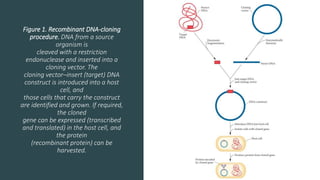
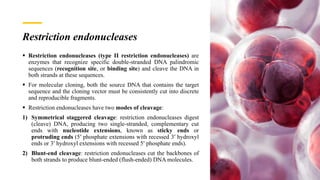
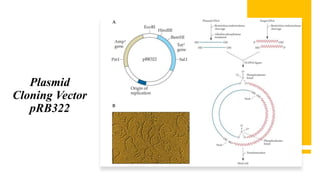
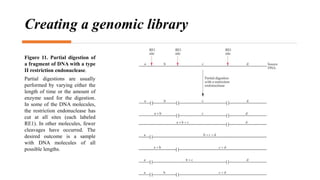
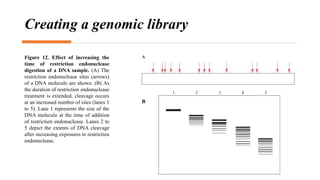
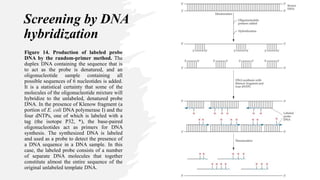
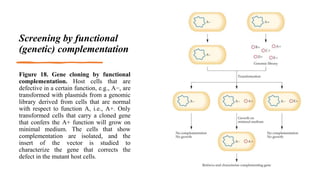
Recombinant DNA technology involves transferring genetic material from one organism to another. A common method is to extract DNA from a donor organism, cut it with restriction enzymes, and ligate it into a vector like a plasmid. This recombinant DNA is then introduced into host cells. Cells containing the recombinant DNA can be identified by screening, such as using hybridization probes to detect the target DNA sequence. Creating a genomic library involves cutting an organism's entire genome into fragments, inserting them into vectors, and transforming host cells to generate a collection containing all the organism's DNA.