Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX




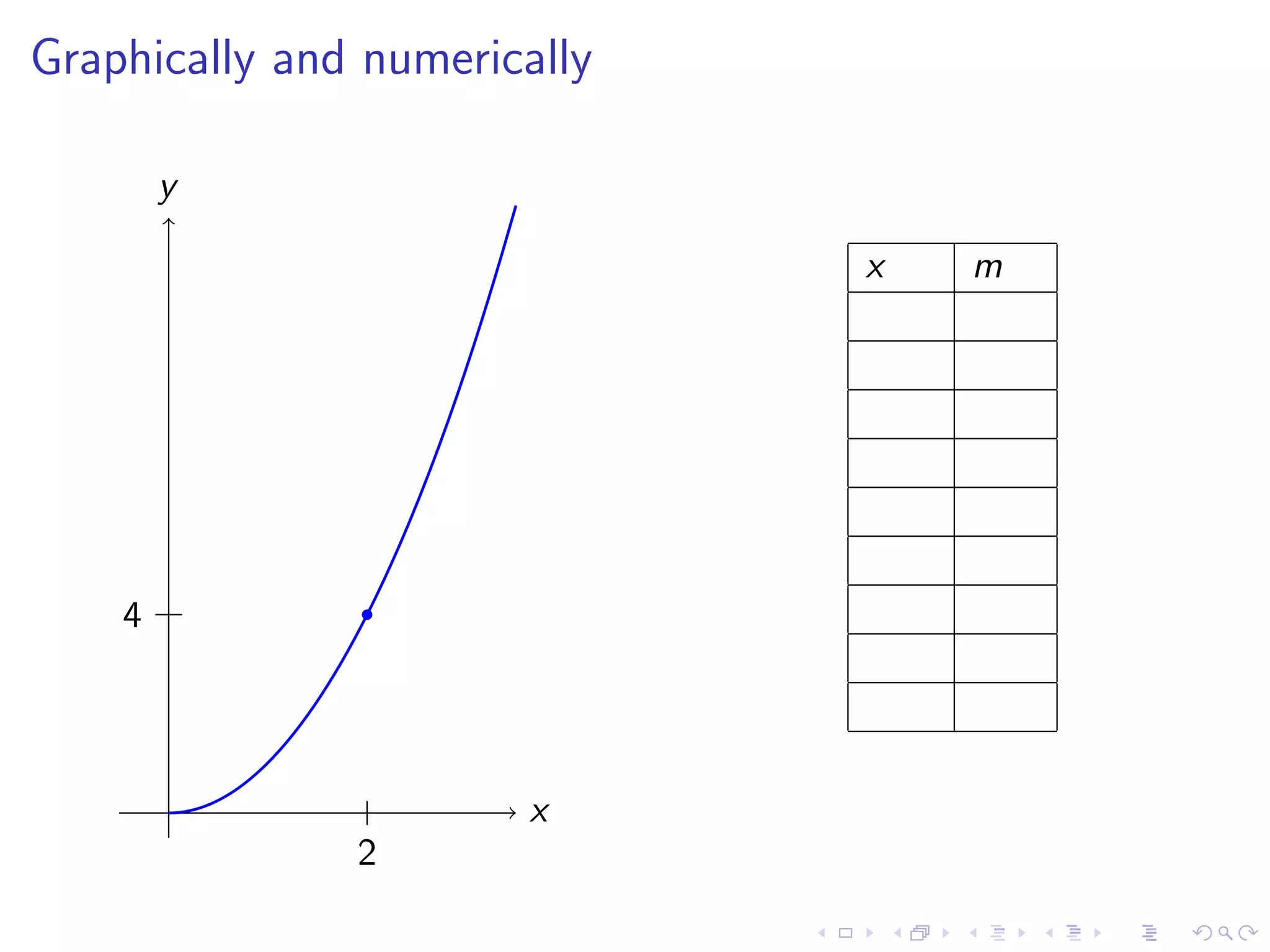
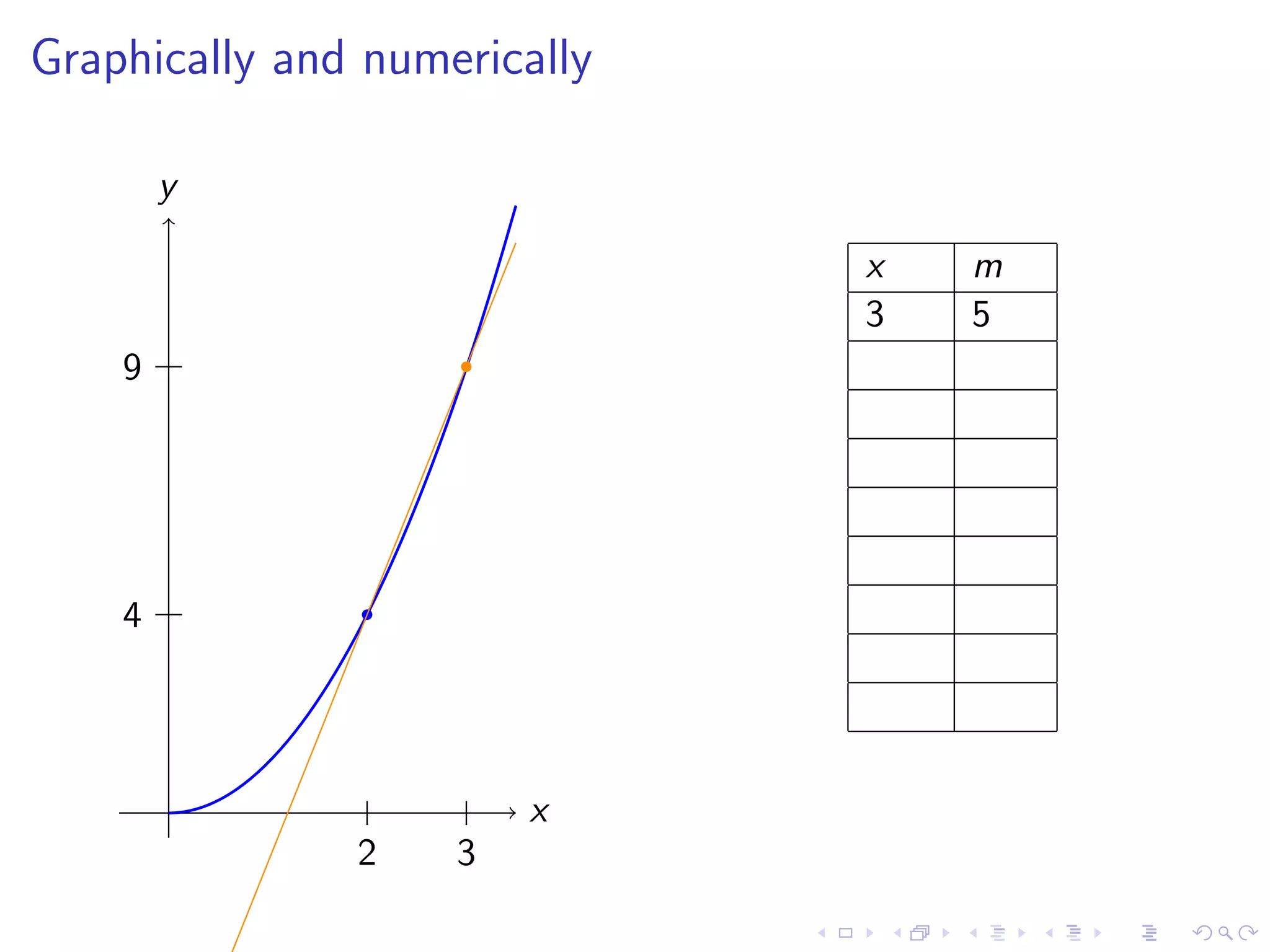
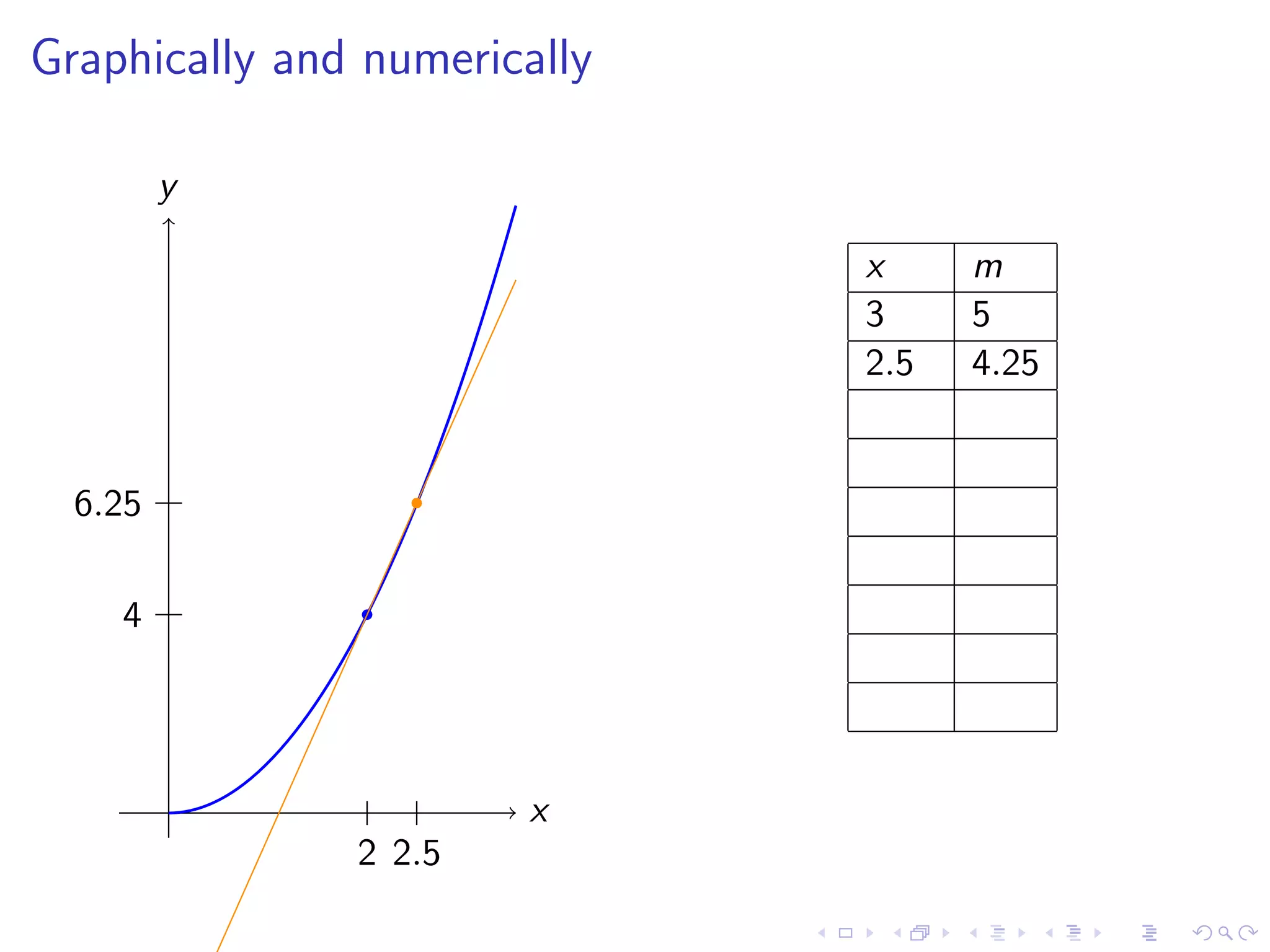
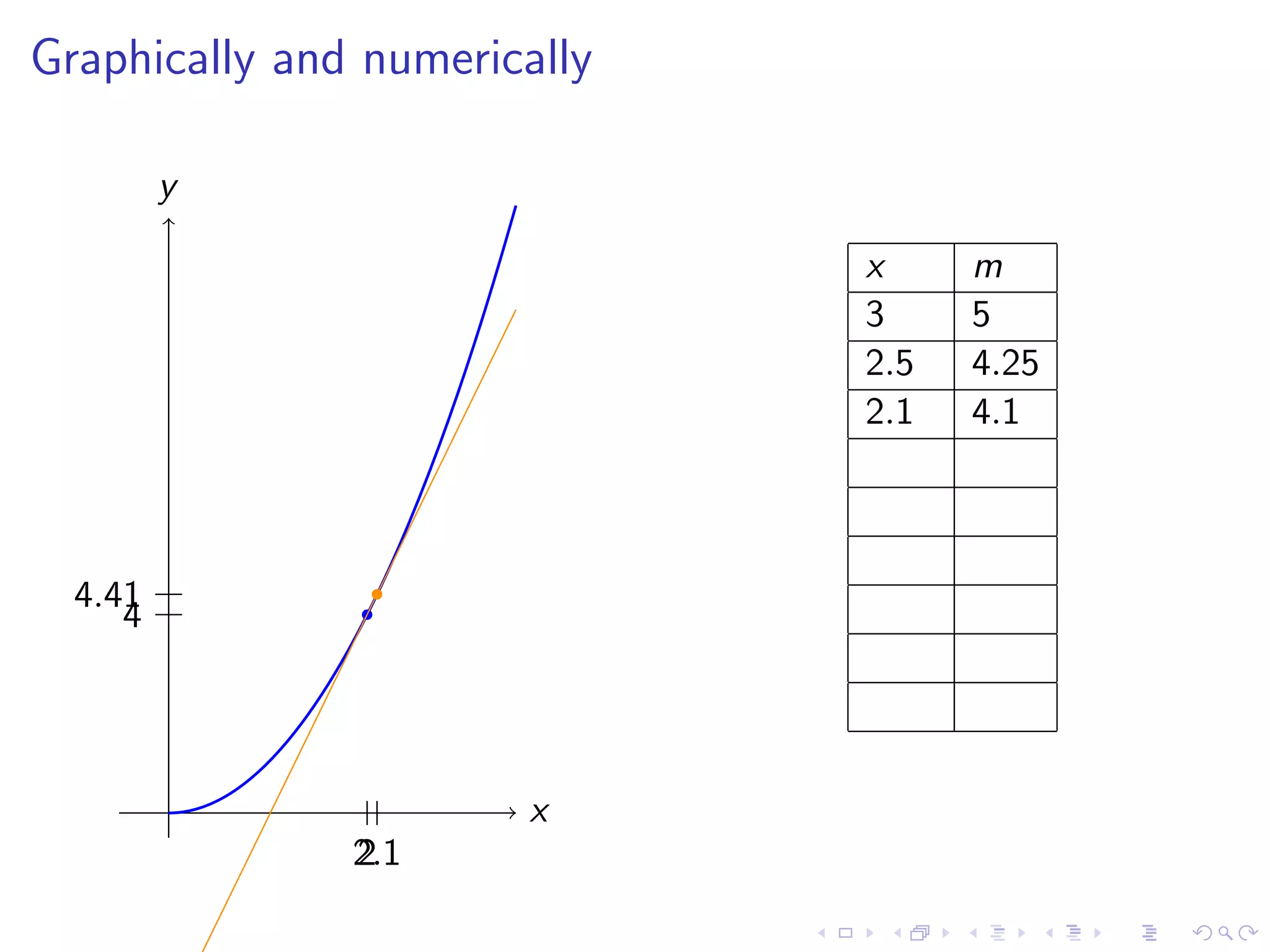
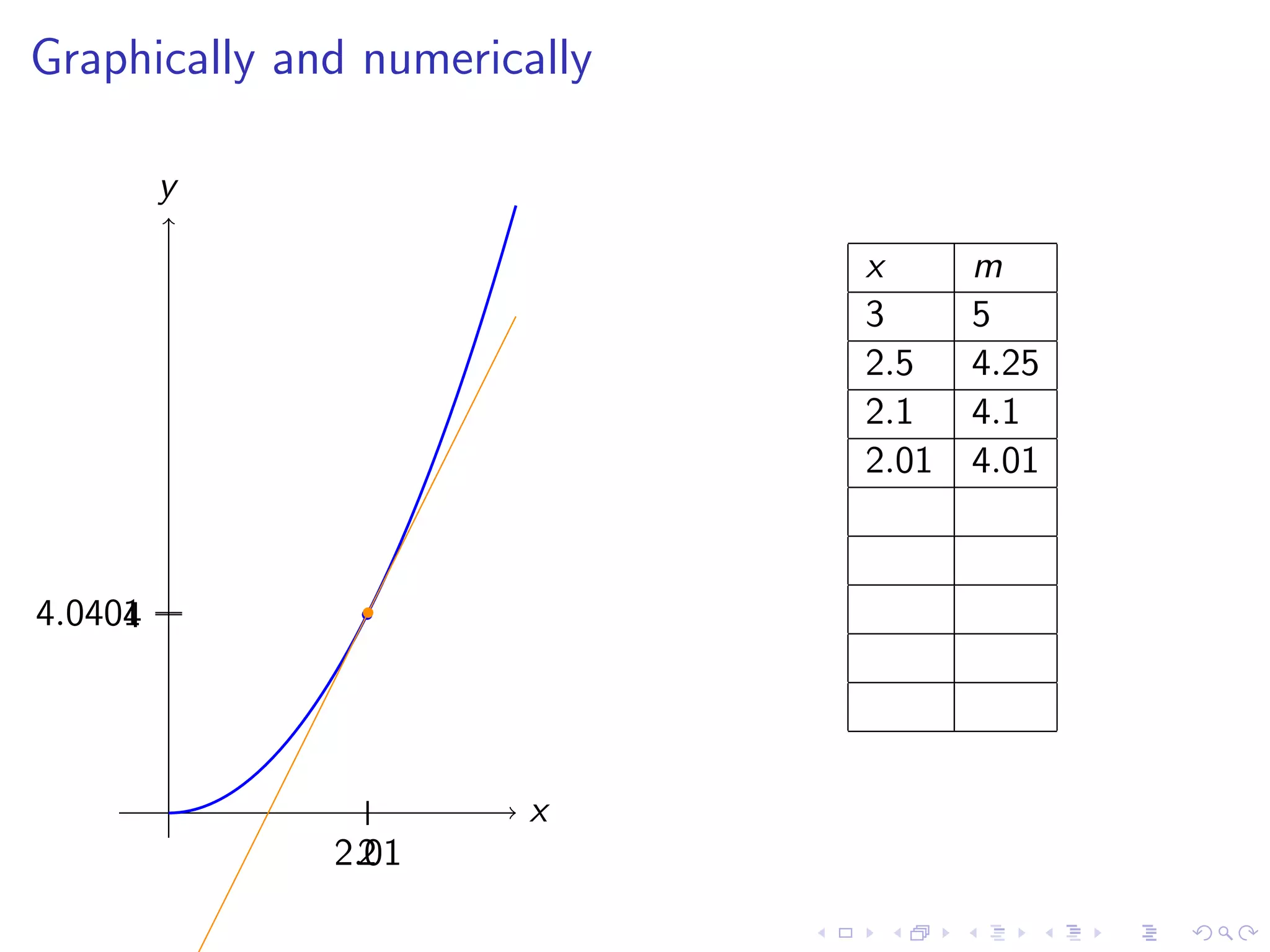
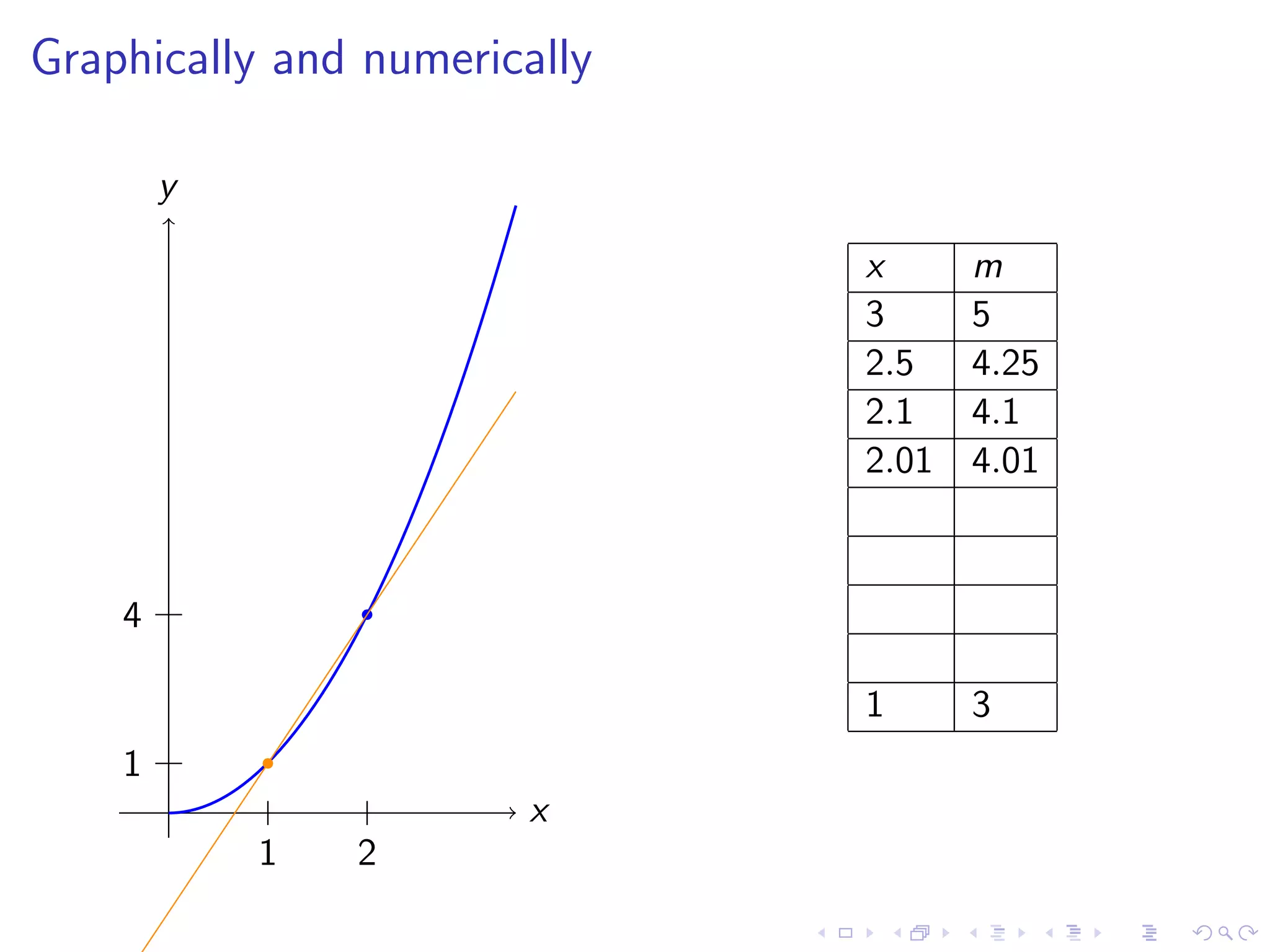
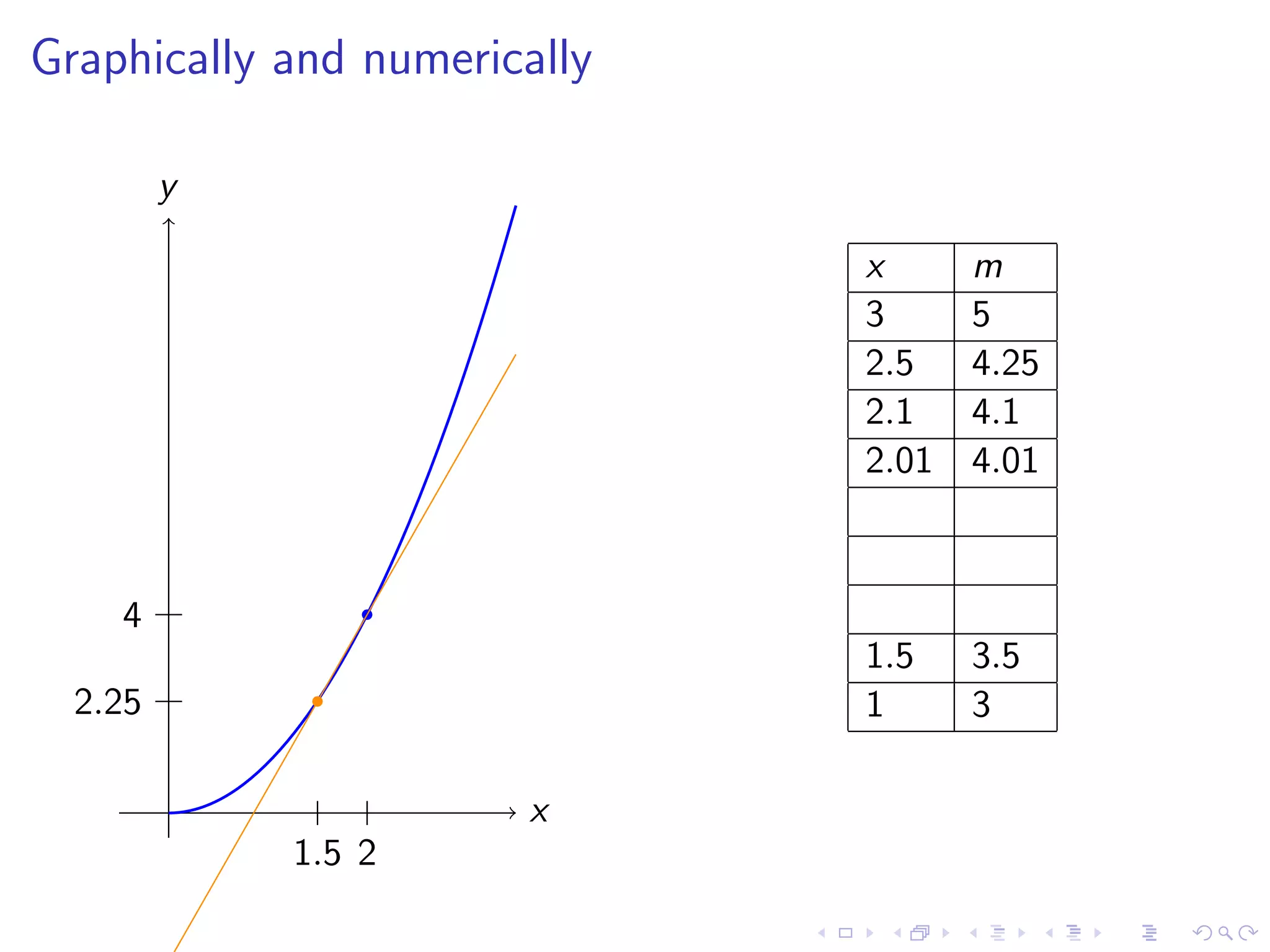
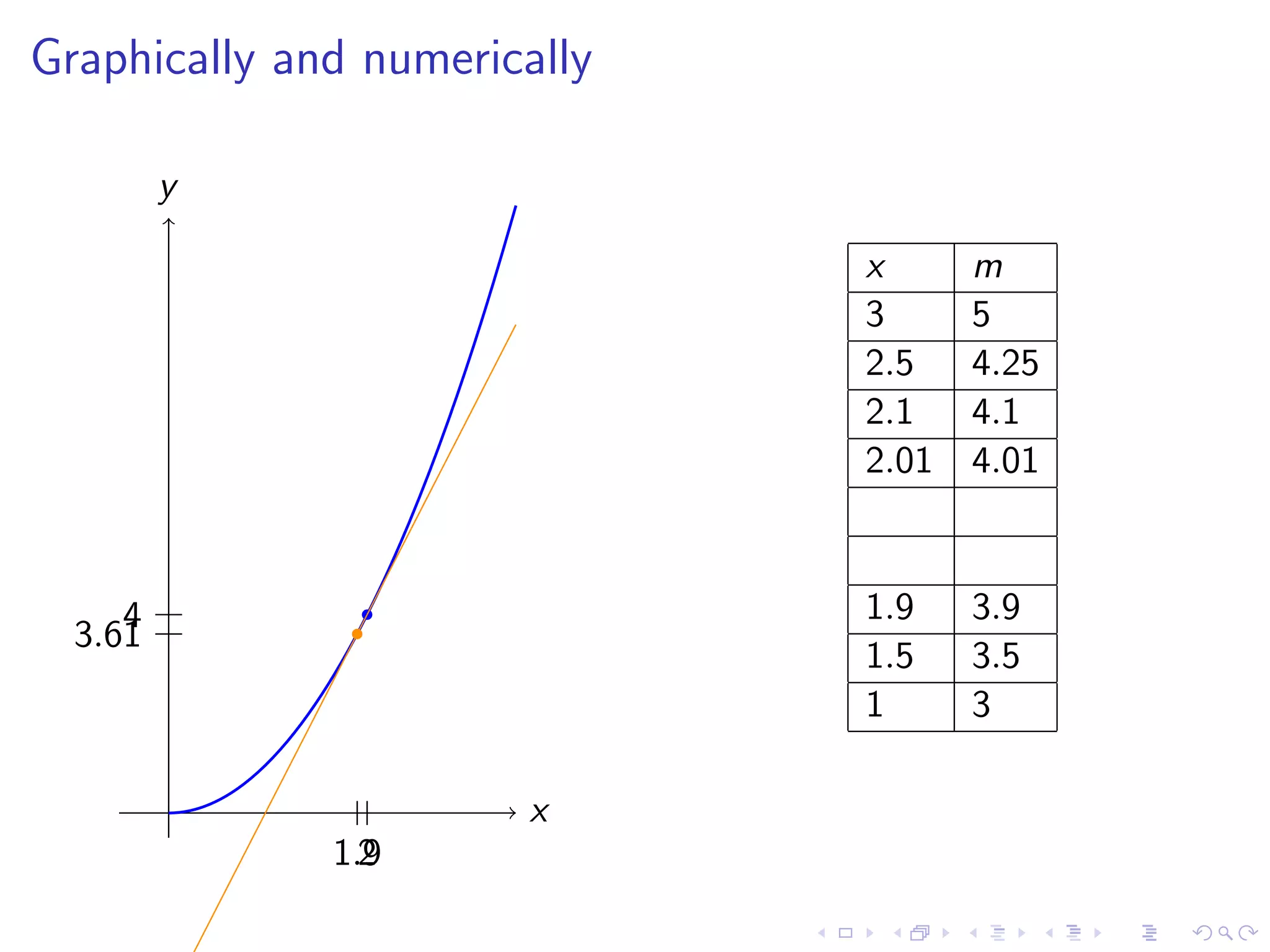





























