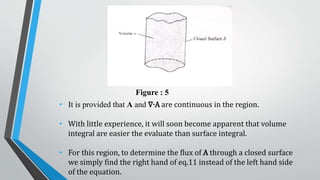
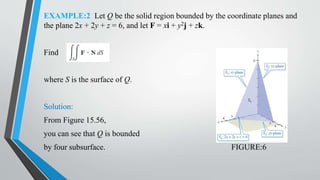
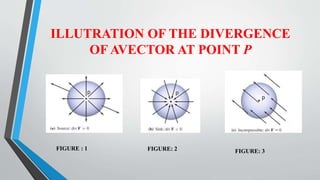
This document discusses the divergence of a vector field and the divergence theorem. It begins by defining the divergence of a vector field as a measure of how much that field diverges from a given point. It then illustrates the divergence of a vector field can be positive, negative, or zero at a point. The document expresses the divergence in Cartesian, cylindrical, and spherical coordinate systems. It proves the divergence theorem, which states that the outward flux of a vector field through a closed surface is equal to the volume integral of the divergence of the field over the enclosed volume. The document provides two examples applying the divergence theorem to calculate outward fluxes.






![• For the front side, x =𝑥0+dx/2 and dS = dy dz 𝑎 𝑥. Then,
• 𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑛𝑡
𝐴 ∙ 𝑑𝑆 = dy dz[𝐴 𝑥(𝑥0, 𝑦0, 𝑧0)+
𝑑𝑥
2
𝜕𝐴 𝑥
𝜕𝑥
∣ 𝑝]+higher-order term
• For the back side, x =𝑥0 −dx/2 and dS = dy dz (−𝑎 𝑥). Then,
• 𝑏𝑎𝑐𝑘
𝐴 ∙ 𝑑𝑆 = -dy dz[𝐴 𝑥(𝑥0, 𝑦0, 𝑧0)−
𝑑𝑥
2
𝜕𝐴 𝑥
𝜕𝑥
∣ 𝑝]+higher-order term
• Hence ,
• 𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑛𝑡
𝐴 ∙ 𝑑𝑆 + 𝑏𝑎𝑐𝑘
𝐴 ∙ 𝑑𝑆 = 𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑦 𝑑𝑧
𝜕𝐴 𝑥
𝜕𝑥
∣ 𝑝+higher-order term…(3)
• By tacking similar step , we obtain
• 𝑙𝑒𝑓𝑡
𝐴 ∙ 𝑑𝑆 + 𝑟𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡
𝐴 ∙ 𝑑𝑆 = 𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑦 𝑑𝑧
𝜕𝐴 𝑦
𝜕𝑦
∣ 𝑝+higher-order term…..(4)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fieldtheory-190418114015/85/divergence-of-vector-and-divergence-theorem-8-320.jpg)