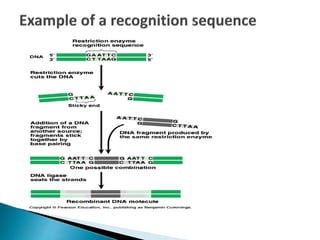
Restriction enzymes were discovered in the 1960s and cut DNA at specific recognition sequences. There are five types of restriction enzymes that differ in subunit composition and sequence recognition. Restriction digestion leaves sticky or blunt ends that can be joined by DNA ligase. Transformation involves the uptake and recombination of extracellular DNA into bacterial cells through natural competence, chemical treatments, or electroporation. Genomic libraries contain fragmented, cloned DNA that represent an organism's entire genome.