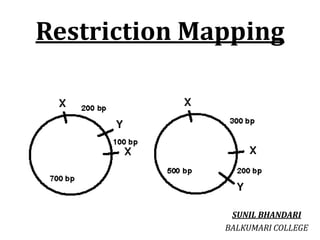
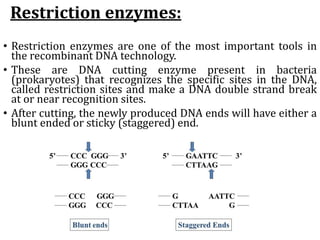
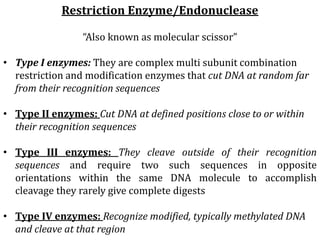
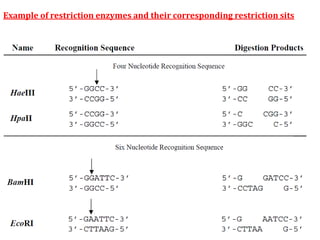
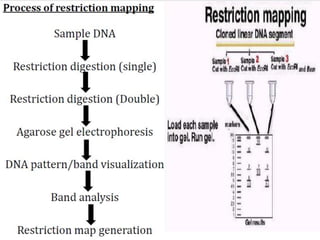
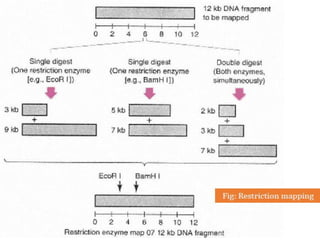
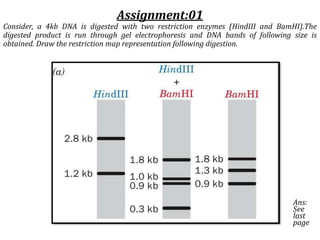
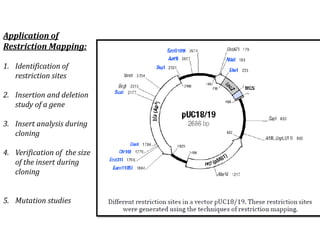
Restriction enzymes cut DNA molecules at specific recognition sites. Restriction mapping involves digesting an unknown DNA segment with restriction enzymes and analyzing the fragment sizes to determine the locations of restriction sites. One method involves single and double digestions with two enzymes followed by gel electrophoresis to separate the fragments by size. By comparing the fragment patterns between single and double digestions, the positions of each restriction site can be mapped, generating a restriction map of the DNA segment. Restriction mapping was previously important for characterizing cloned DNA but is now easier using DNA sequencing, though analysis of restriction sites remains useful for comparing chromosomal organization between strains.