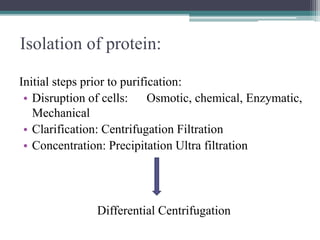
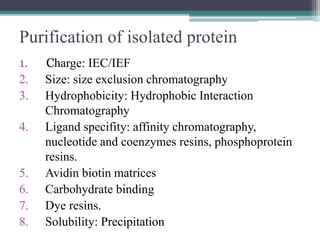
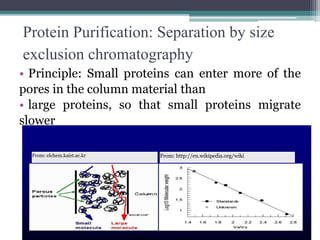
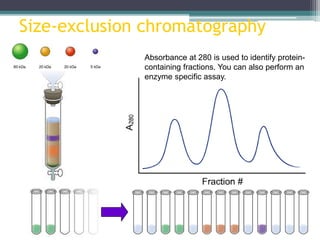
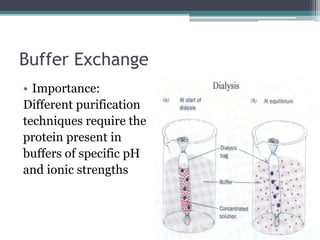
This document discusses methods for expressing and purifying recombinant proteins. It describes commonly used vectors for inserting genes of interest, such as plasmids and artificial chromosomes. The basic steps are outlined as amplifying the gene, inserting it into a cloning vector, subcloning into an expression vector, transforming the vector into a protein-expressing organism, and testing for protein identification. Methods for isolating and purifying the protein include cell disruption, centrifugation, concentration techniques, and differential centrifugation. Common purification methods described are based on separating proteins by charge, size, hydrophobicity, and specific binding sites using techniques like ion exchange chromatography, size exclusion chromatography, and affinity chromatography.