The document discusses fundamental concepts in calculus, focusing on derivatives, rates of change, and how they are applied to various problems such as tangent lines, velocity, population growth, and marginal costs. It outlines definitions, provides examples, and explains mathematical notations related to derivatives. Additionally, it covers the conditions under which functions are differentiable and introduces the concept of the second derivative as a measure of the rate of change of the rate of change.
Overview of derivatives, tangent lines, velocity, population growth, marginal costs, and quiz announcements.
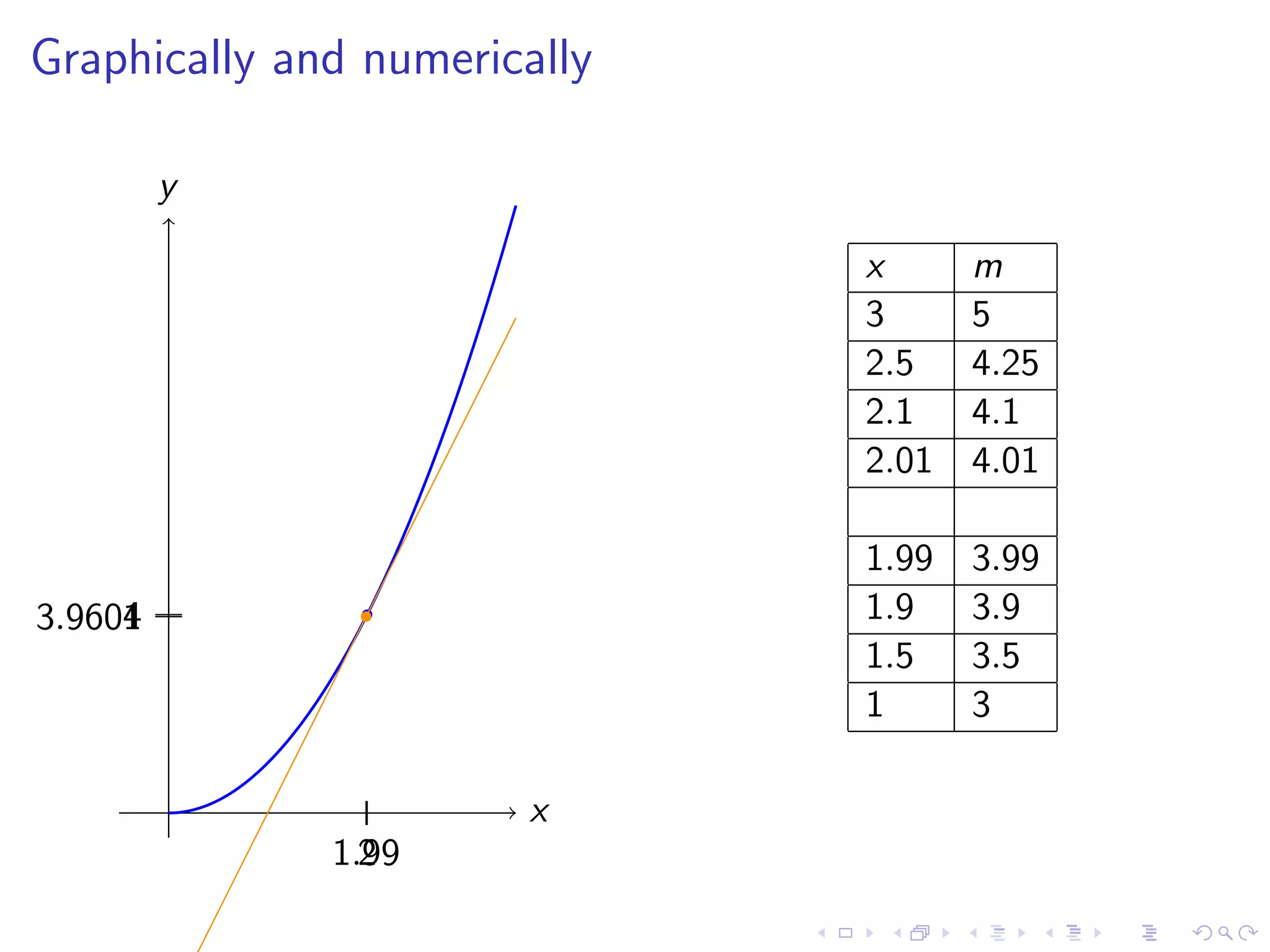
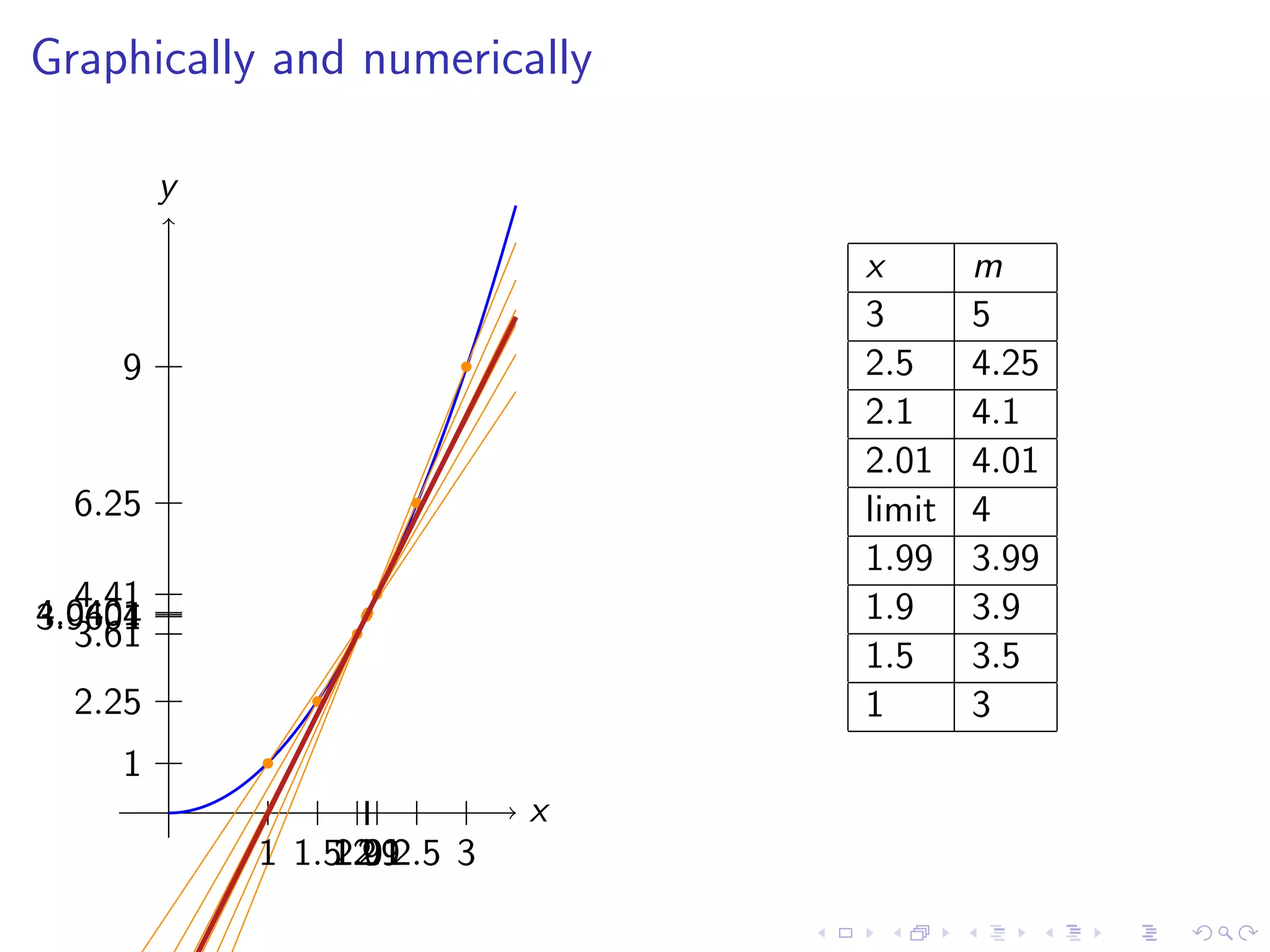
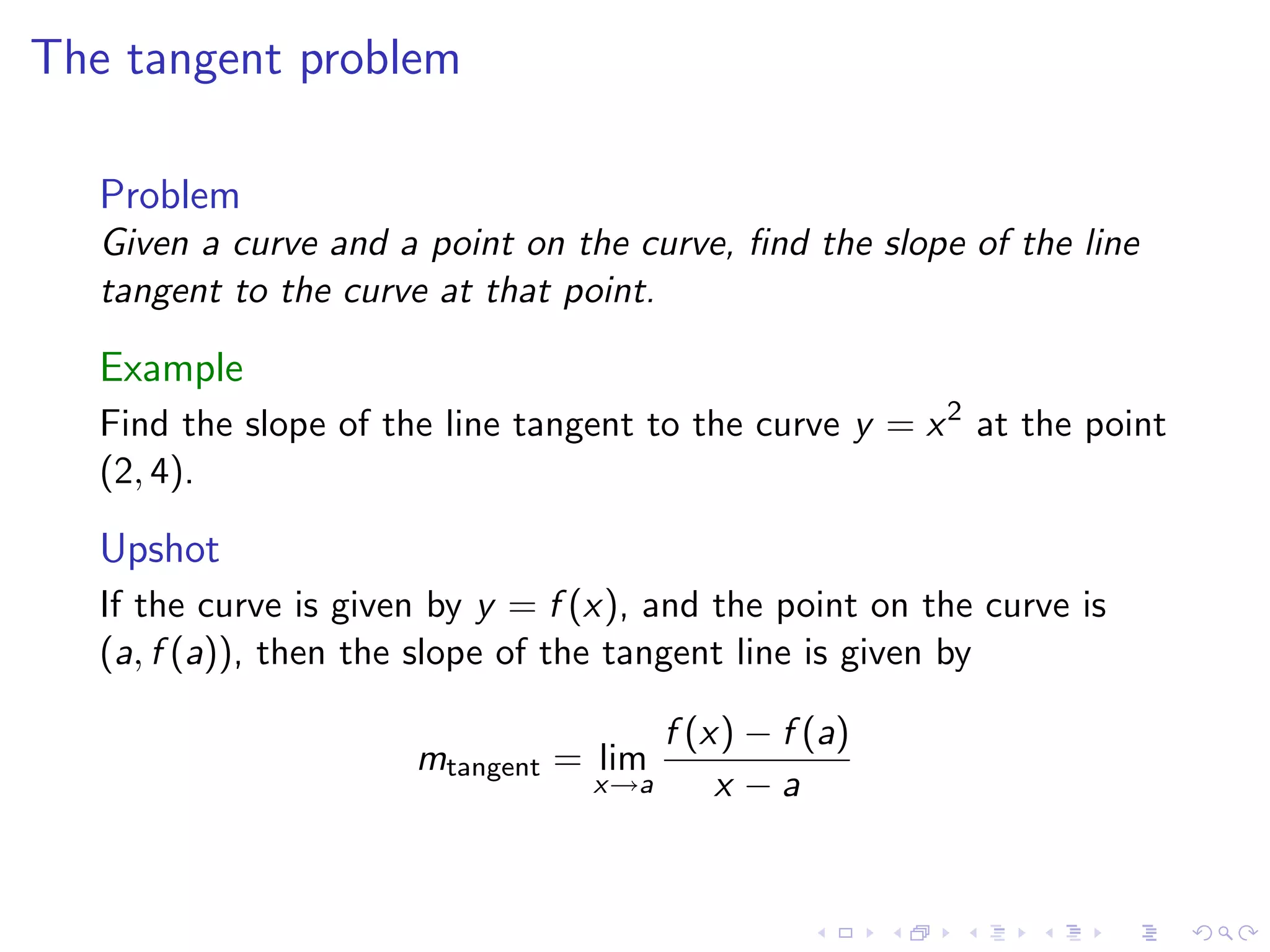
Discusses finding the slope of a tangent line at a point on a