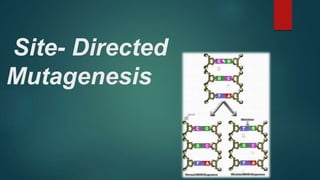
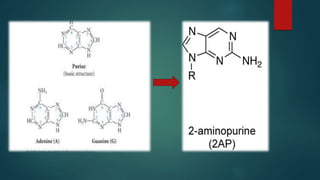
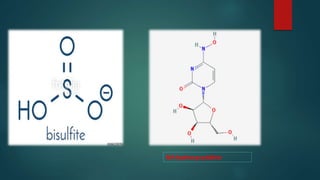
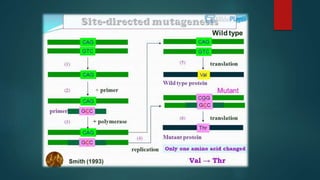
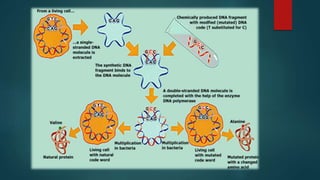
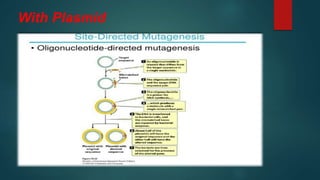
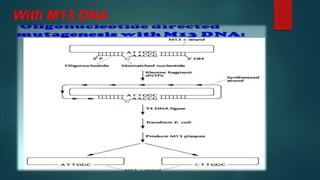
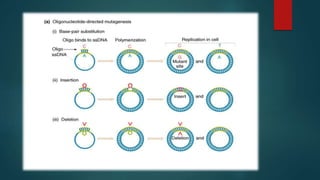
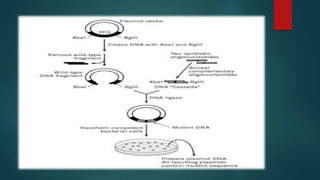
Site-directed mutagenesis is a technique used to introduce specific changes to the DNA sequence of a gene by altering the nucleotide sequence. It allows researchers to study the impact of mutations by changing individual bases, deleting bases, or inserting new bases. There are different methods of site-directed mutagenesis including oligonucleotide-based methods and PCR-based methods. Site-directed mutagenesis has applications in research, production of desired proteins, and development of engineered proteins for commercial uses like detergents.