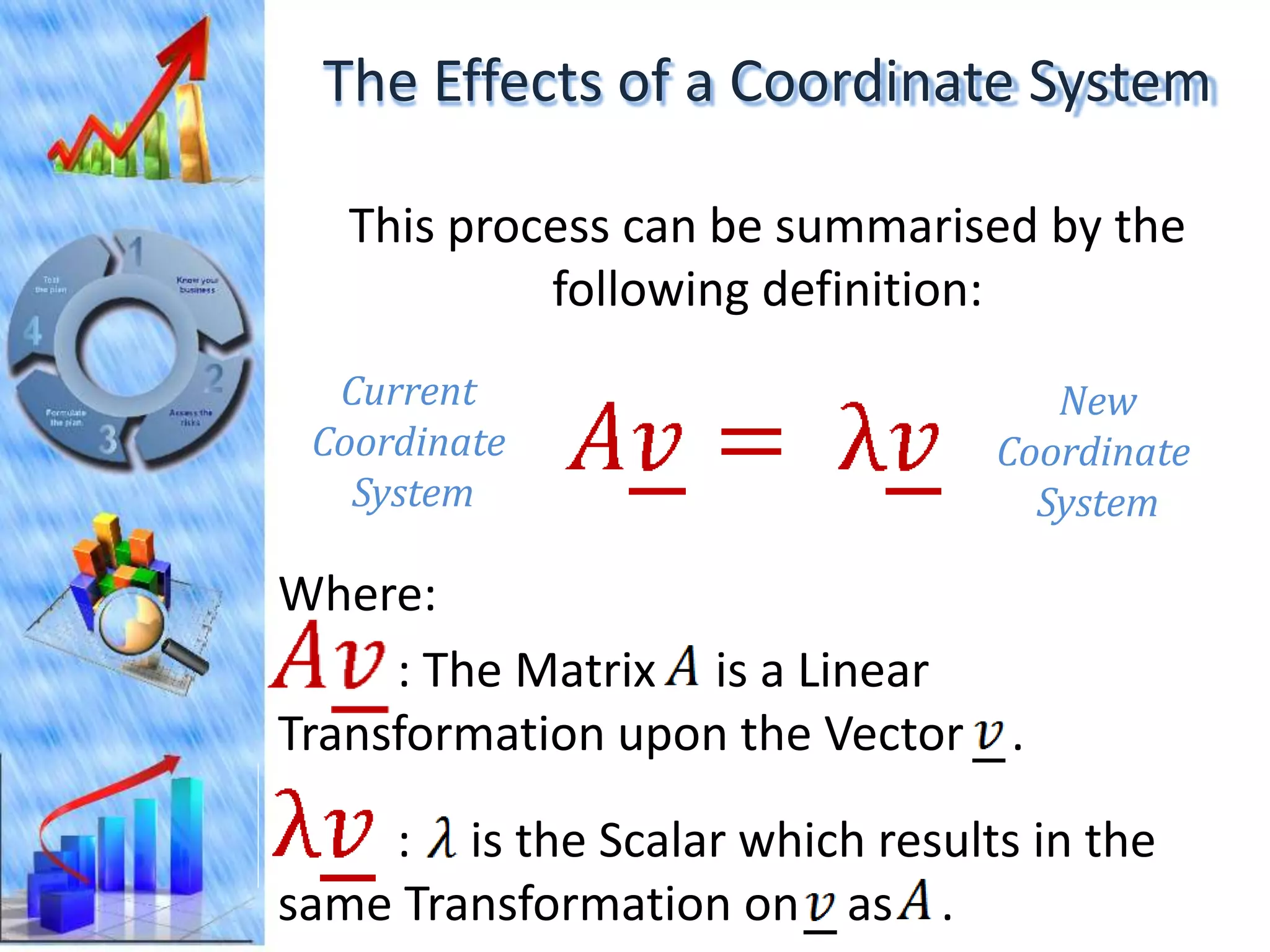
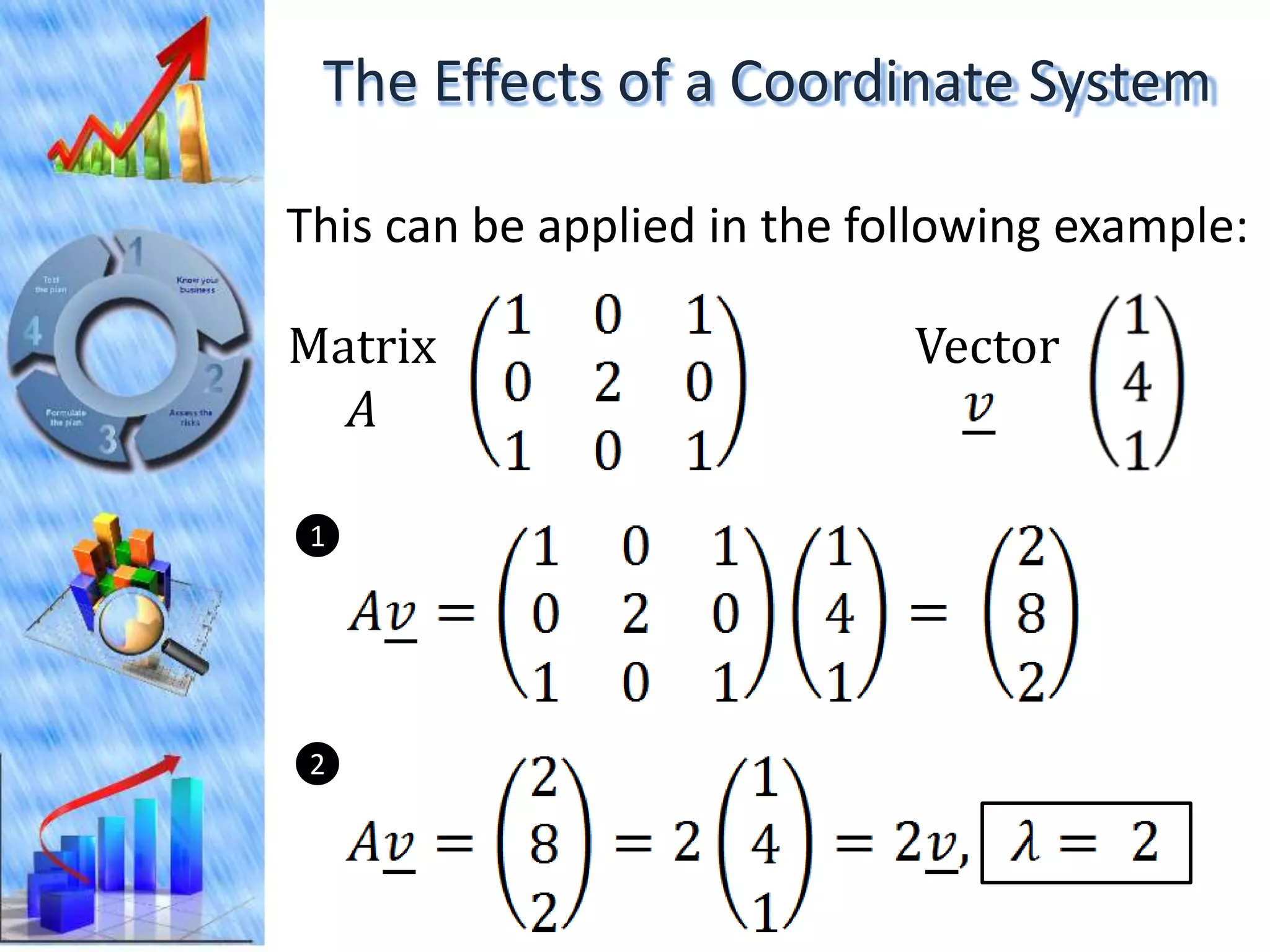
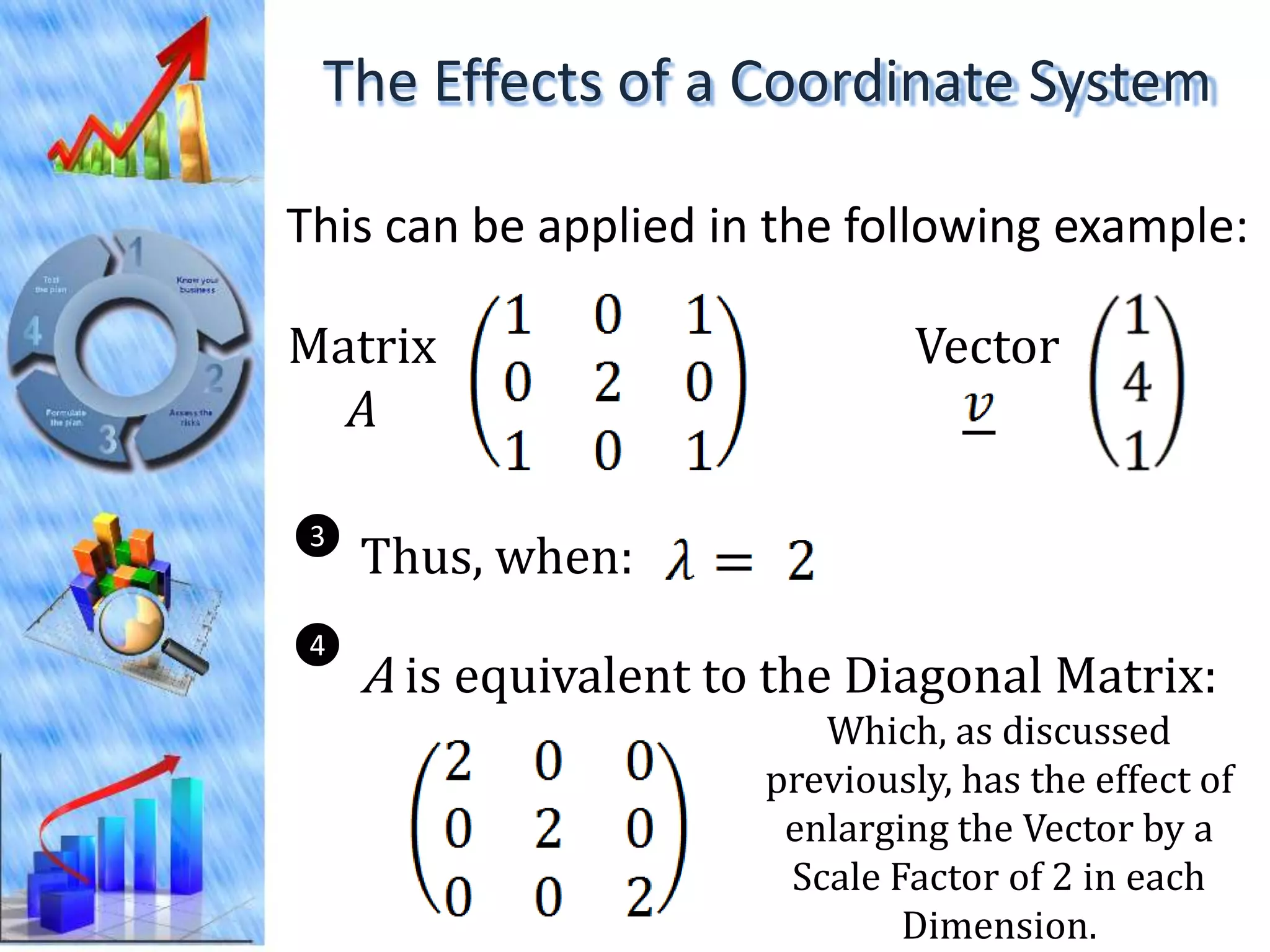
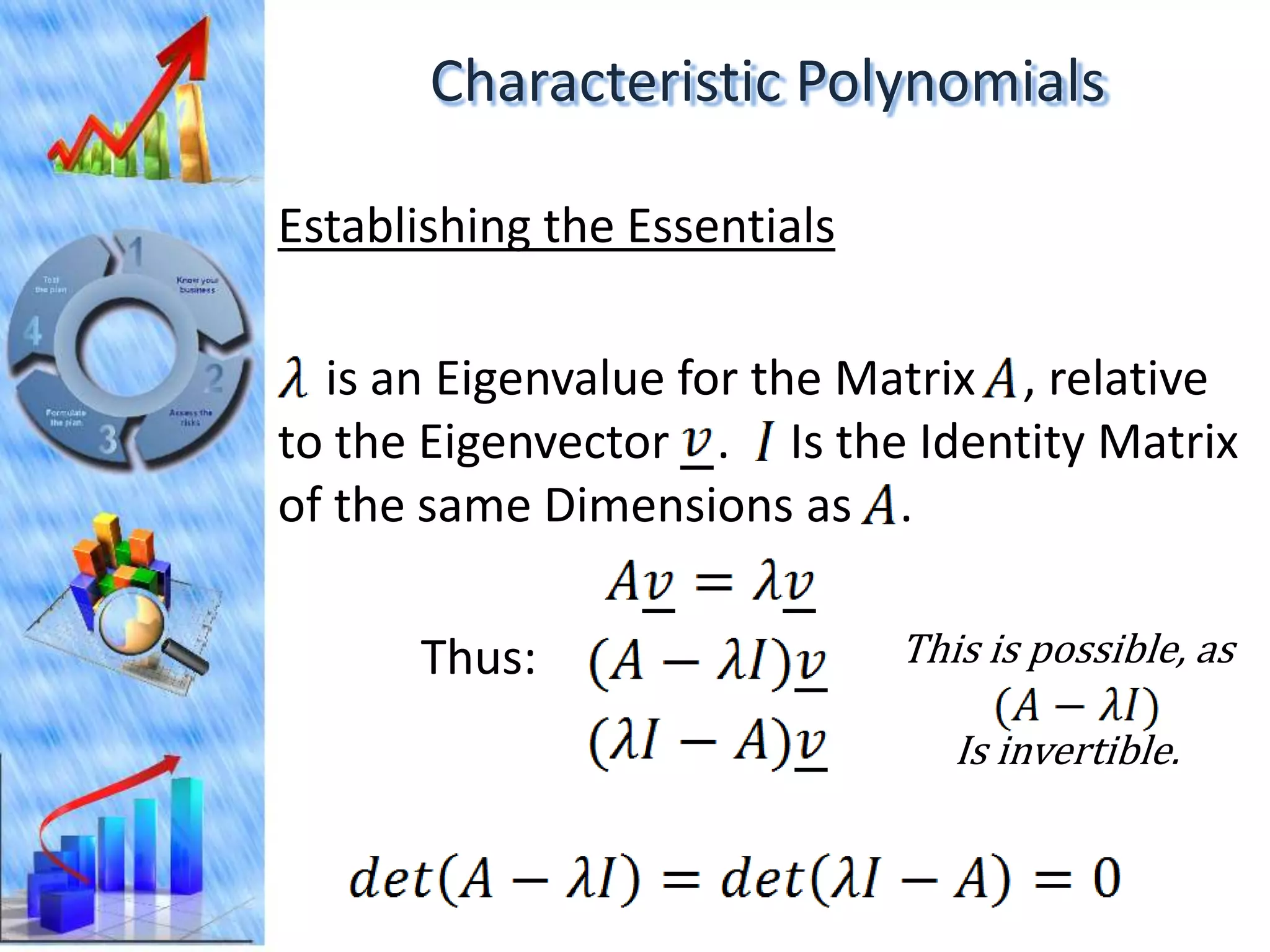
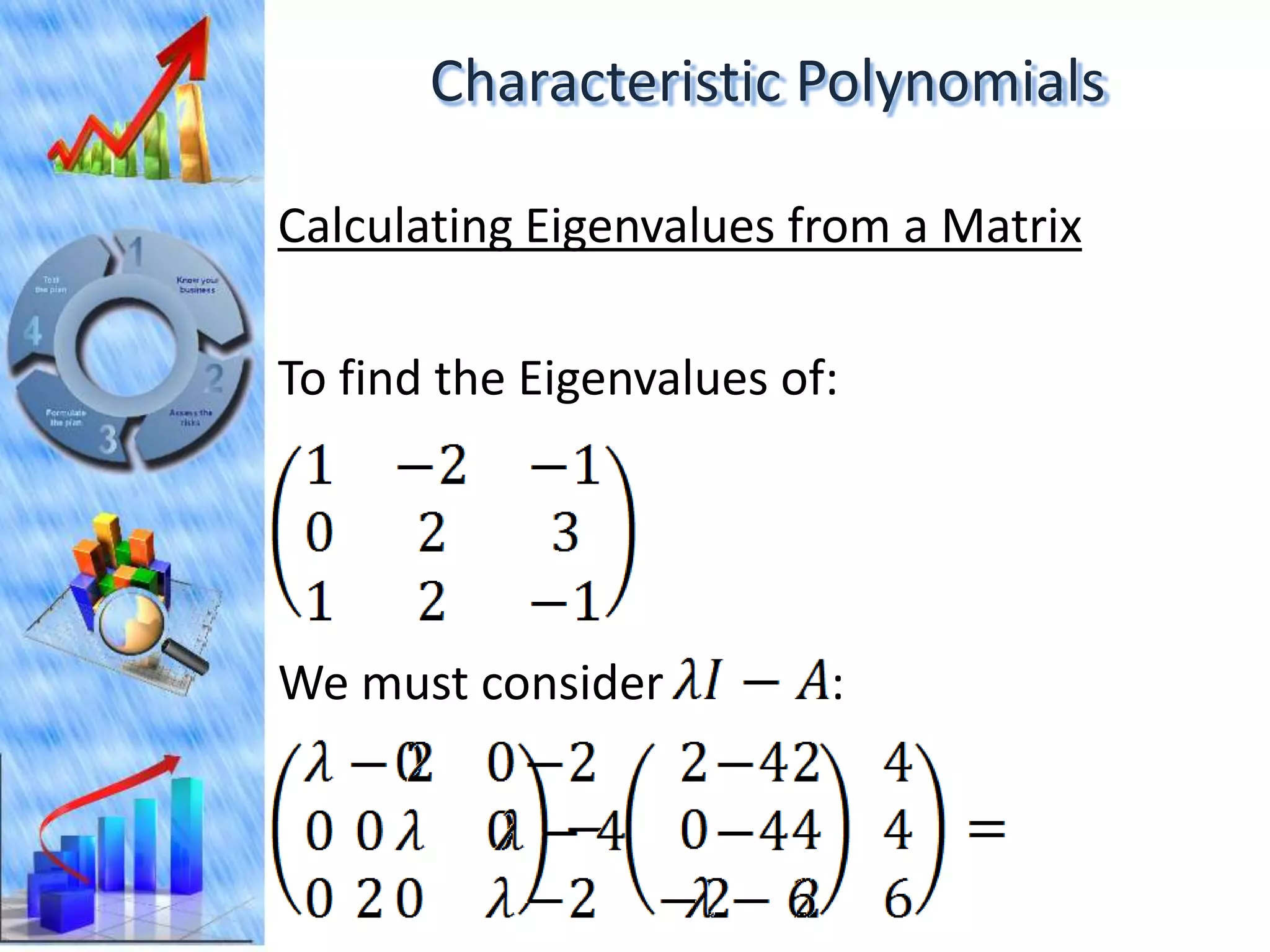