curve, with examples including y=x² and various graphical representations.
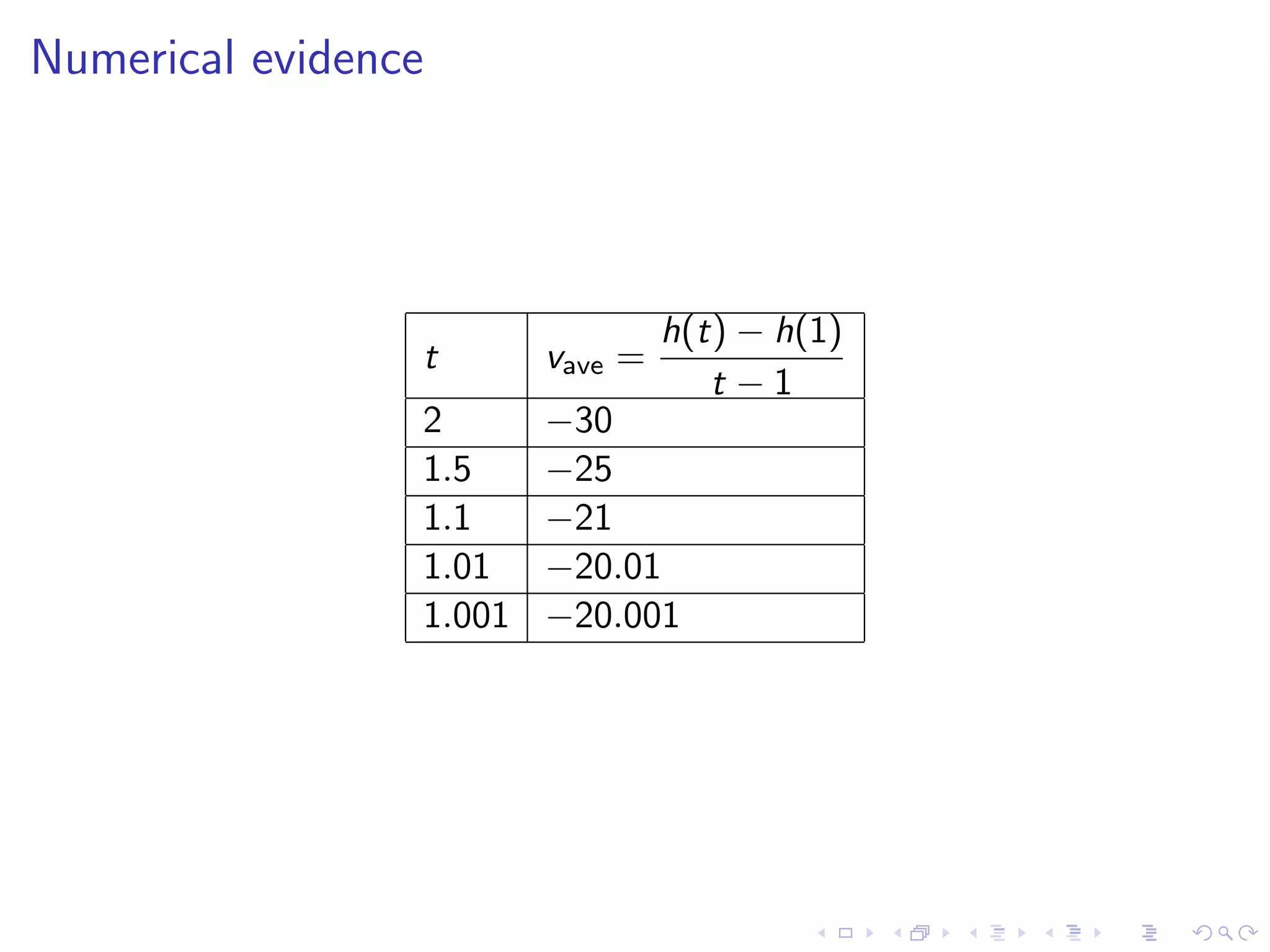
Describes finding the instantaneous velocity using position functions, with a specific example of a ball's height and velocity after dropping.
Explores finding the growth rate of a population over time with a specific fish population model, providing numerical evidences for different years.
