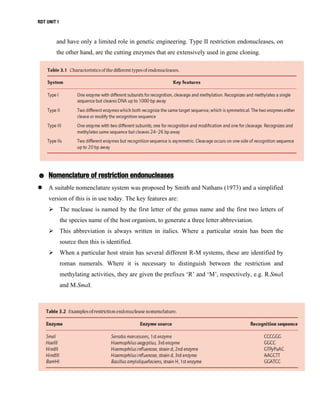
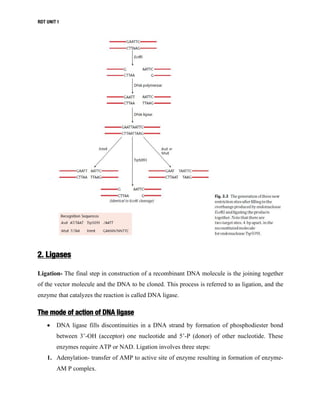
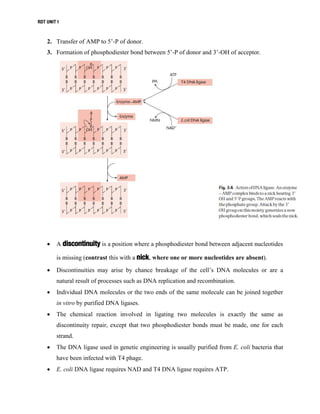
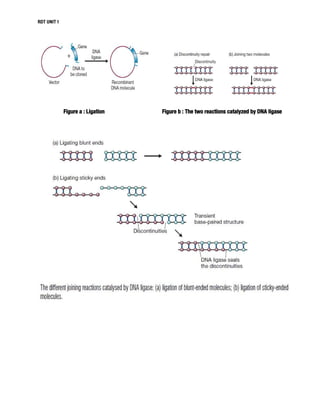
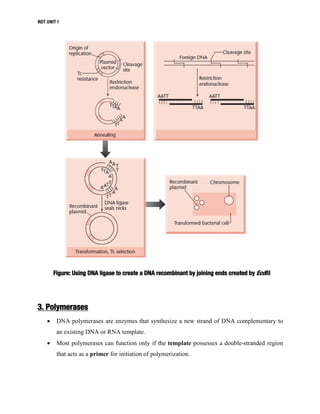
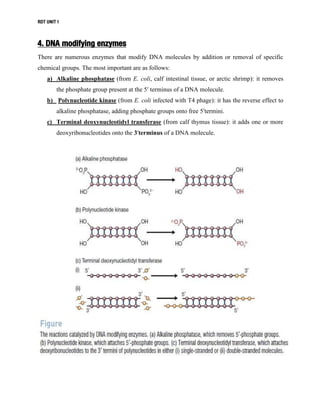
DNA manipulative enzymes can be grouped into four classes: nucleases cut DNA, ligases join DNA, polymerases copy DNA, and modifying enzymes add or remove chemical groups from DNA. Restriction endonucleases are nucleases that cut DNA at specific recognition sequences and are important for gene cloning. They produce either blunt or sticky ends. DNA ligase joins DNA fragments together by forming phosphodiester bonds. Polymerases like Klenow fragment and Taq polymerase copy DNA. Modifying enzymes alter DNA through addition or removal of chemical groups from the DNA backbone. Together, these enzymes enable the precise cutting and joining of DNA required for gene cloning experiments.