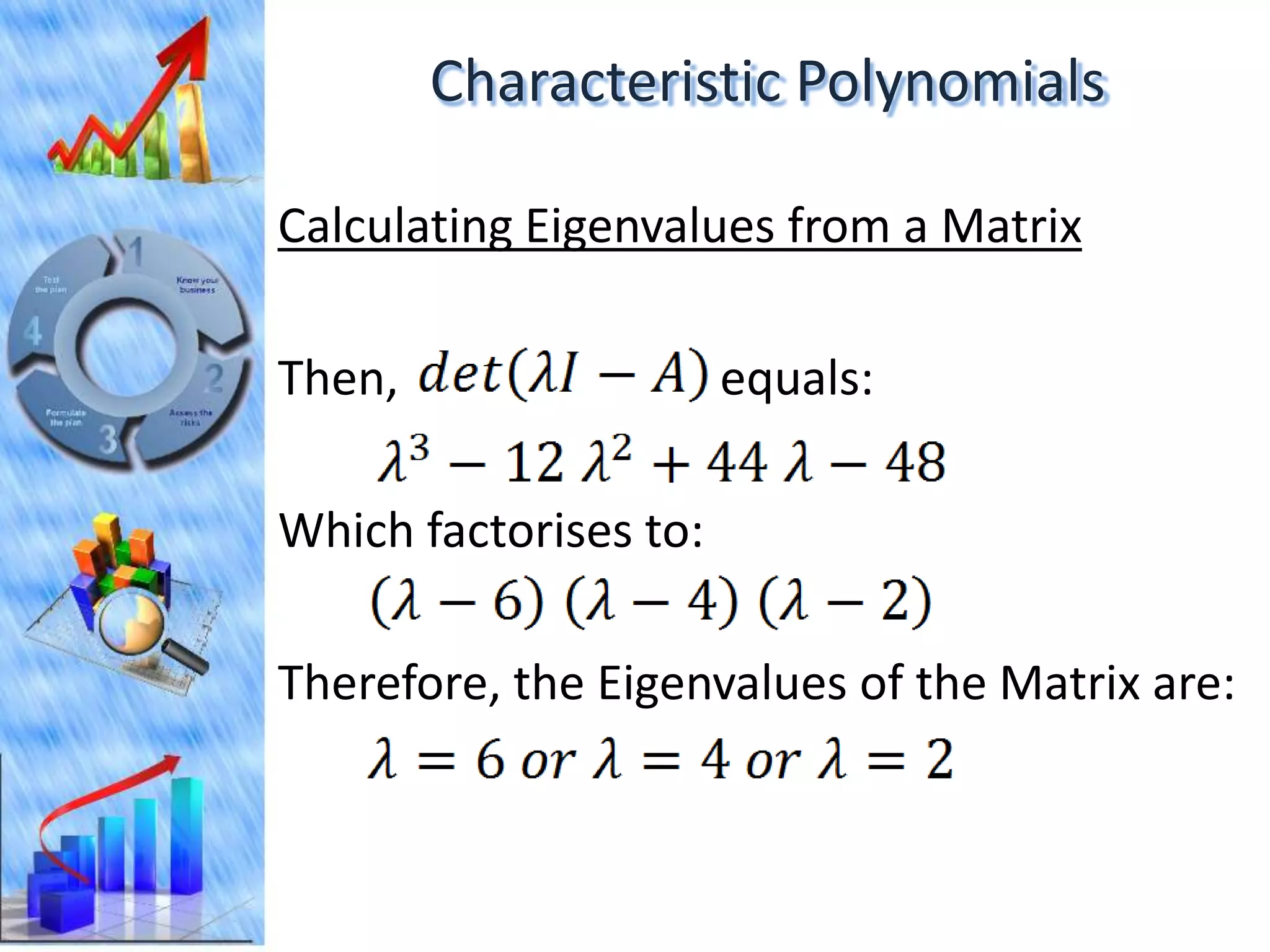
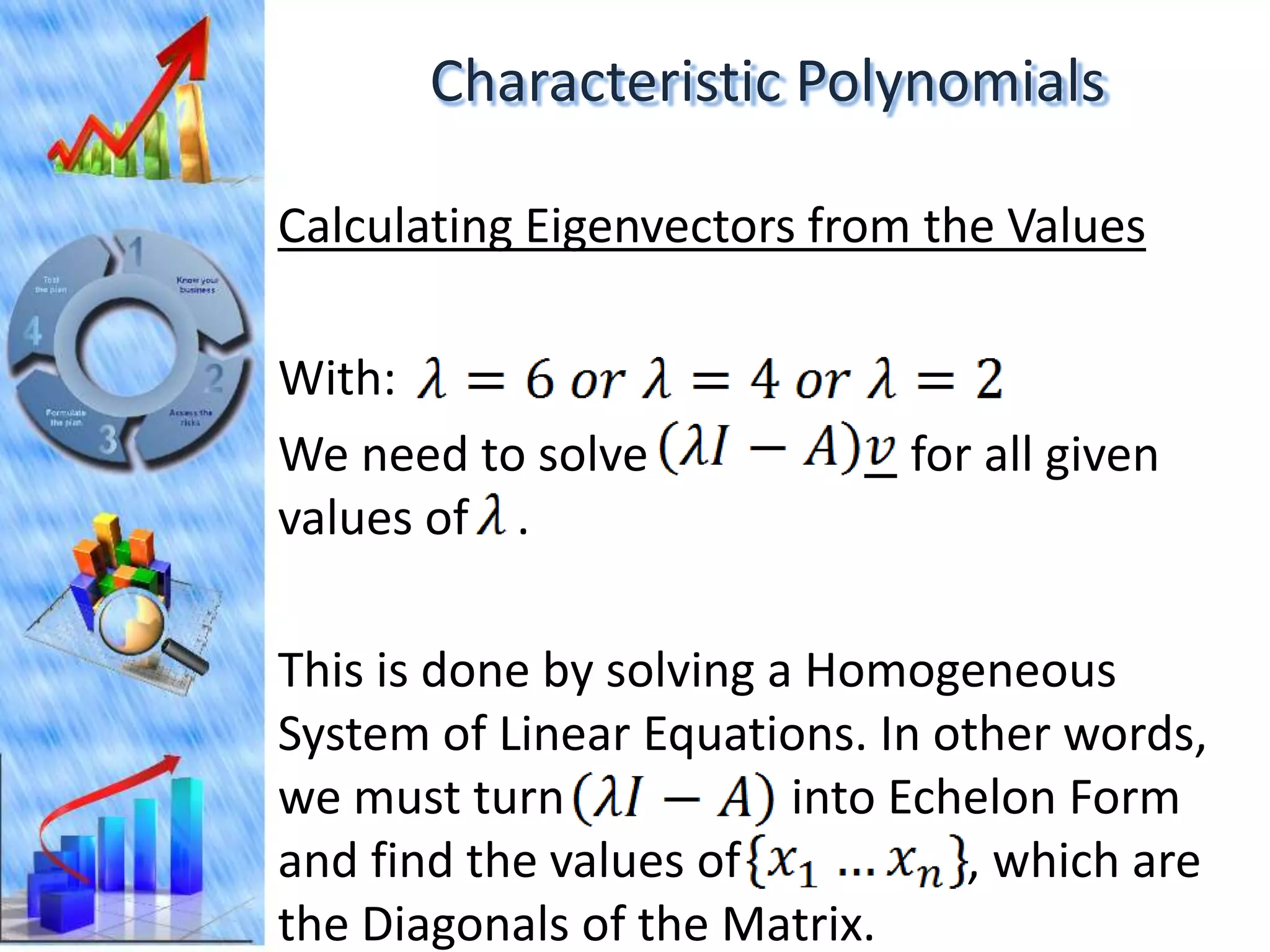
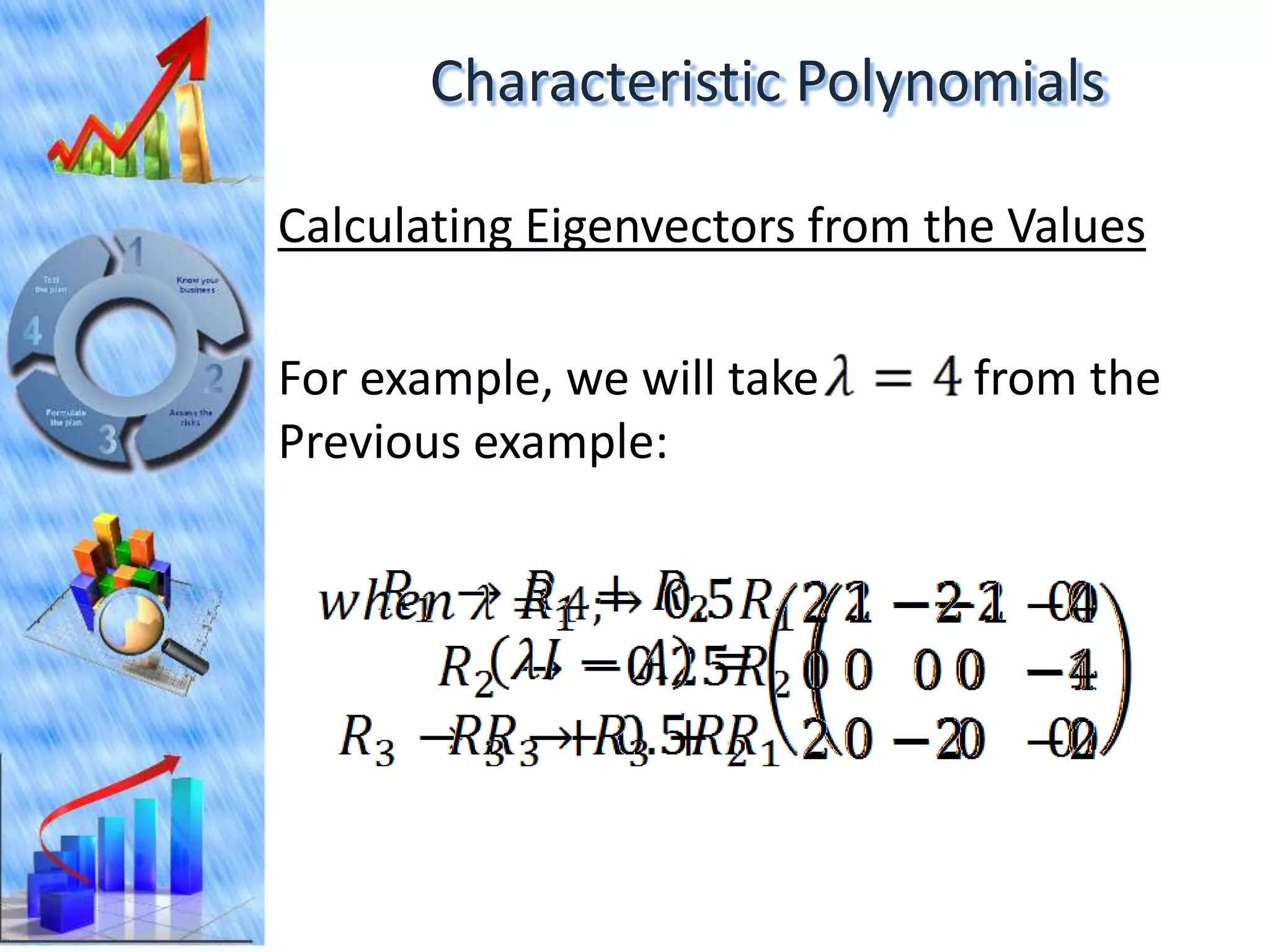
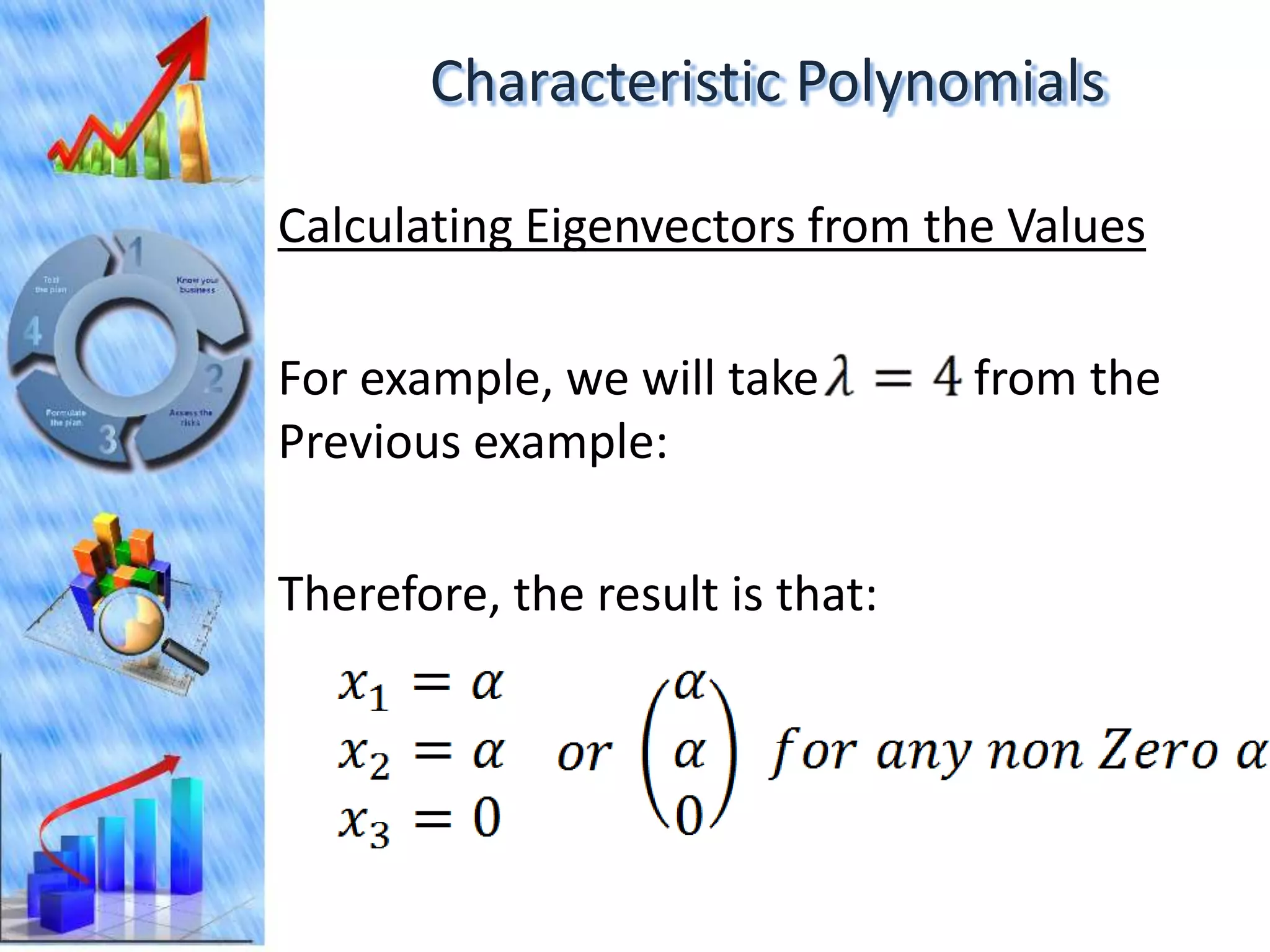
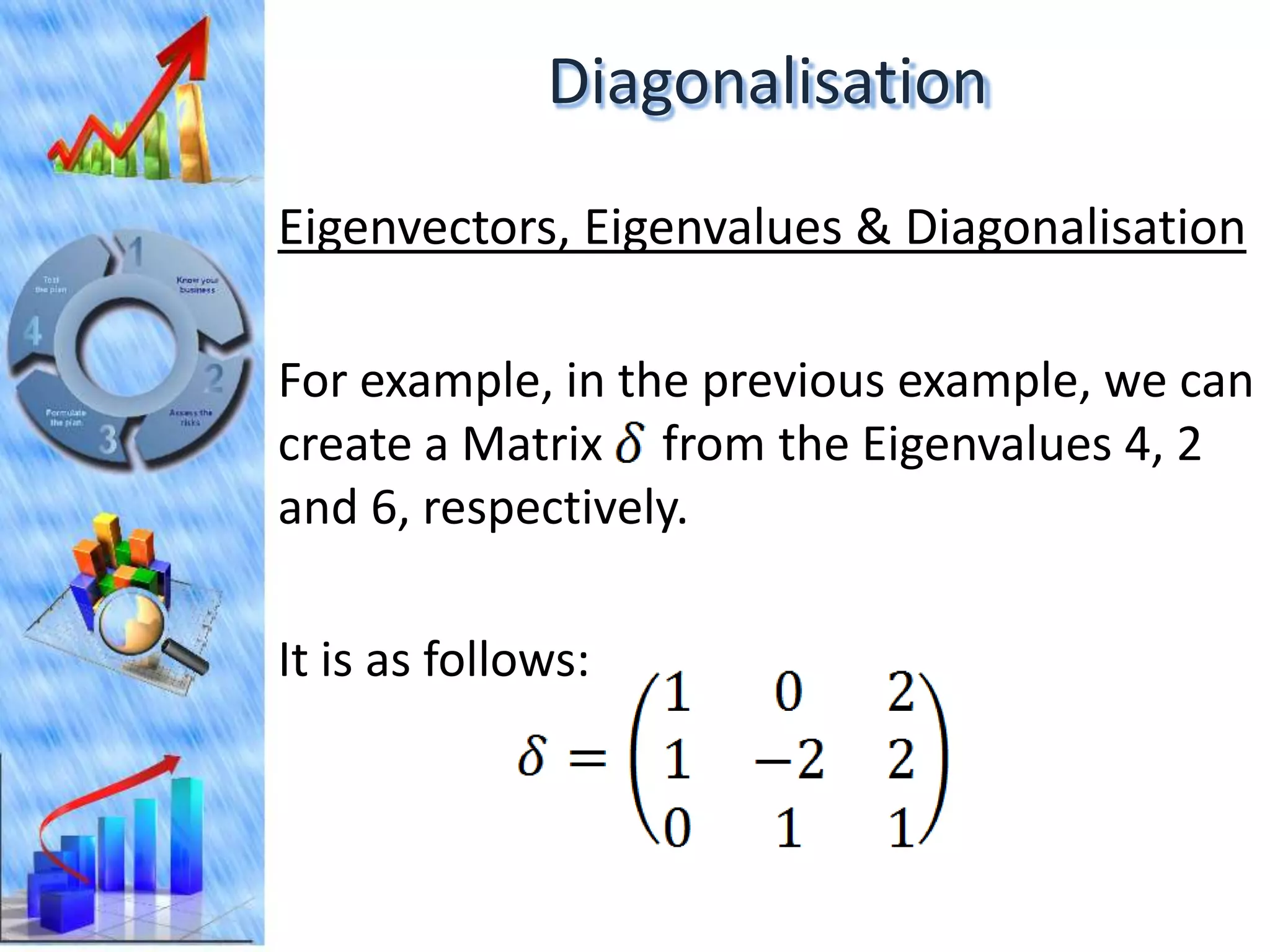
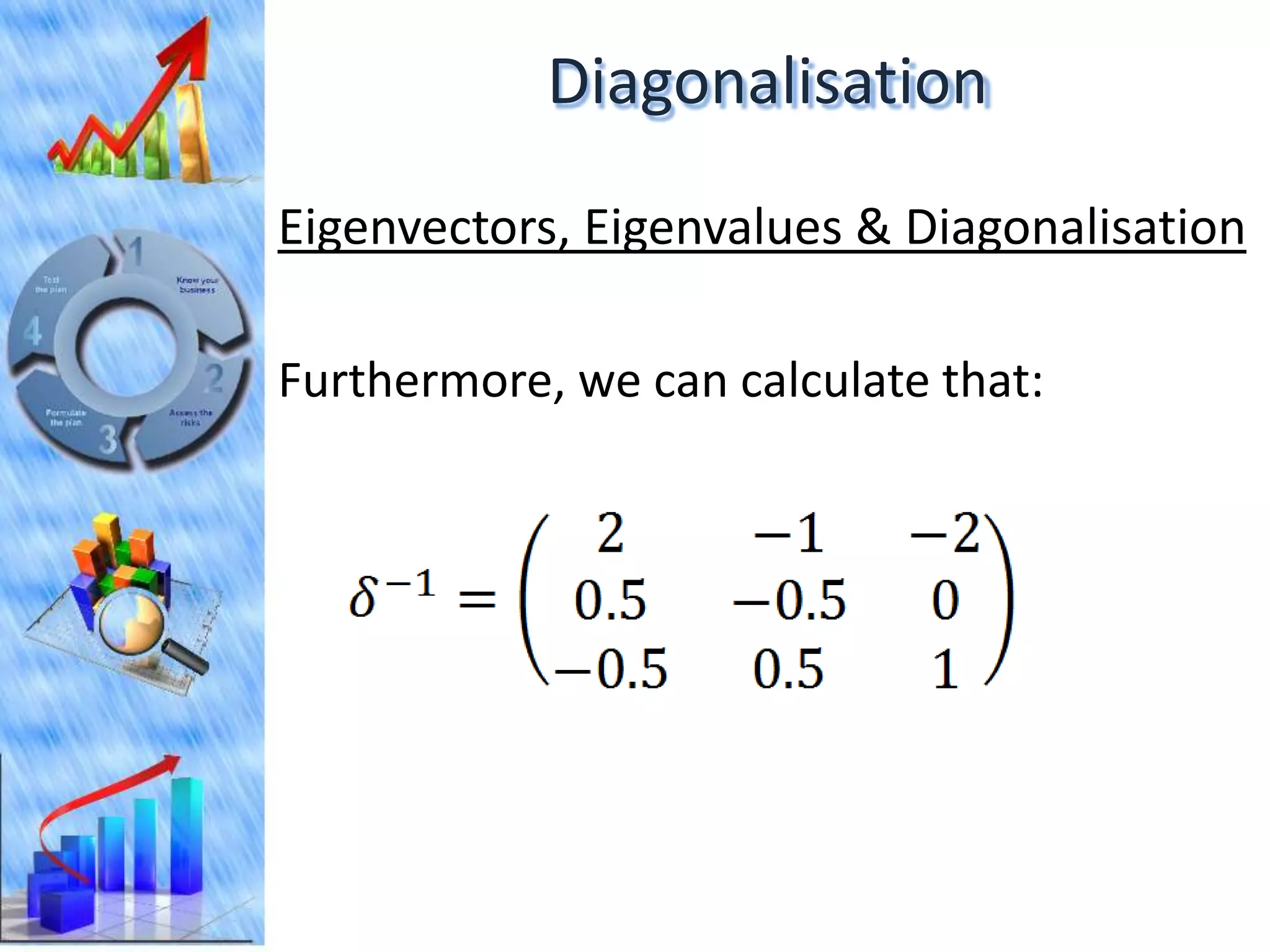