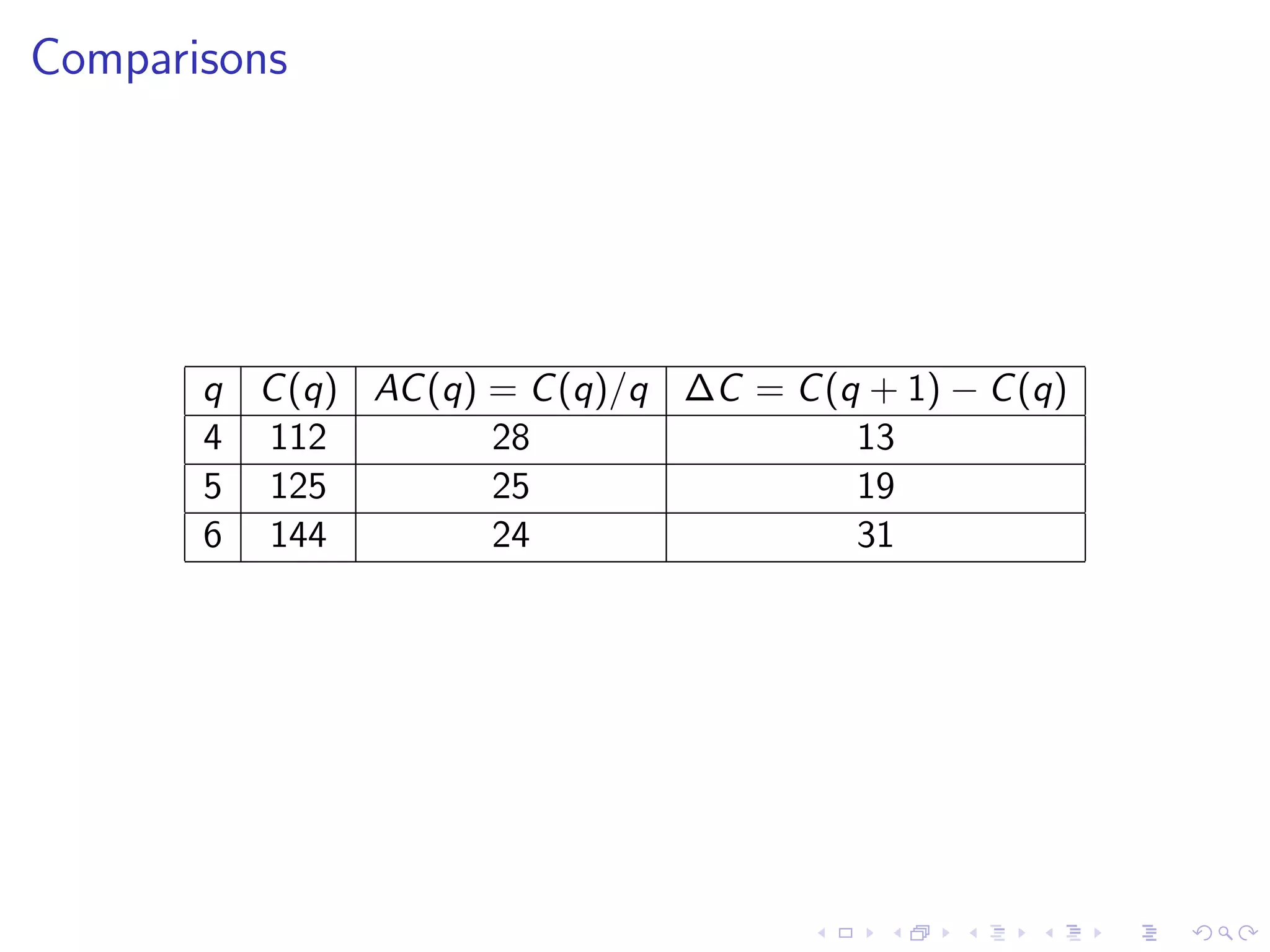
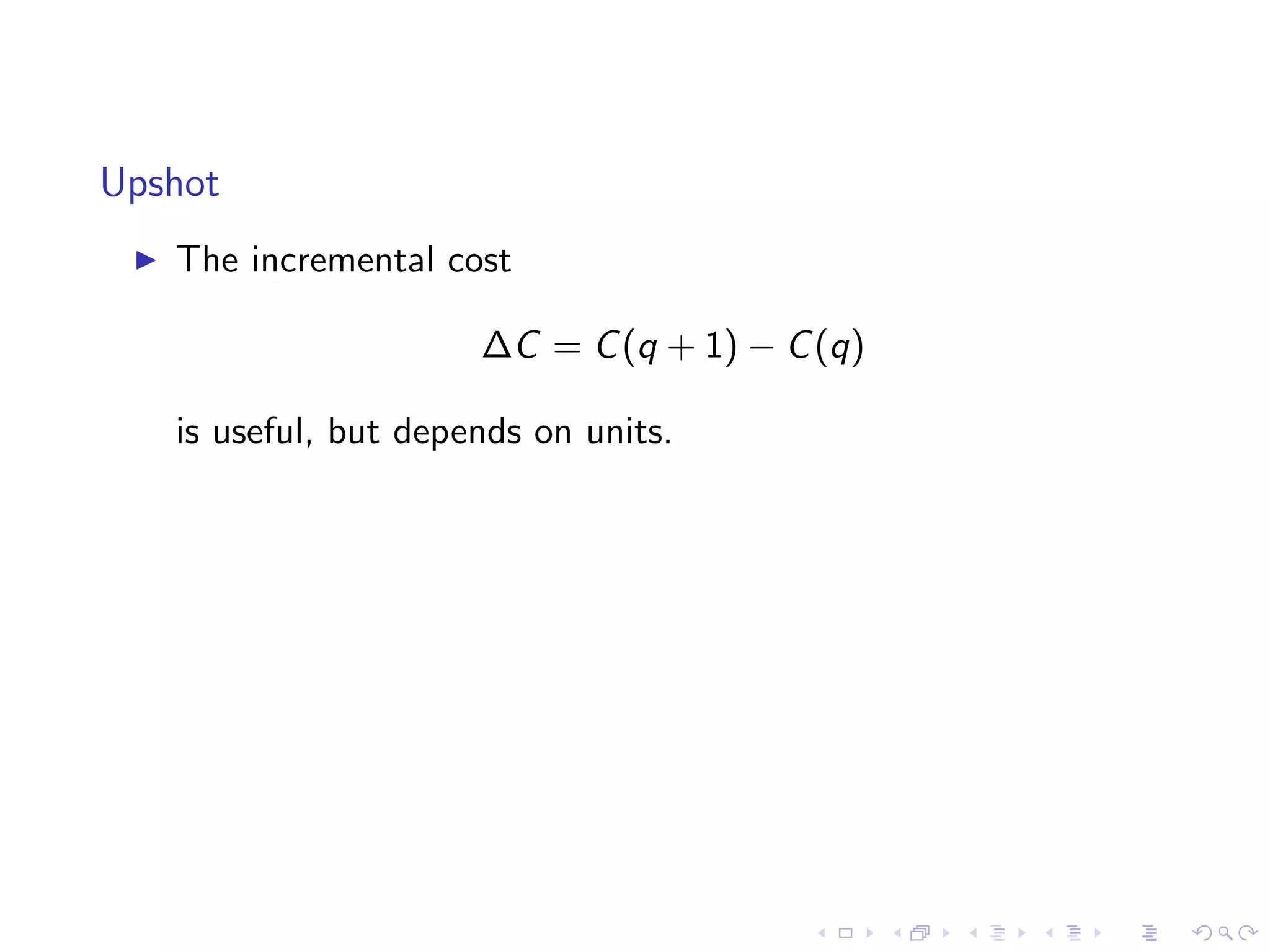
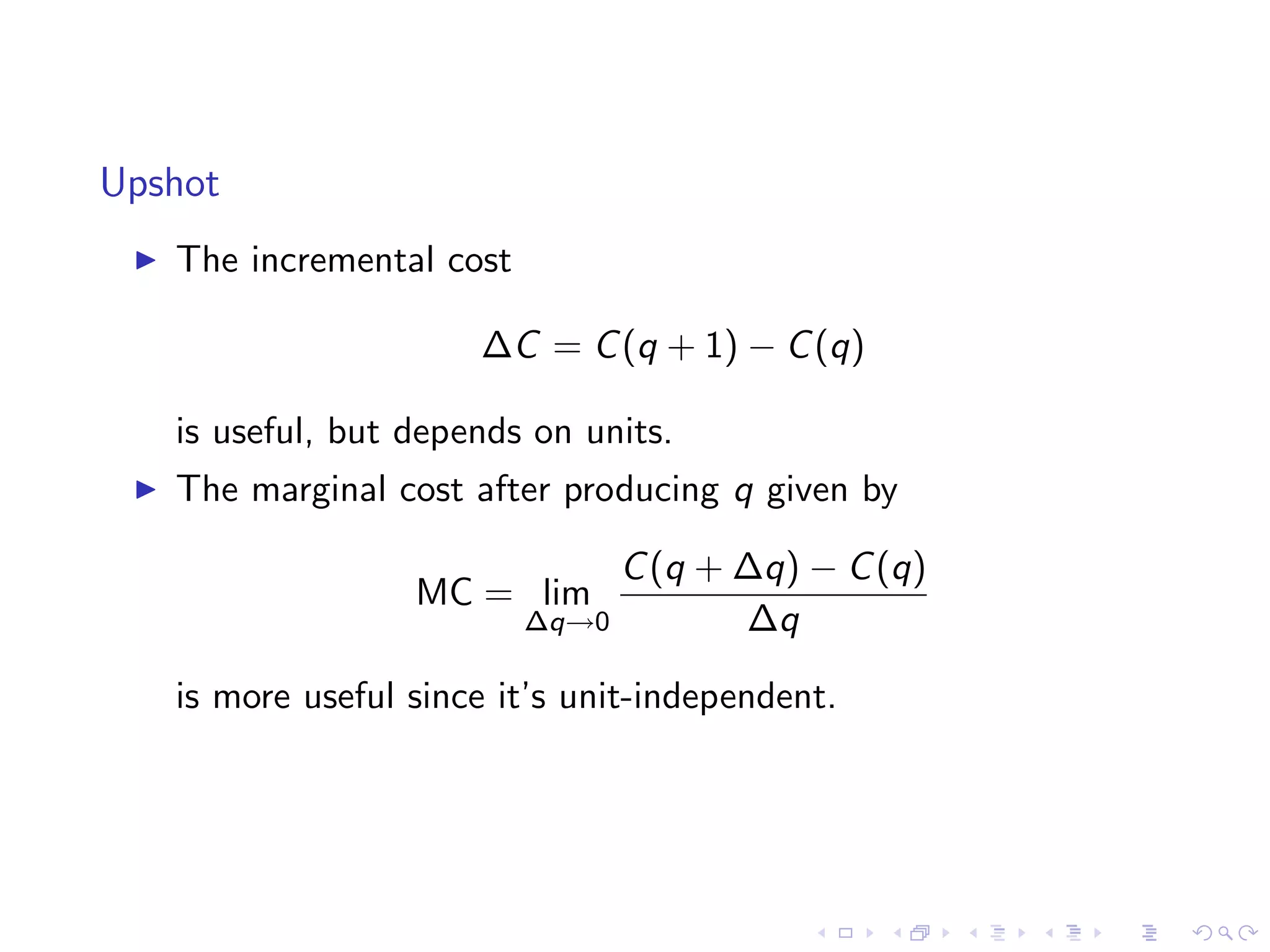
Analyzes marginal costs in production using a cost function example for rice, including comparisons of costs at different production levels.
