1. Vector calculus deals with vector-valued functions and their derivatives. It includes vector point functions that assign vectors to points in space, as well as scalar point functions that assign real numbers.
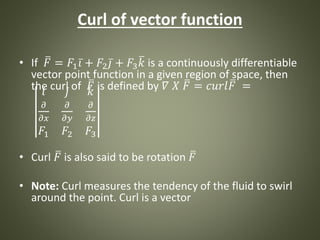
2. Key concepts include the gradient of a scalar function, the divergence and curl of a vector function, and vector fields to describe variations of quantities like velocity over a region of space.
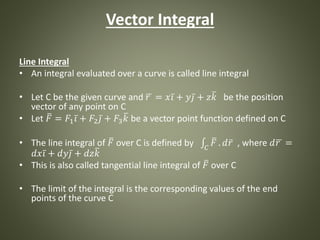
3. Vector calculus theorems relate integrals over surfaces to integrals over bounding curves or volumes, such as Green's theorem, Stokes' theorem, and the divergence theorem. These allow problems involving surfaces and volumes to be solved via line and surface integrals.