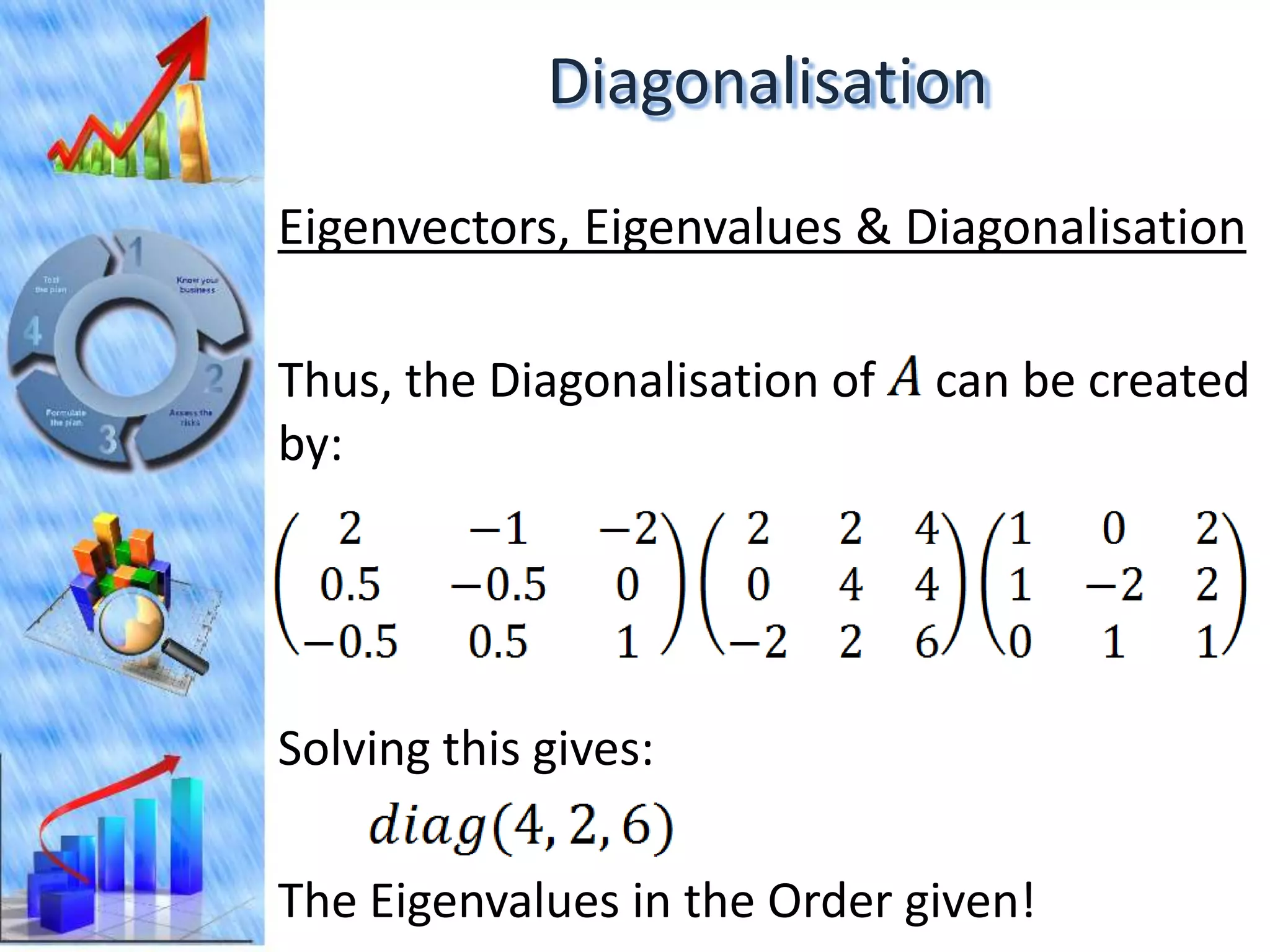
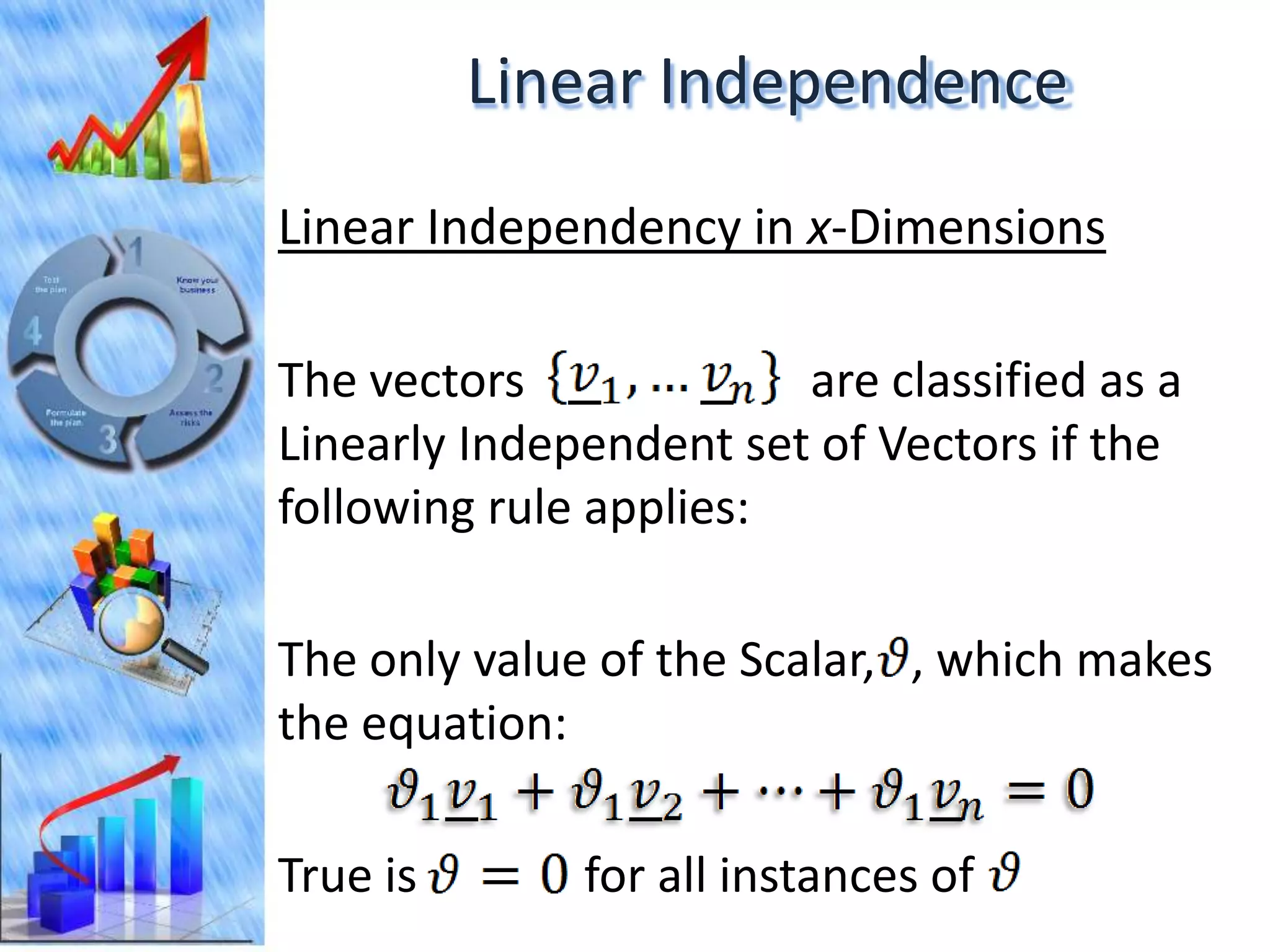
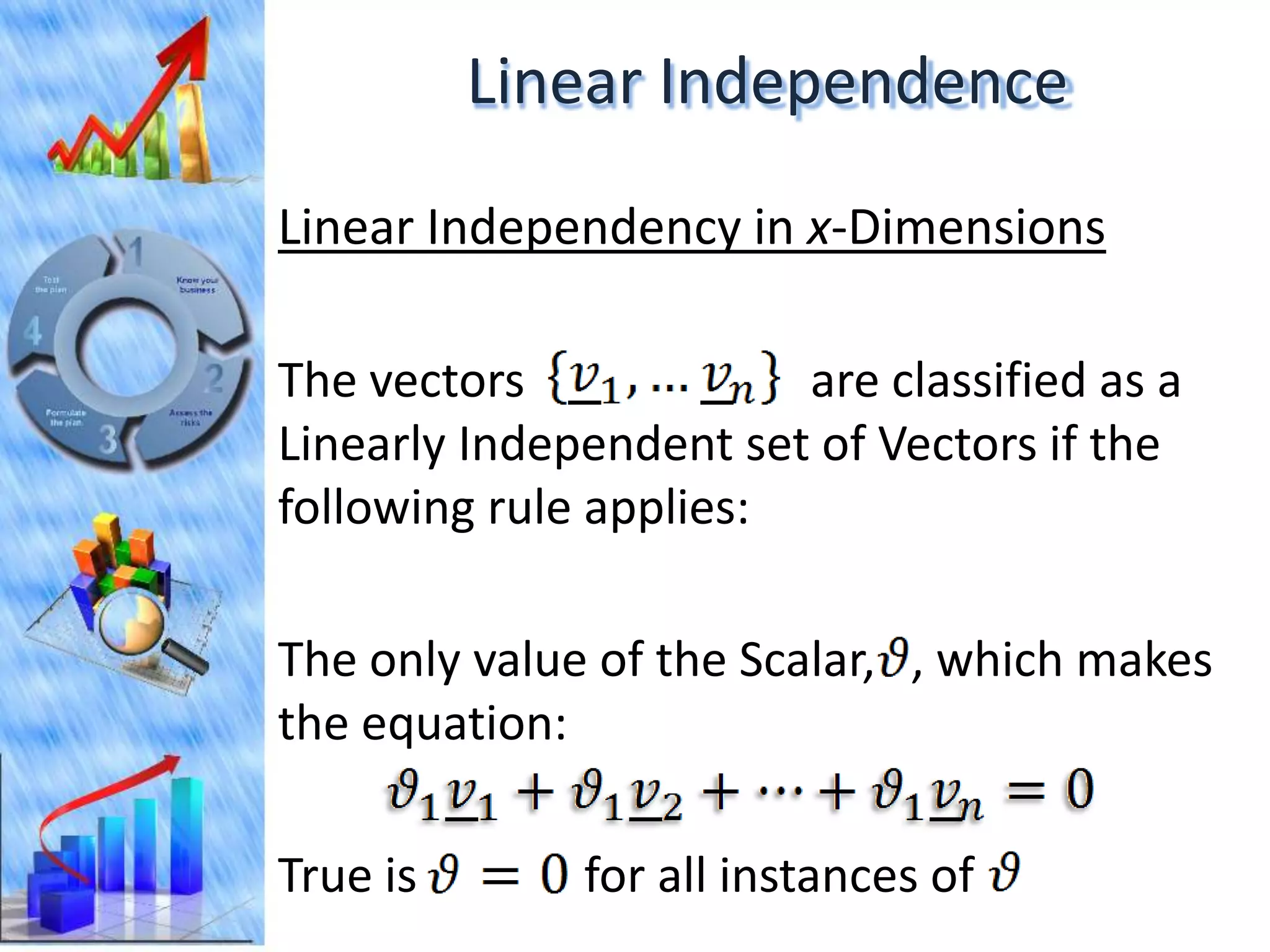
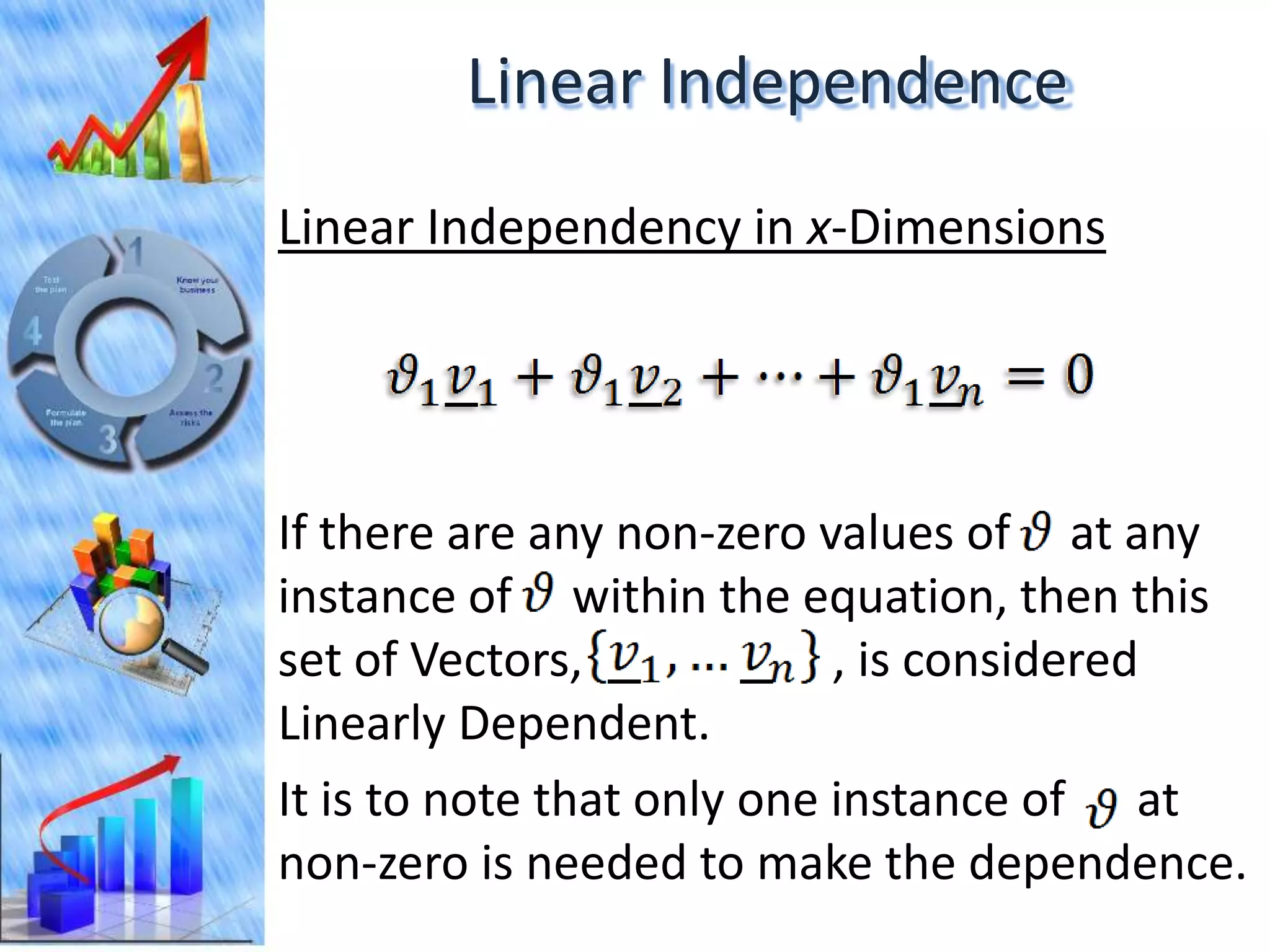
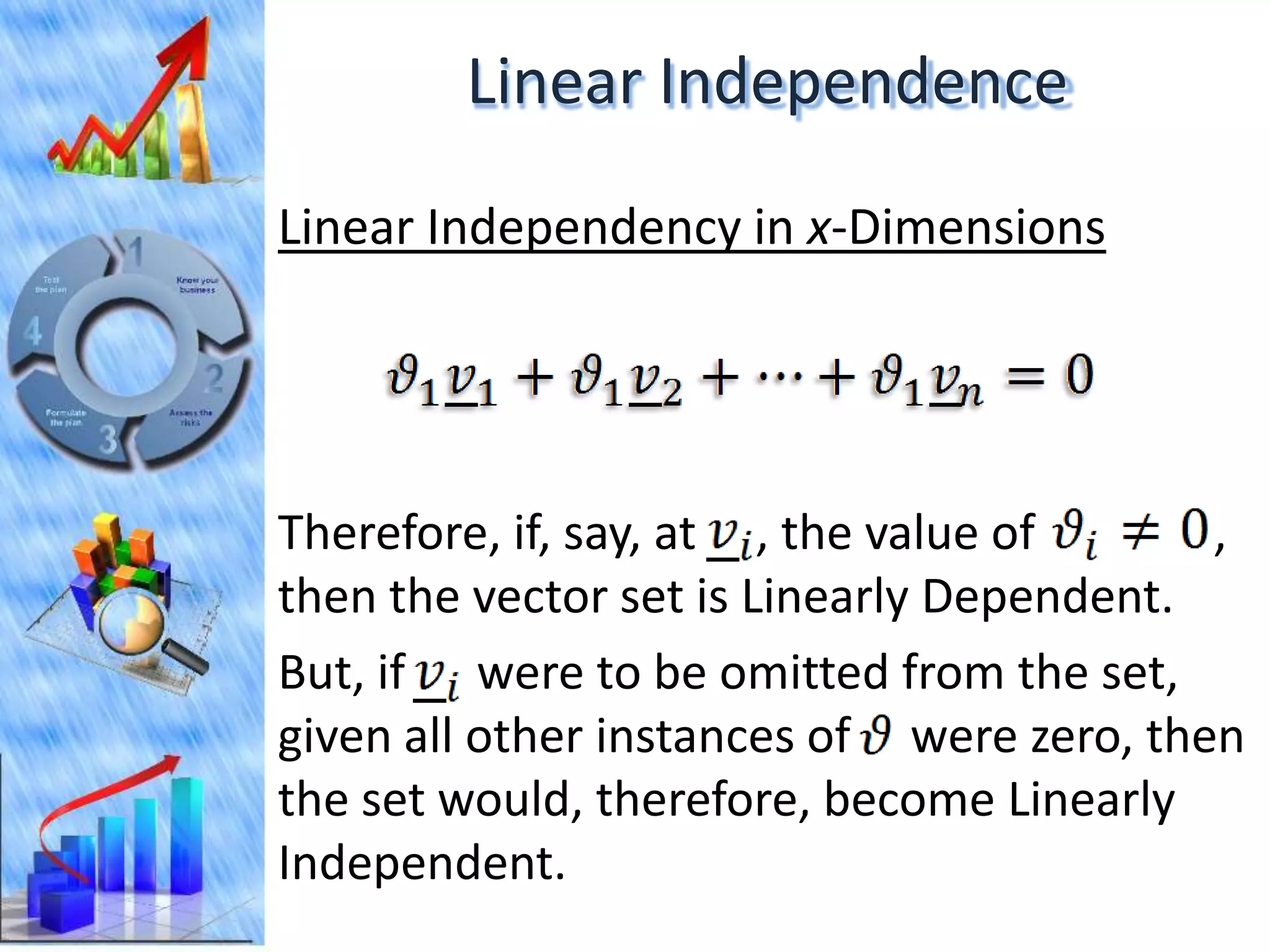