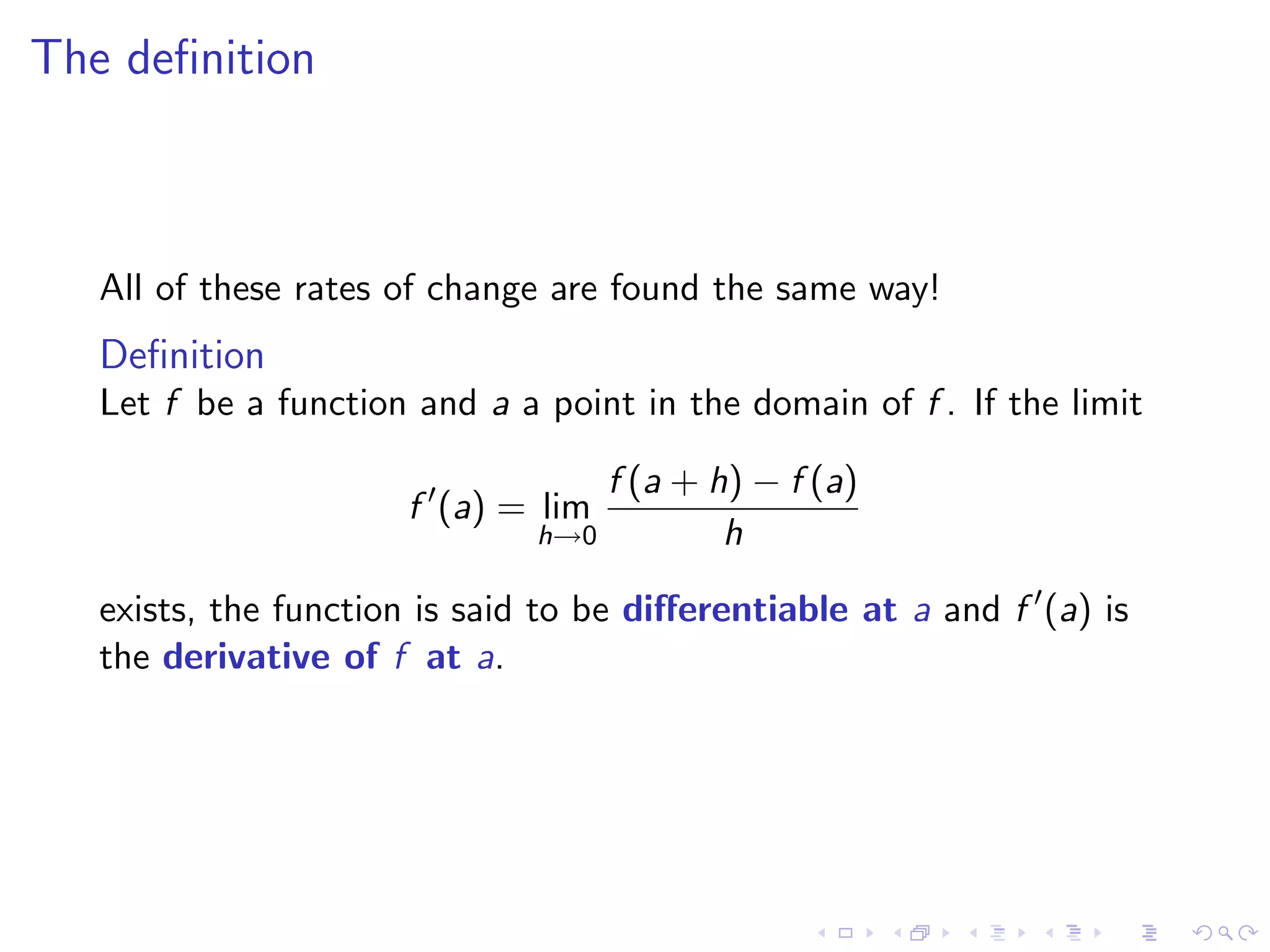
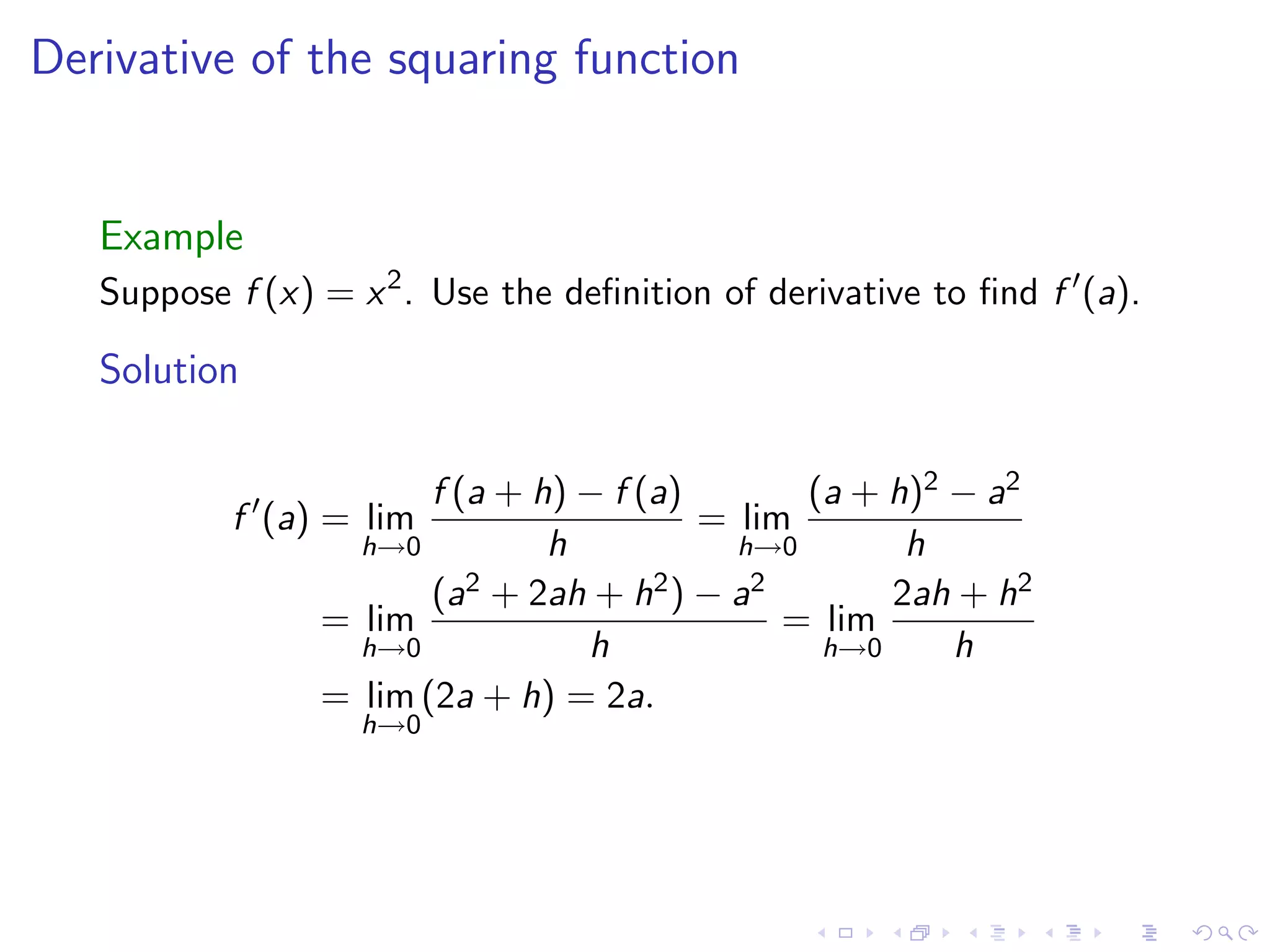
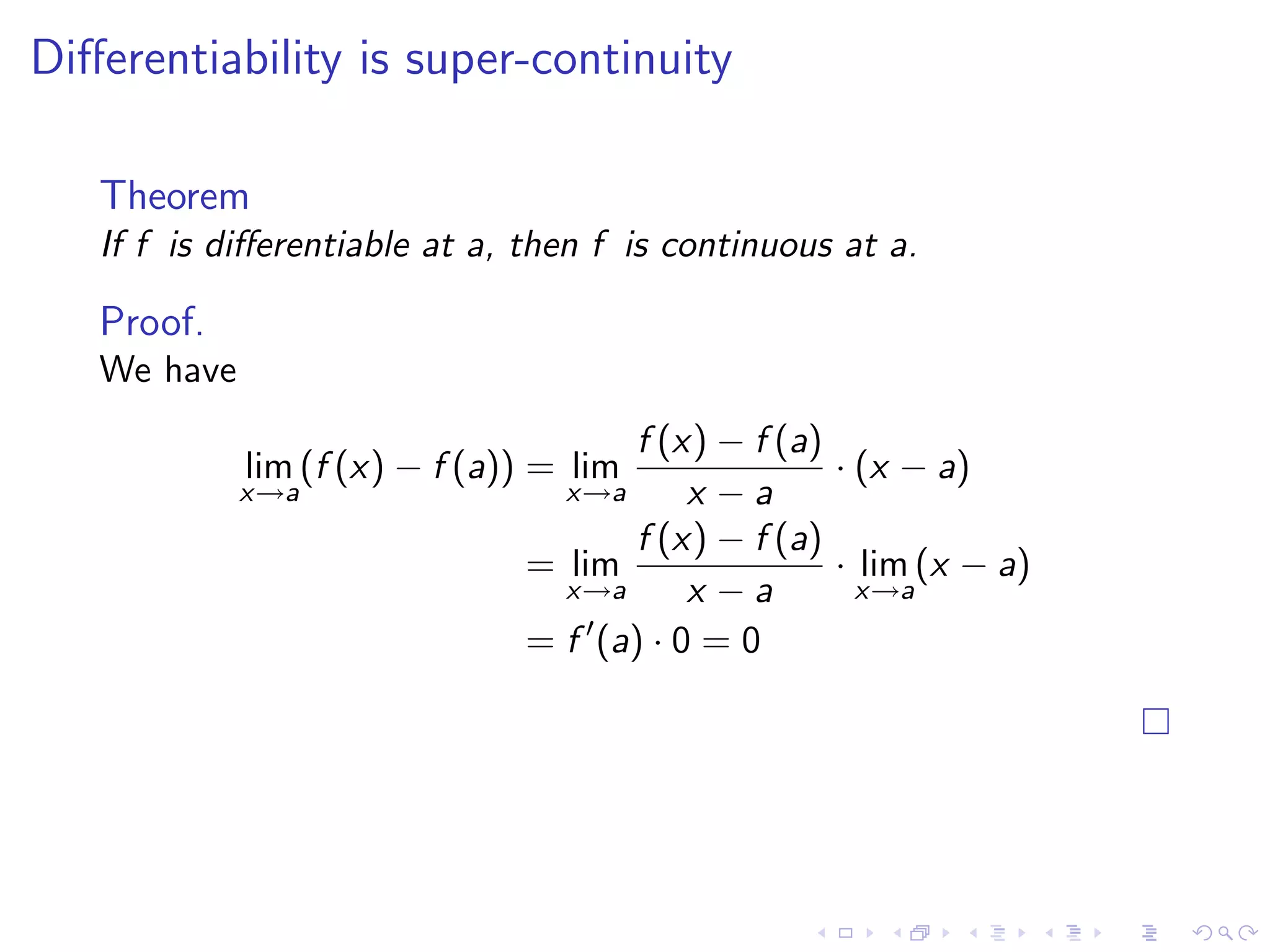
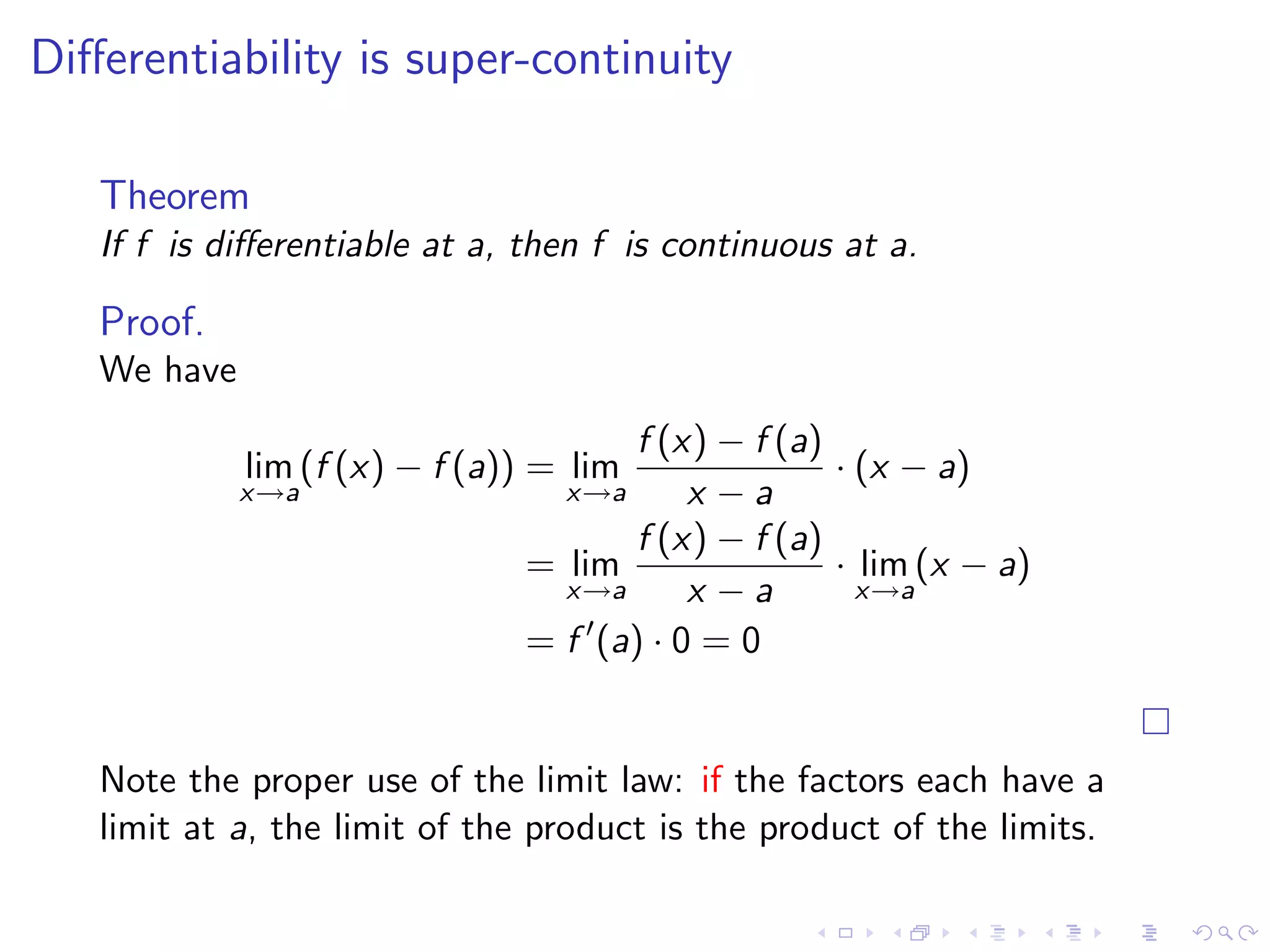
Introduction to the derivative definition, its significance, the continuity associated with differentiability, and common notations.
