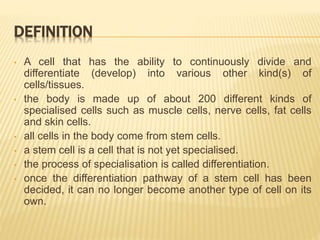
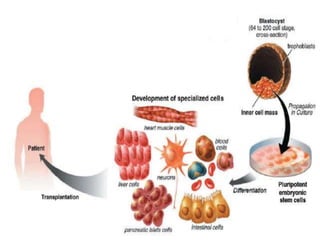
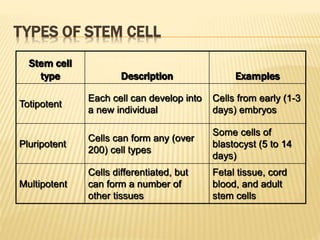
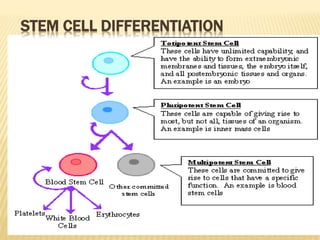
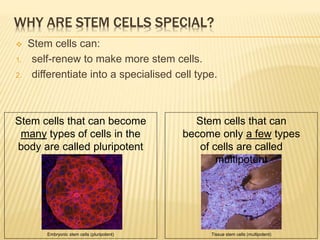
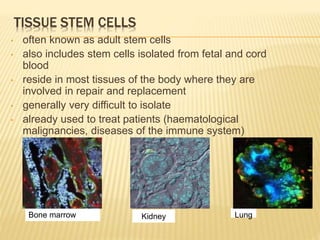
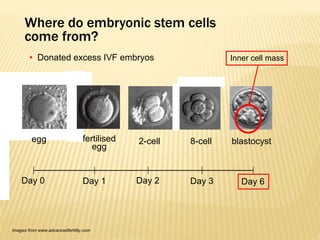
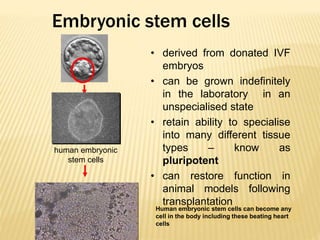
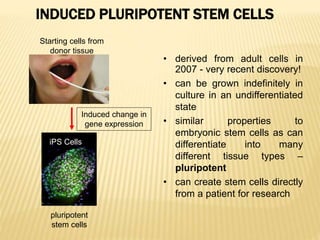
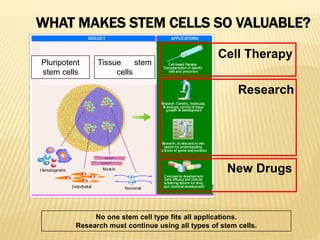
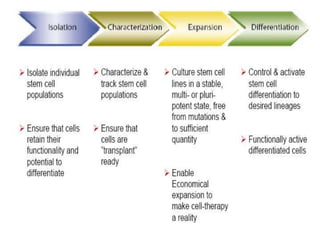
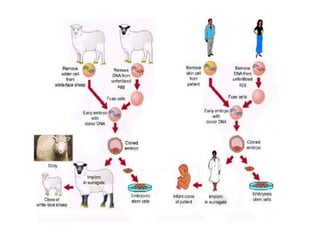
Stem cells are unspecialized cells that have the ability to differentiate into specialized cell types. There are several types of stem cells including embryonic stem cells, which can differentiate into any cell type, and adult or tissue stem cells, which can only differentiate into a limited number of cell types. Stem cells offer potential applications for cell therapy and drug development due to their unique abilities to self-renew and differentiate. However, there are still many challenges to the clinical application of stem cells, such as controlling differentiation and preventing immune rejection.