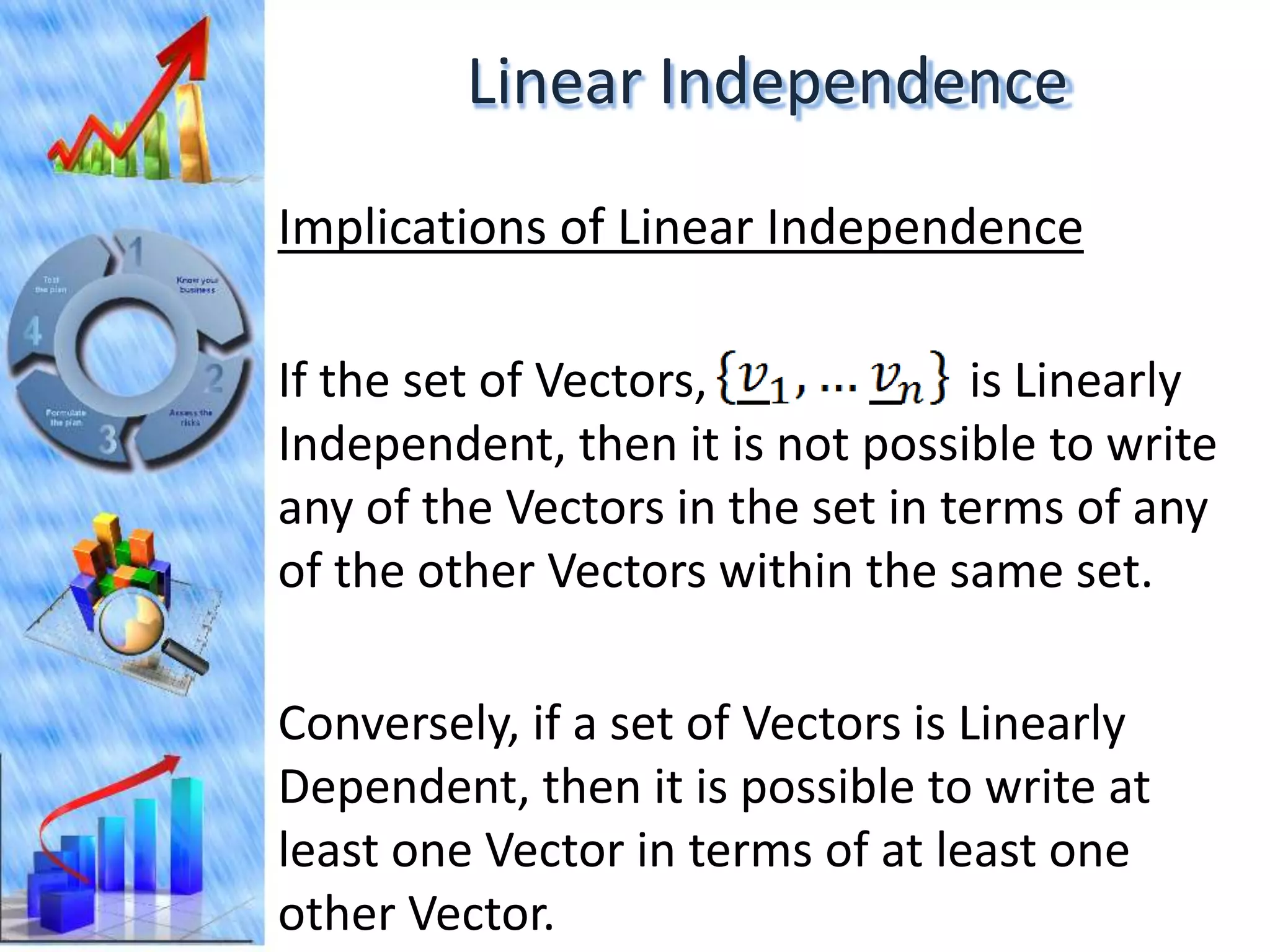
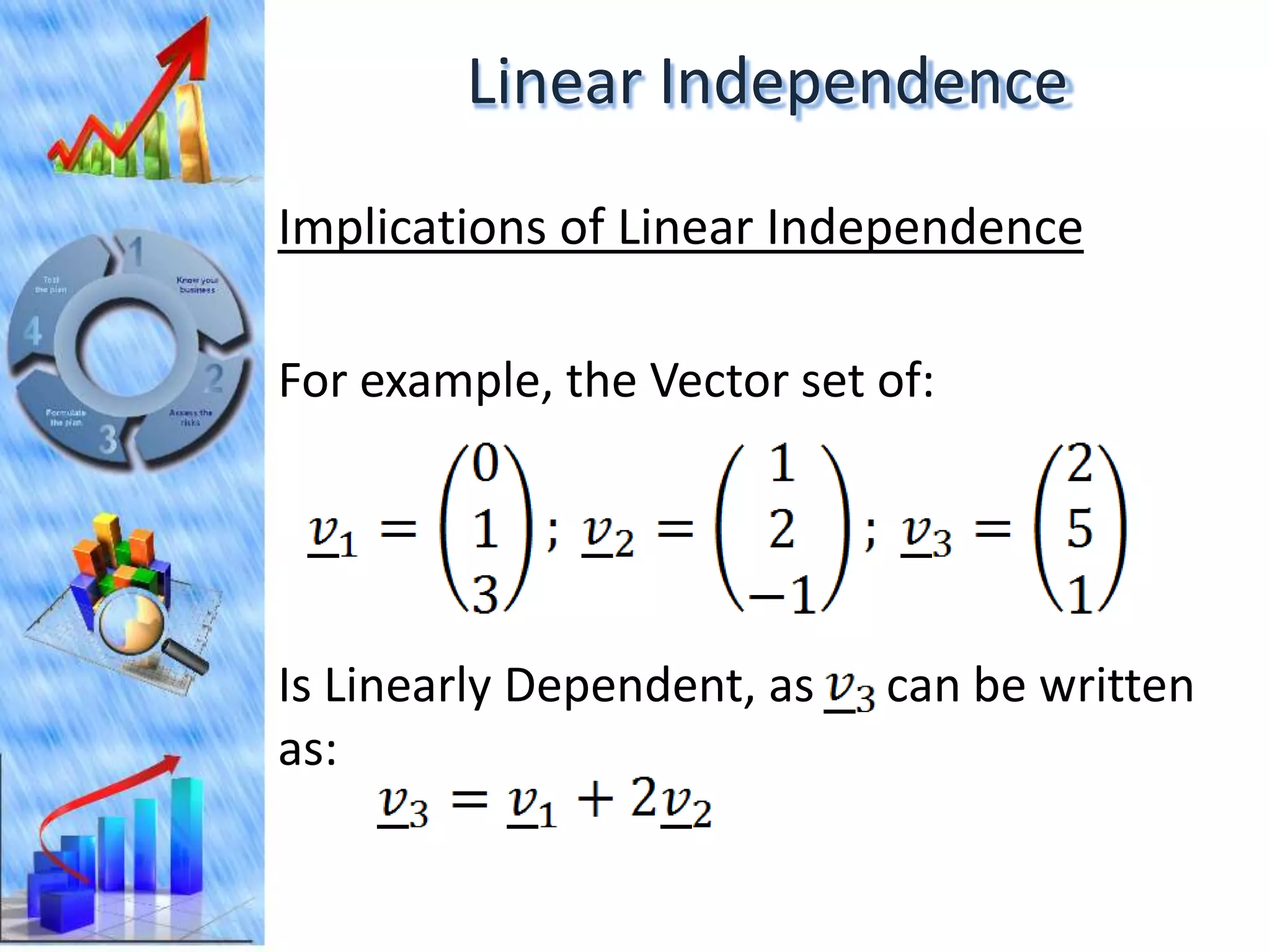
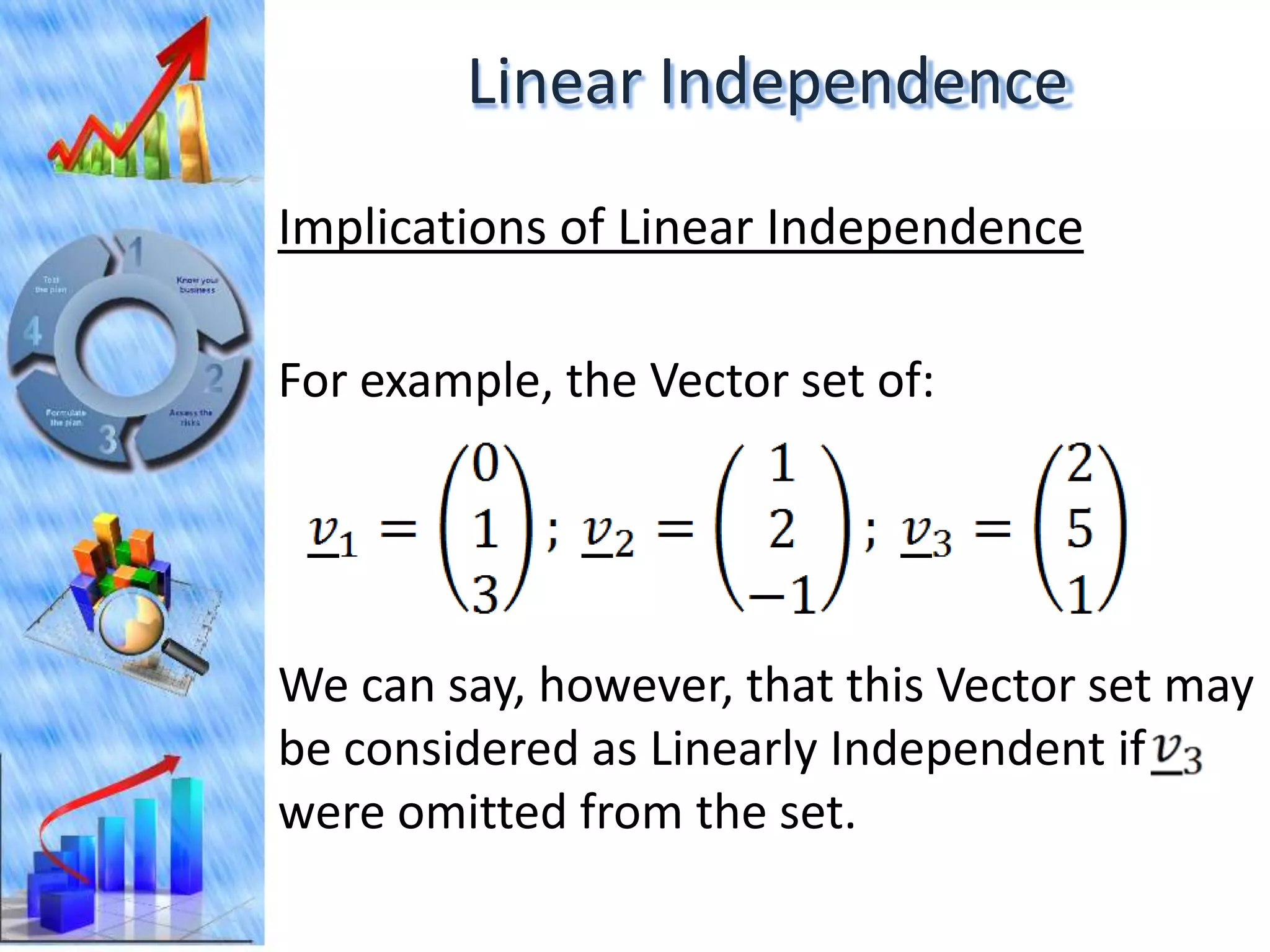
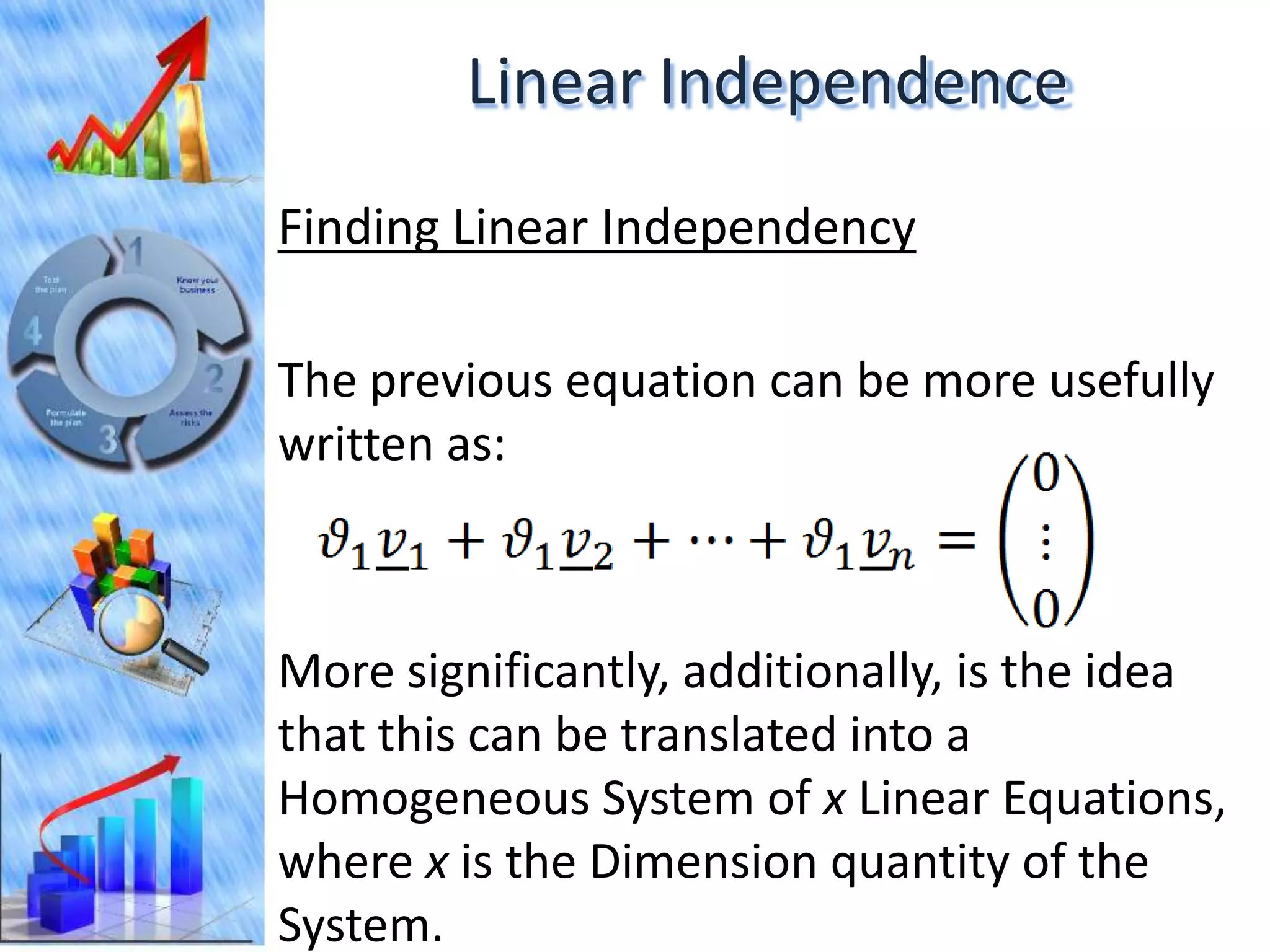
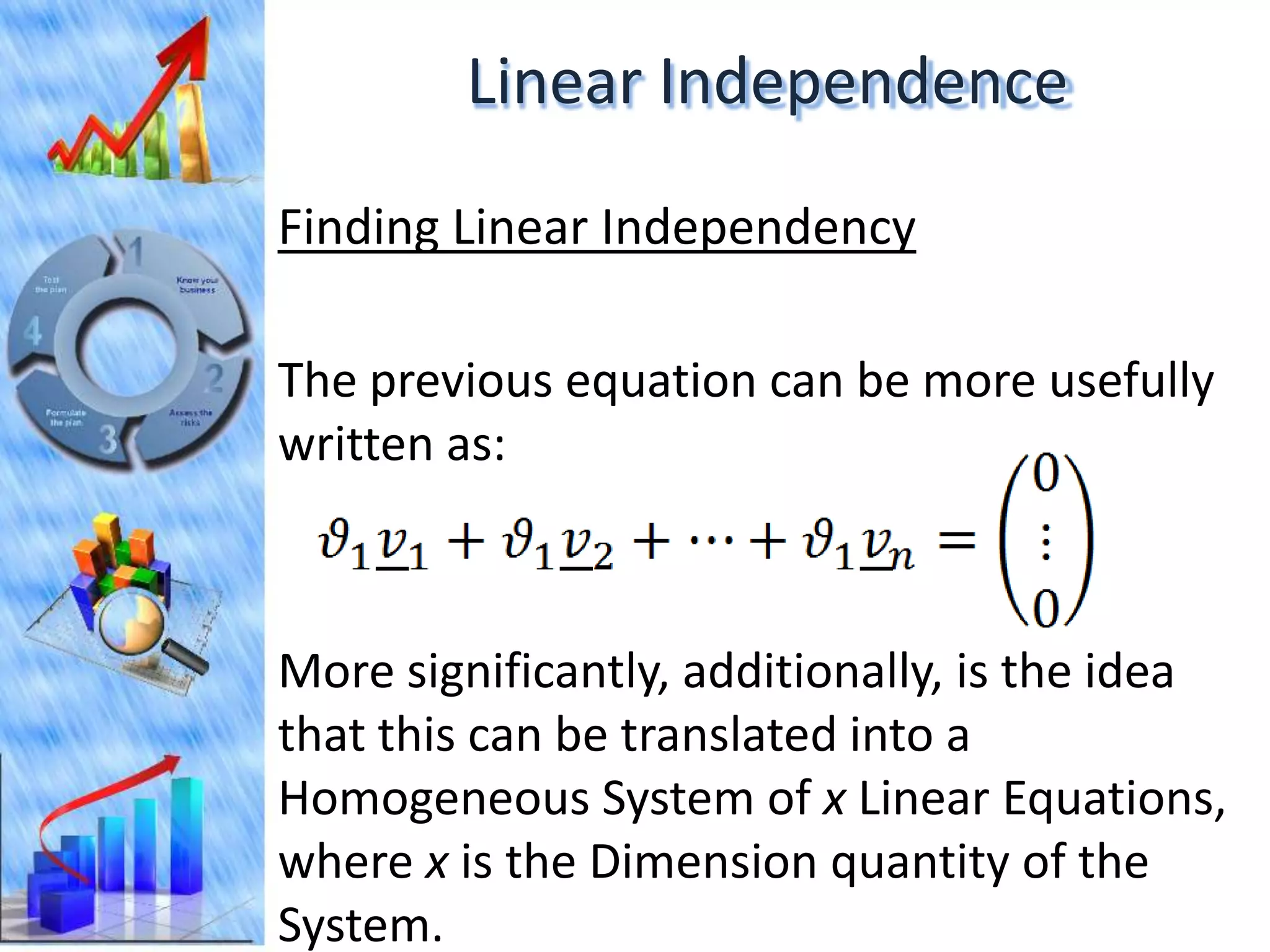