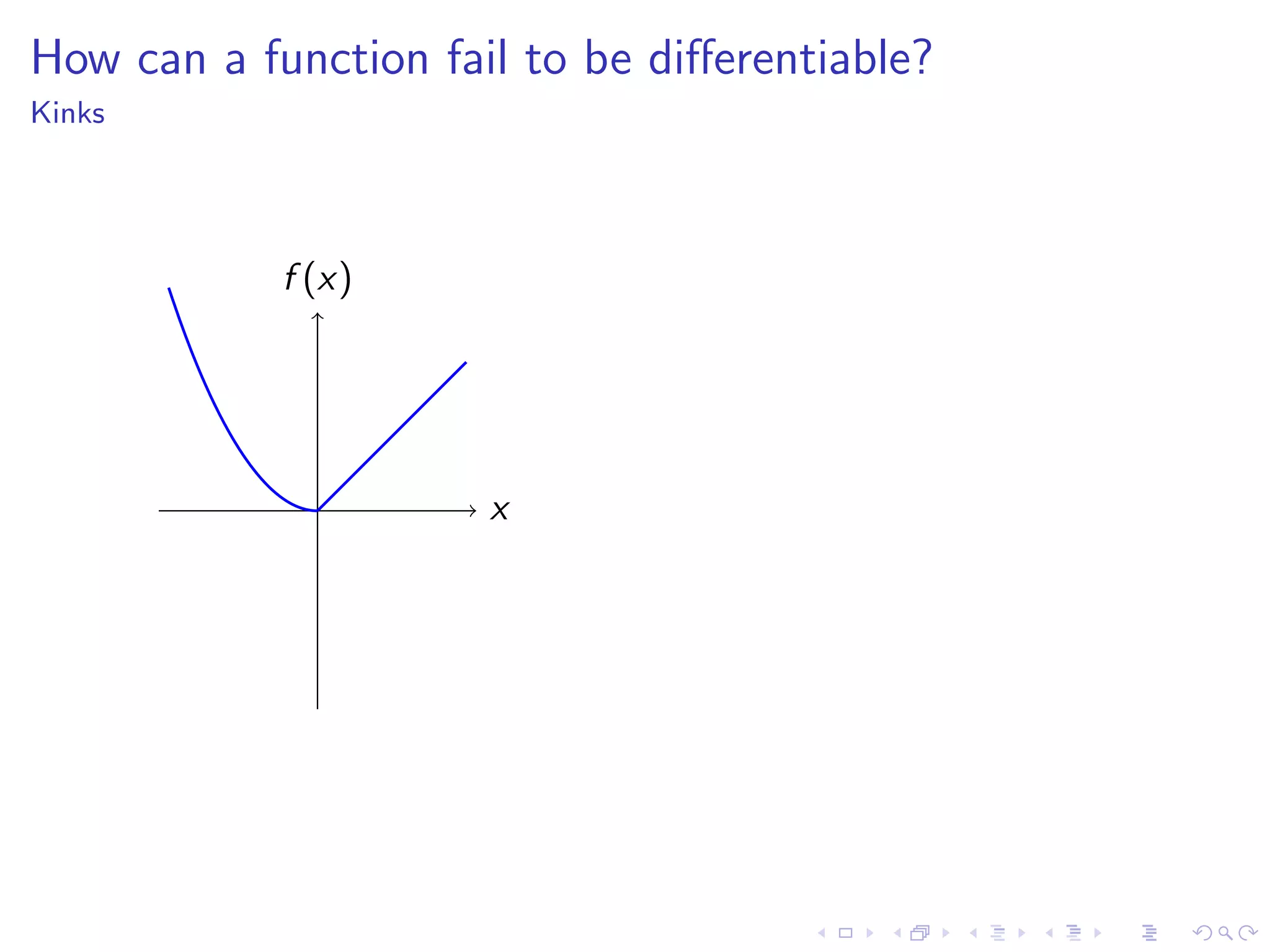
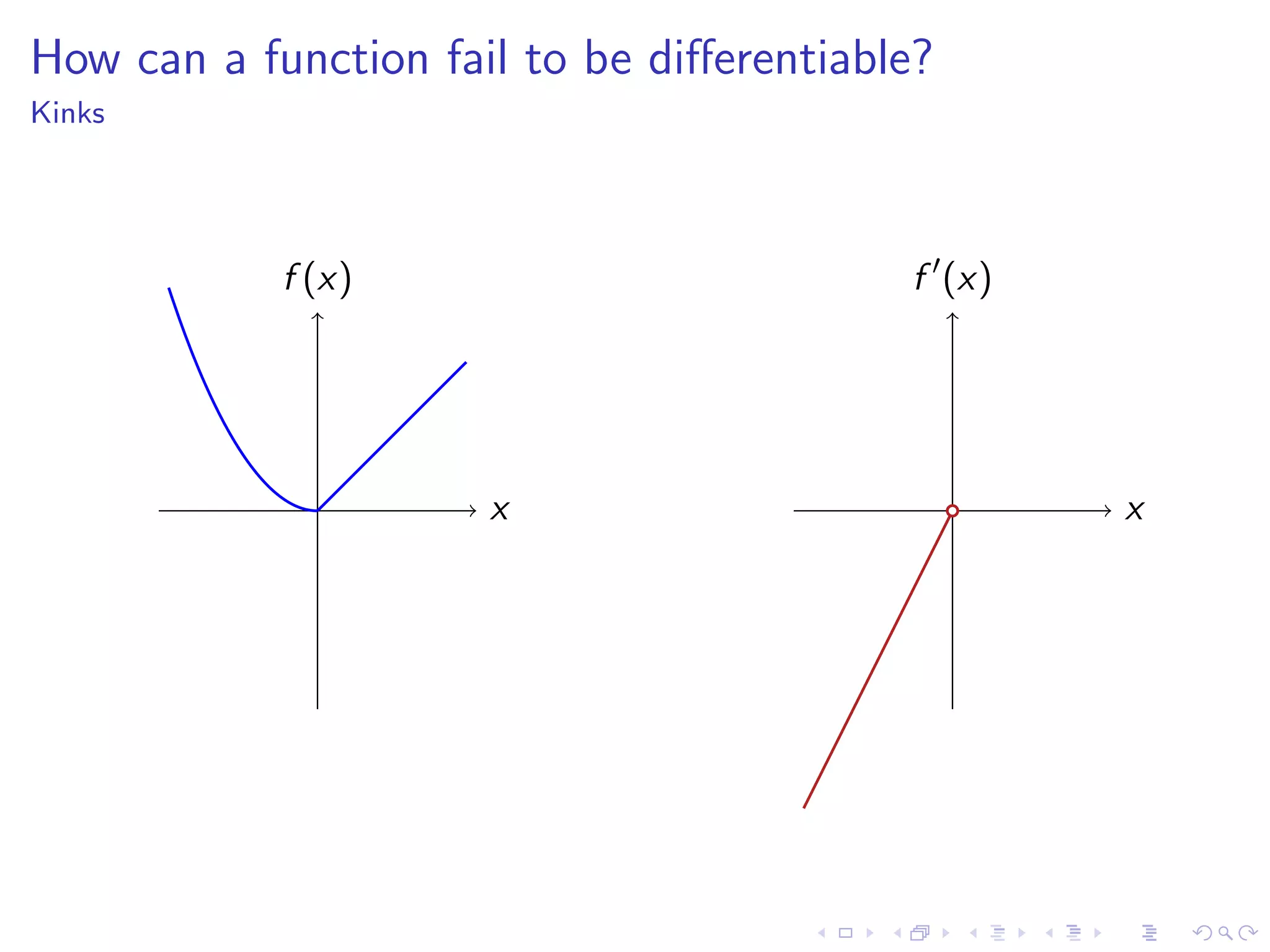
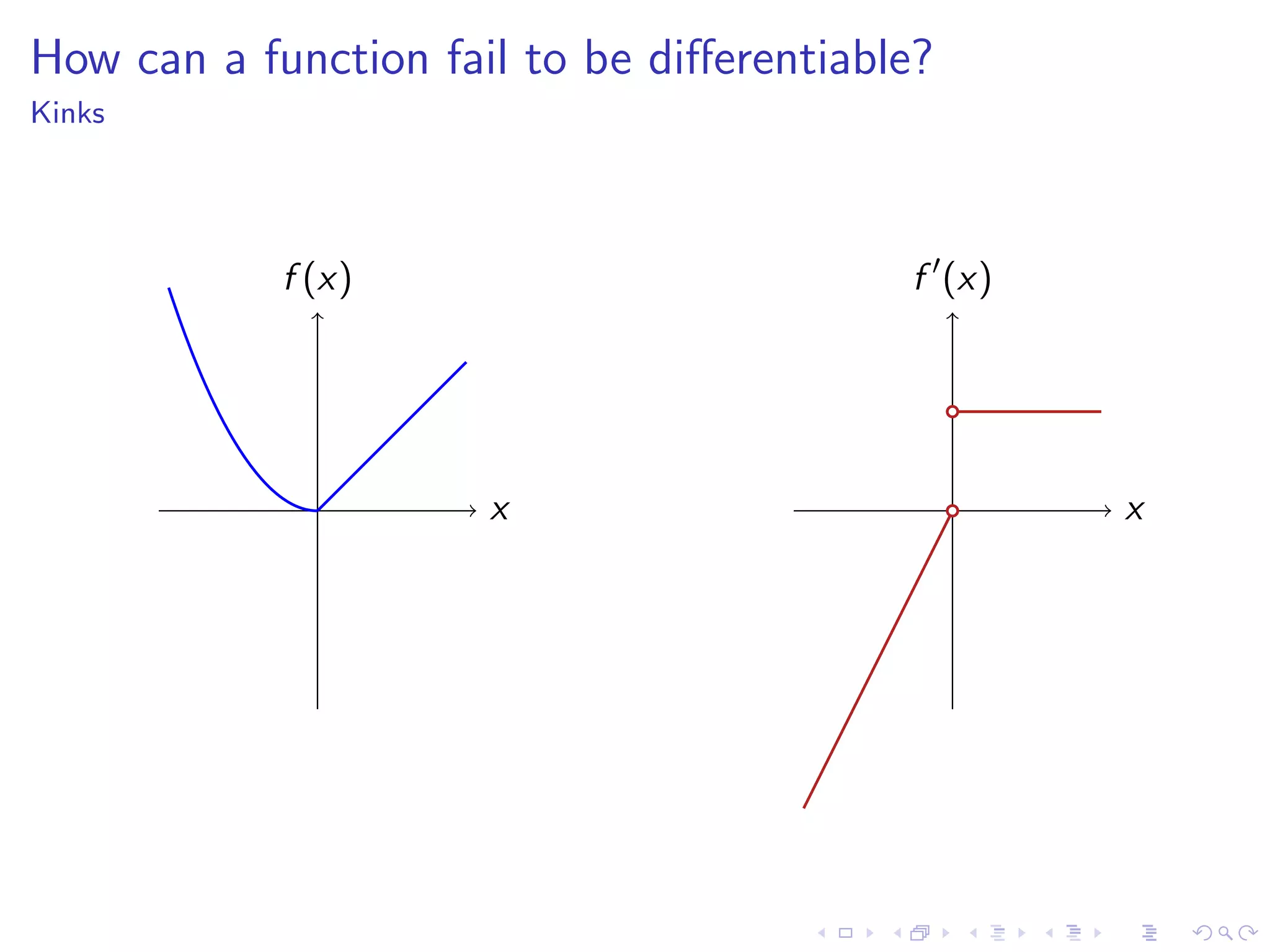
