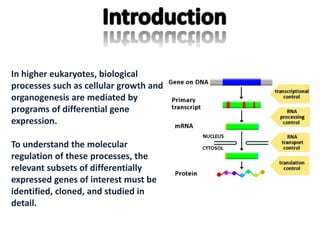
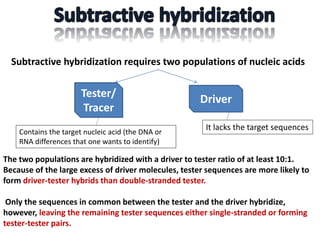
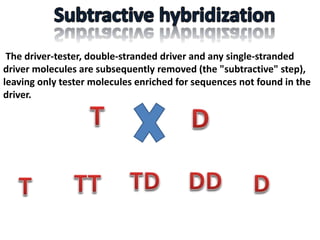
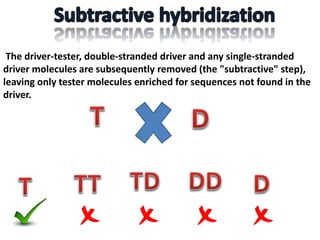
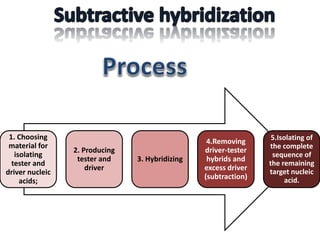
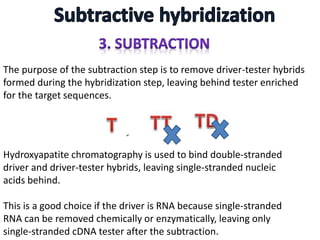
The document discusses the technique of subtractive hybridization, which is used to identify and characterize differences between populations of nucleic acids, specifically for understanding gene expression in higher eukaryotes. It details the processes involved, including material selection for tester and driver nucleic acids, hybridization, and the steps to isolate target sequences. The procedures emphasize the enrichment of unique tester sequences through hybridization and subtraction methods to allow for further analysis of these genes.