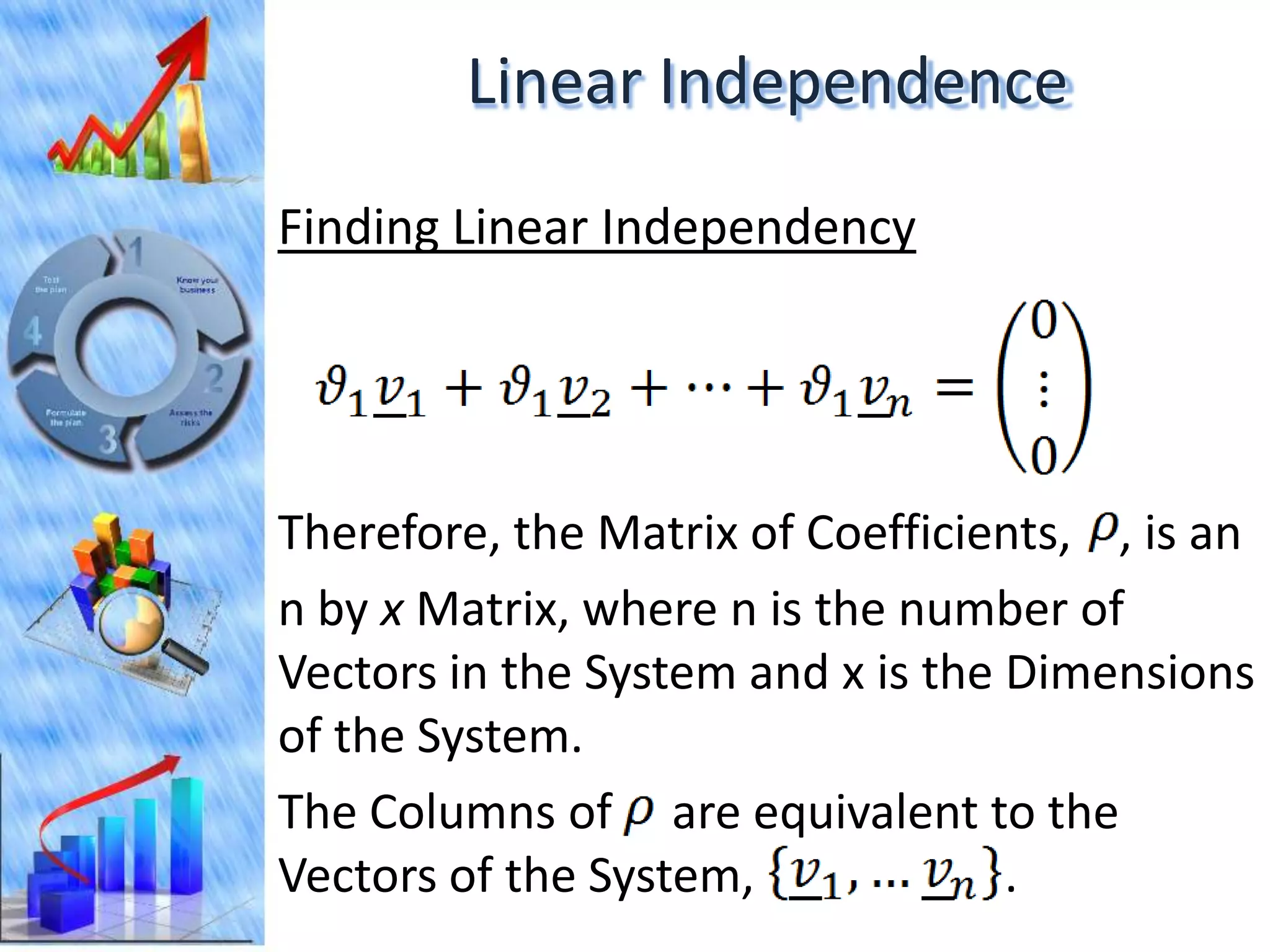
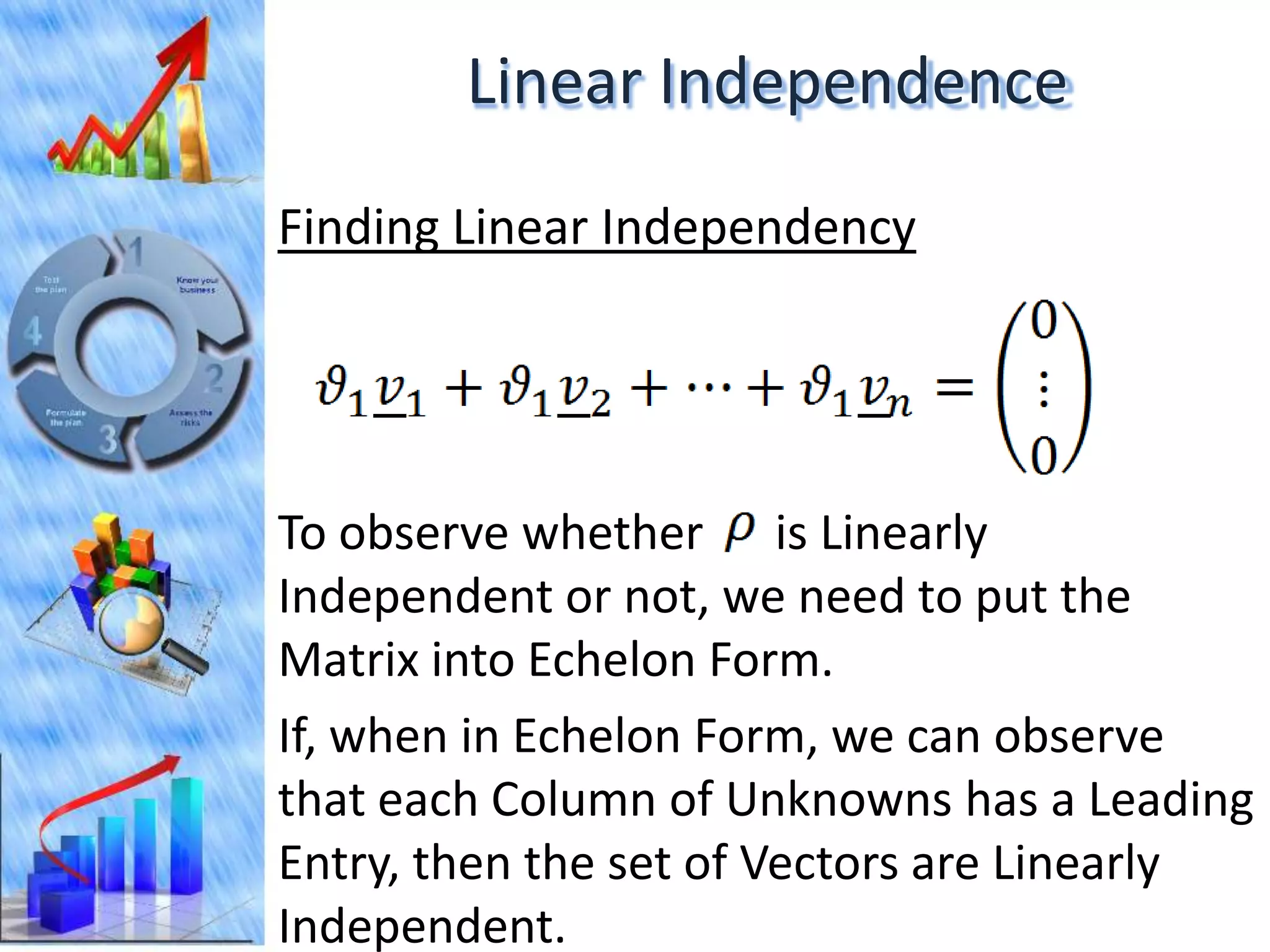
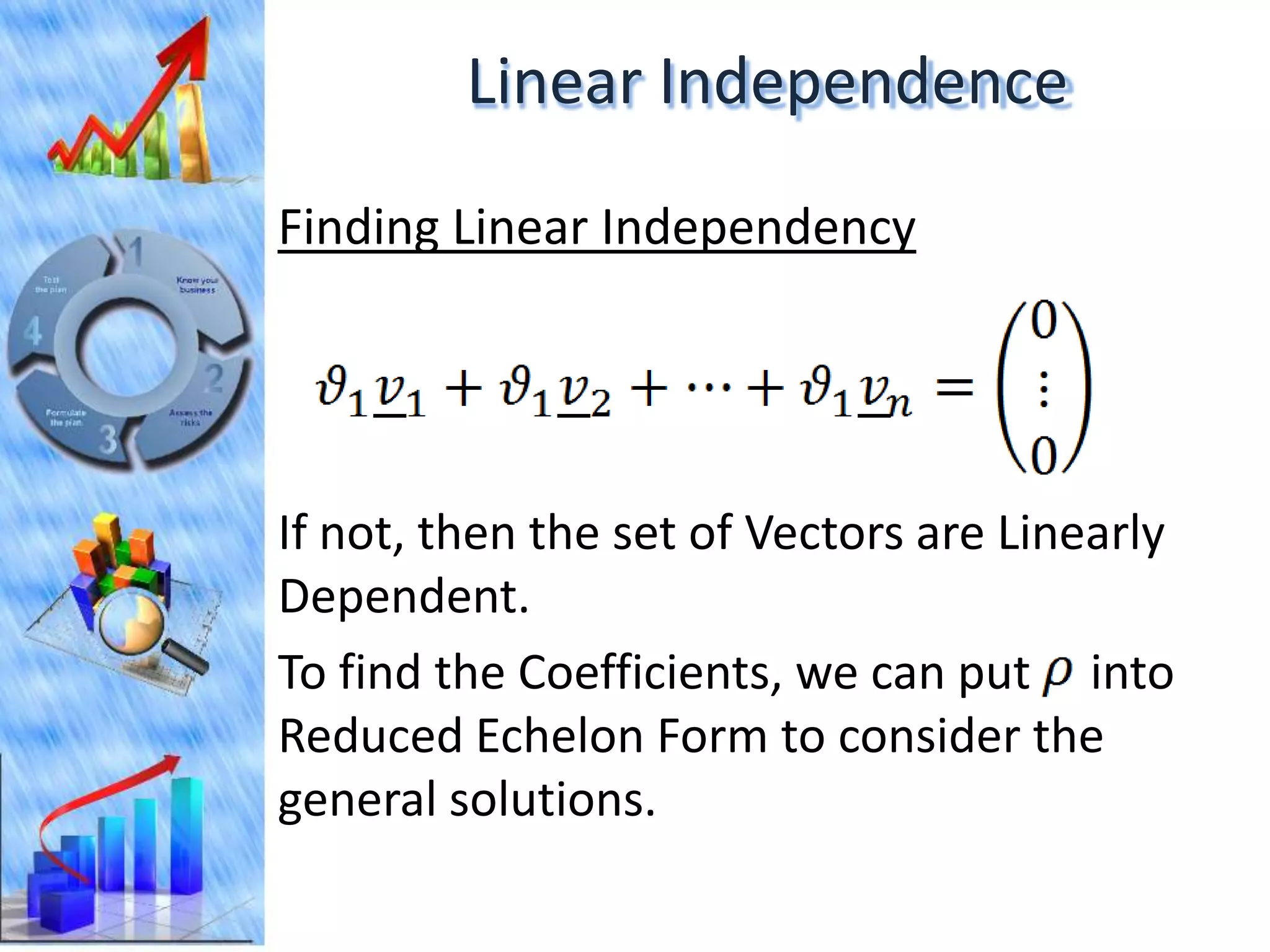
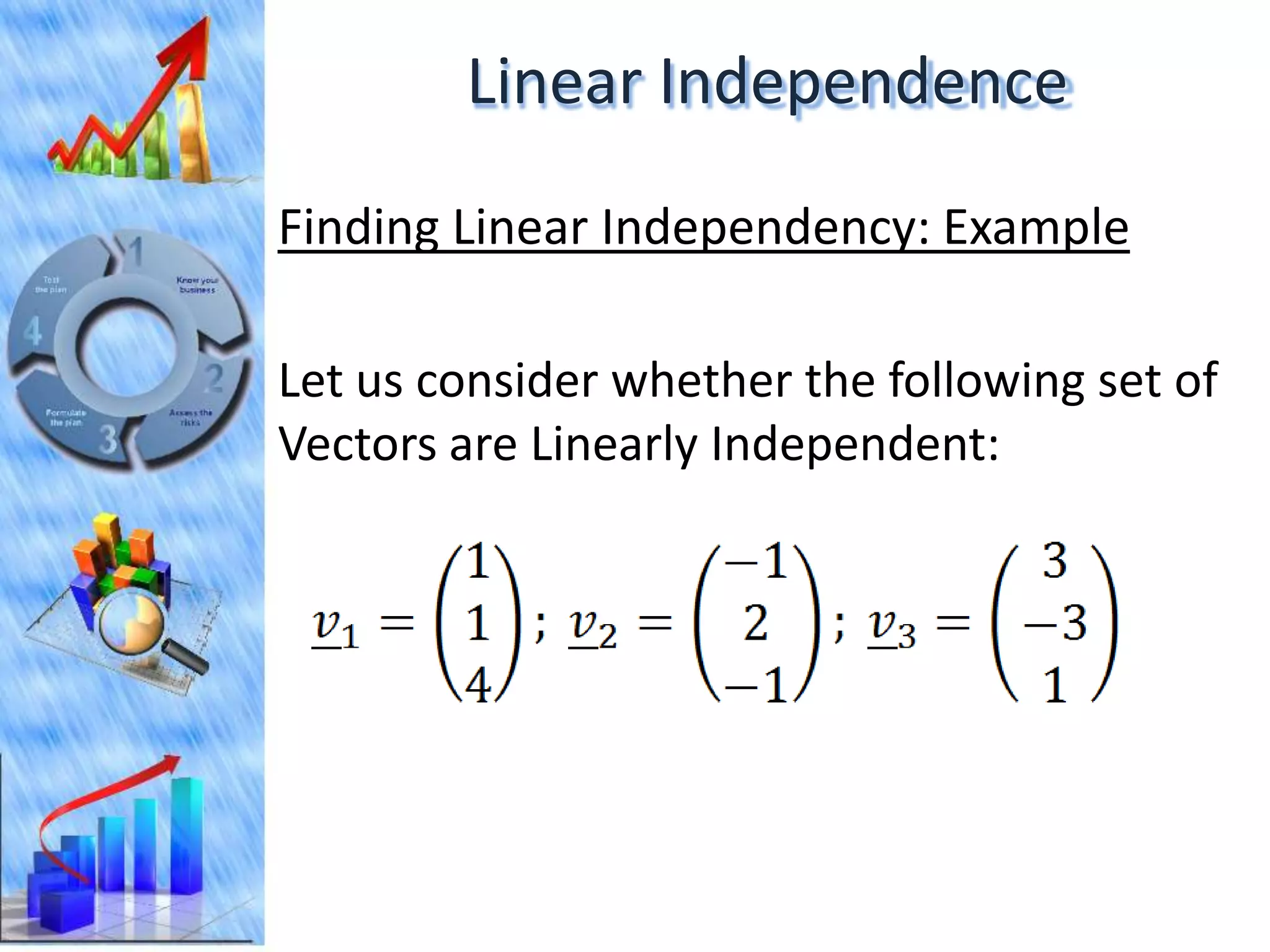
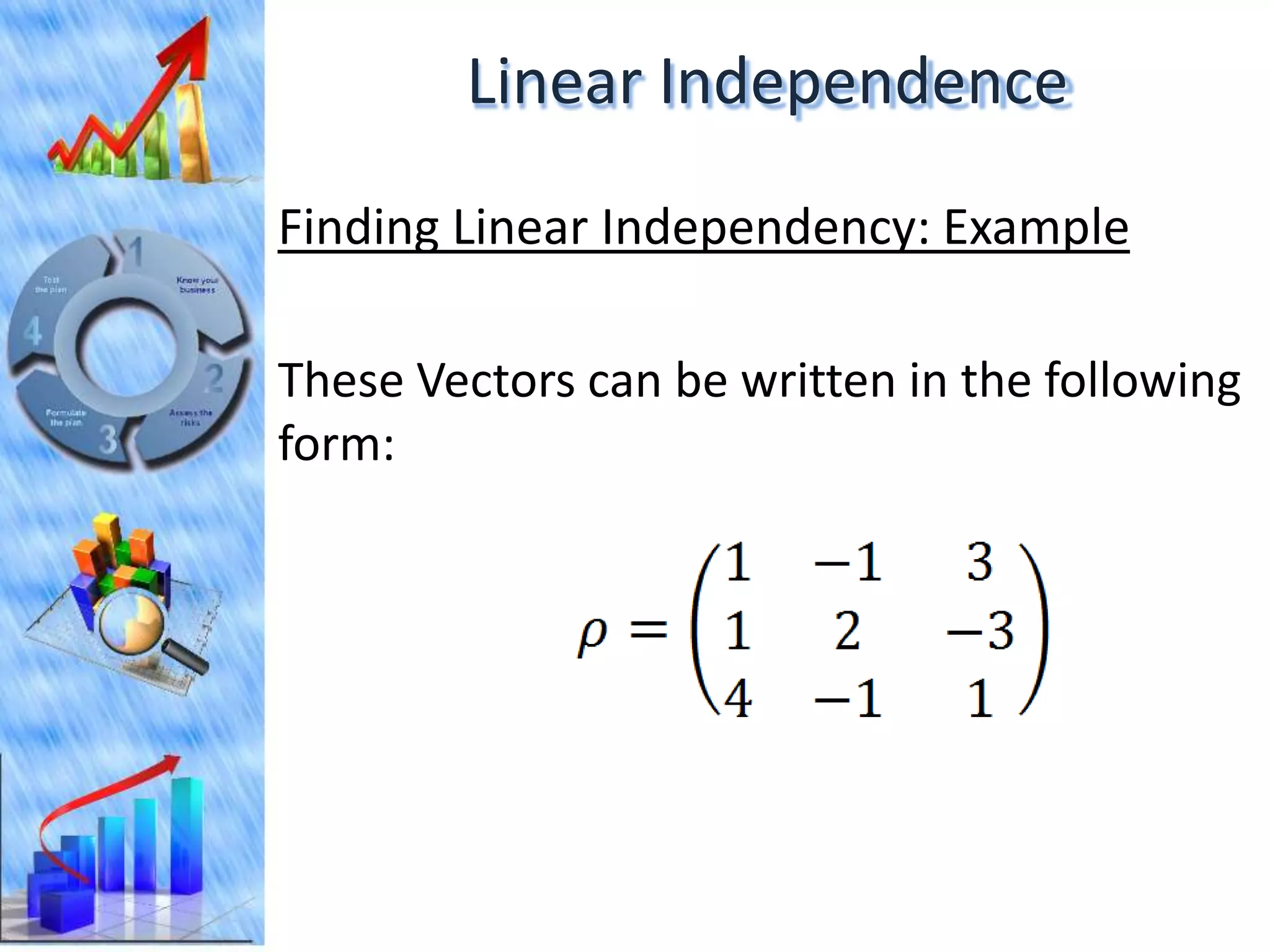
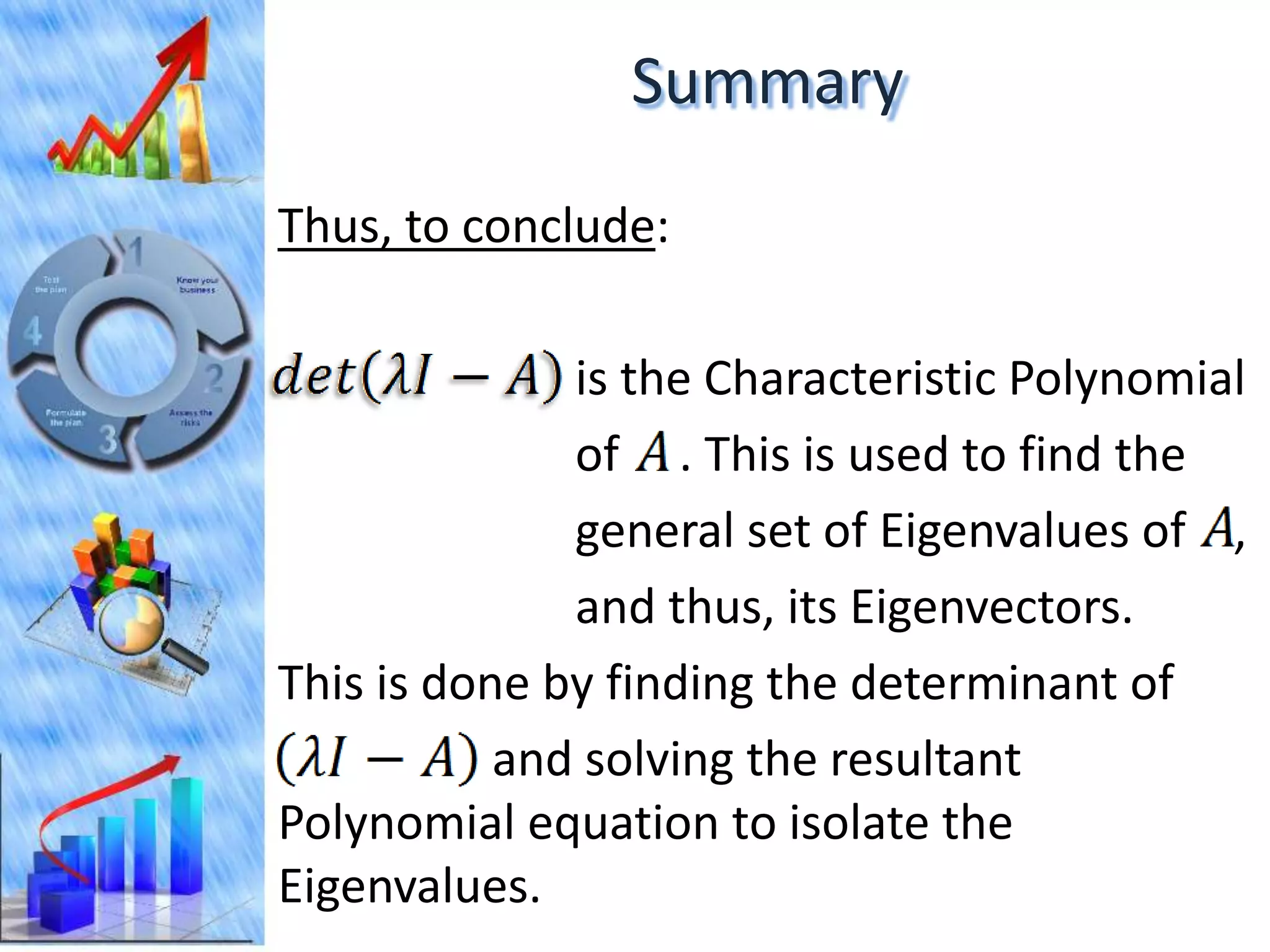
The document discusses eigenvectors and eigenvalues. It begins by defining diagonal matrices and provides examples. It then states that the goal is to understand diagonalization using eigenvectors and eigenvalues. Diagonalization involves finding a matrix such that when it transforms another matrix, the result is a diagonal matrix. This requires the eigenvectors of the original matrix to be linearly independent. The document provides examples of calculating eigenvectors and eigenvalues from matrices and shows how this relates to diagonalization. It also gives a brief introduction to linear independence and its implications for diagonalization.