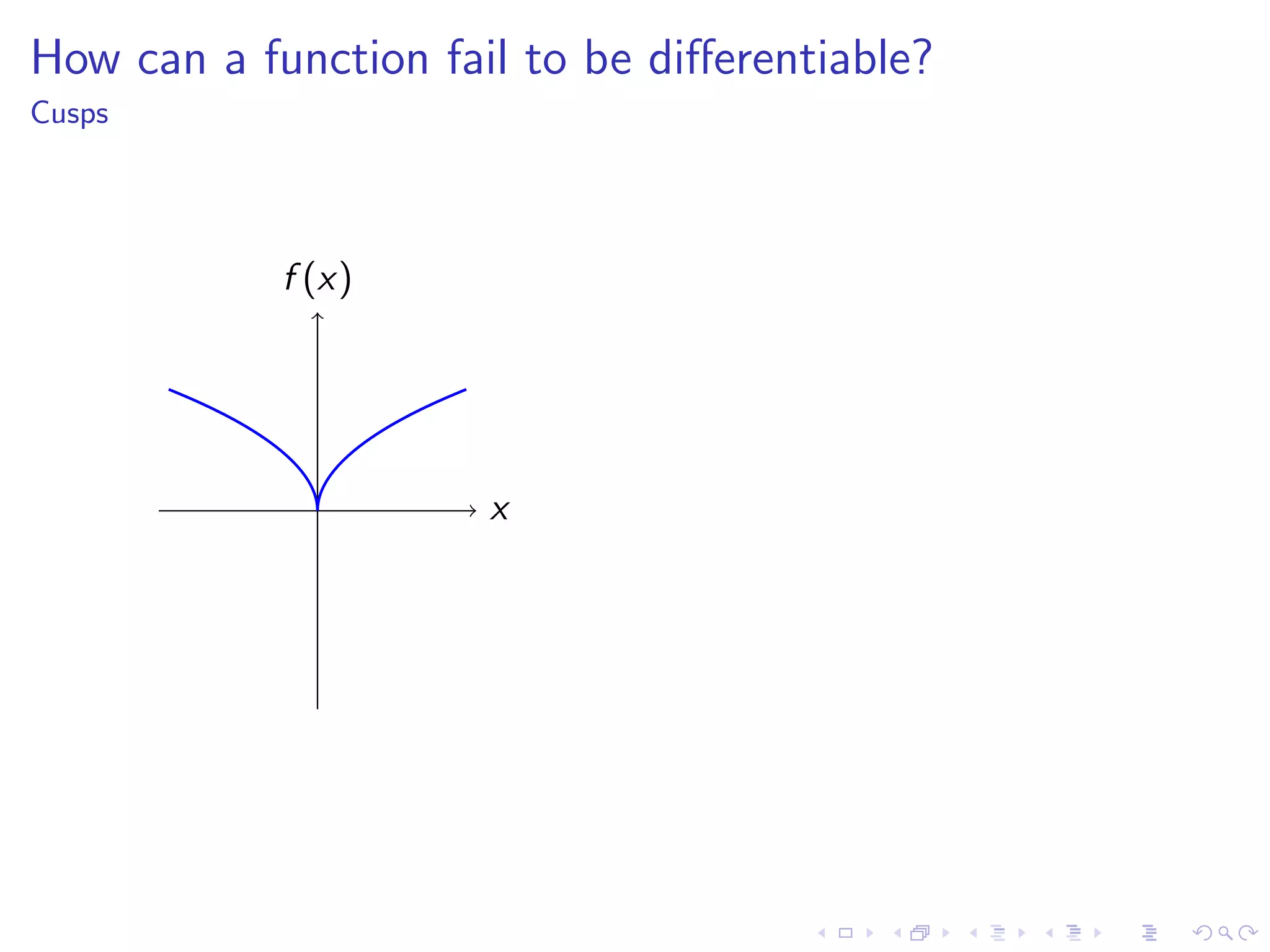
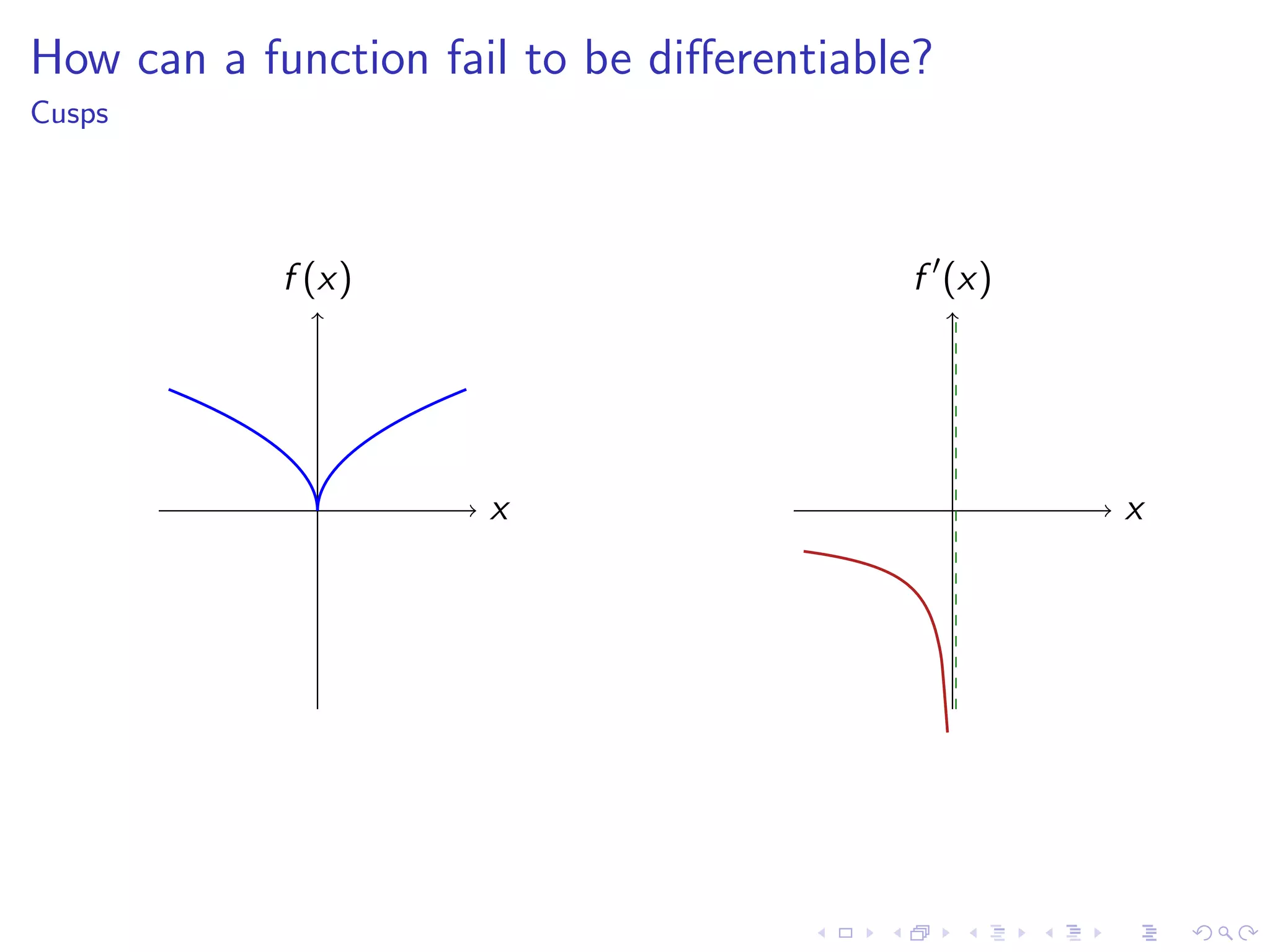
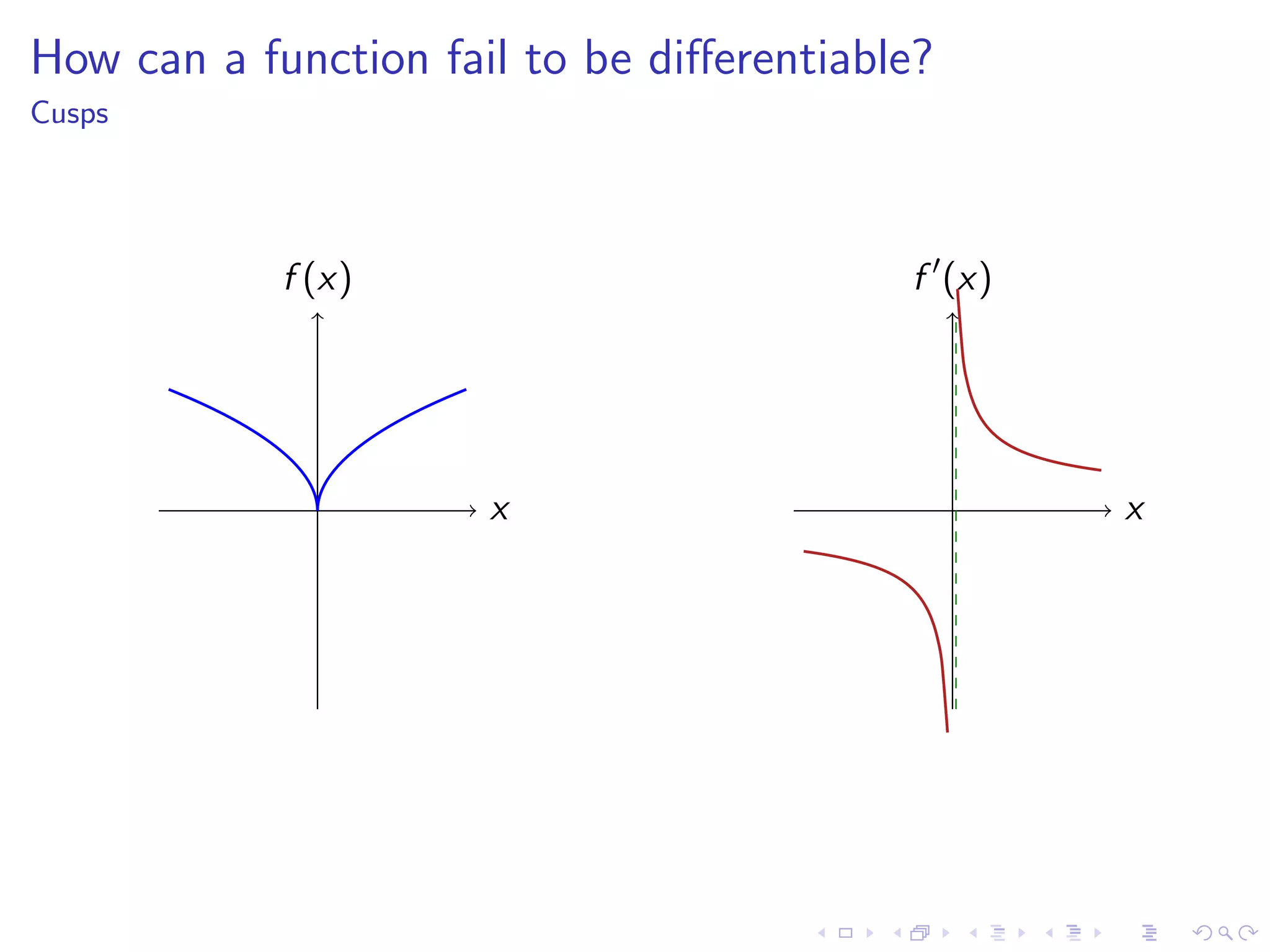
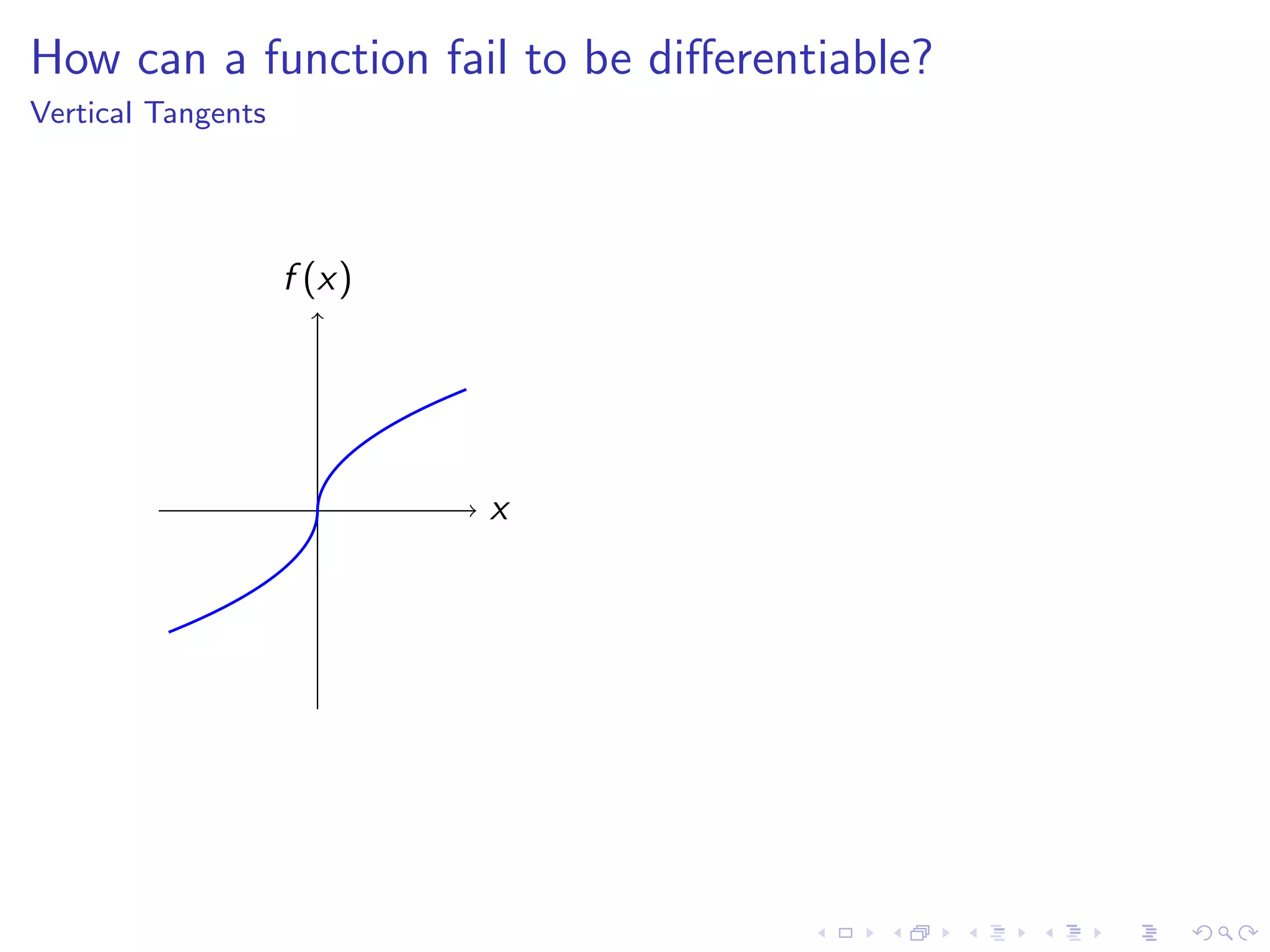
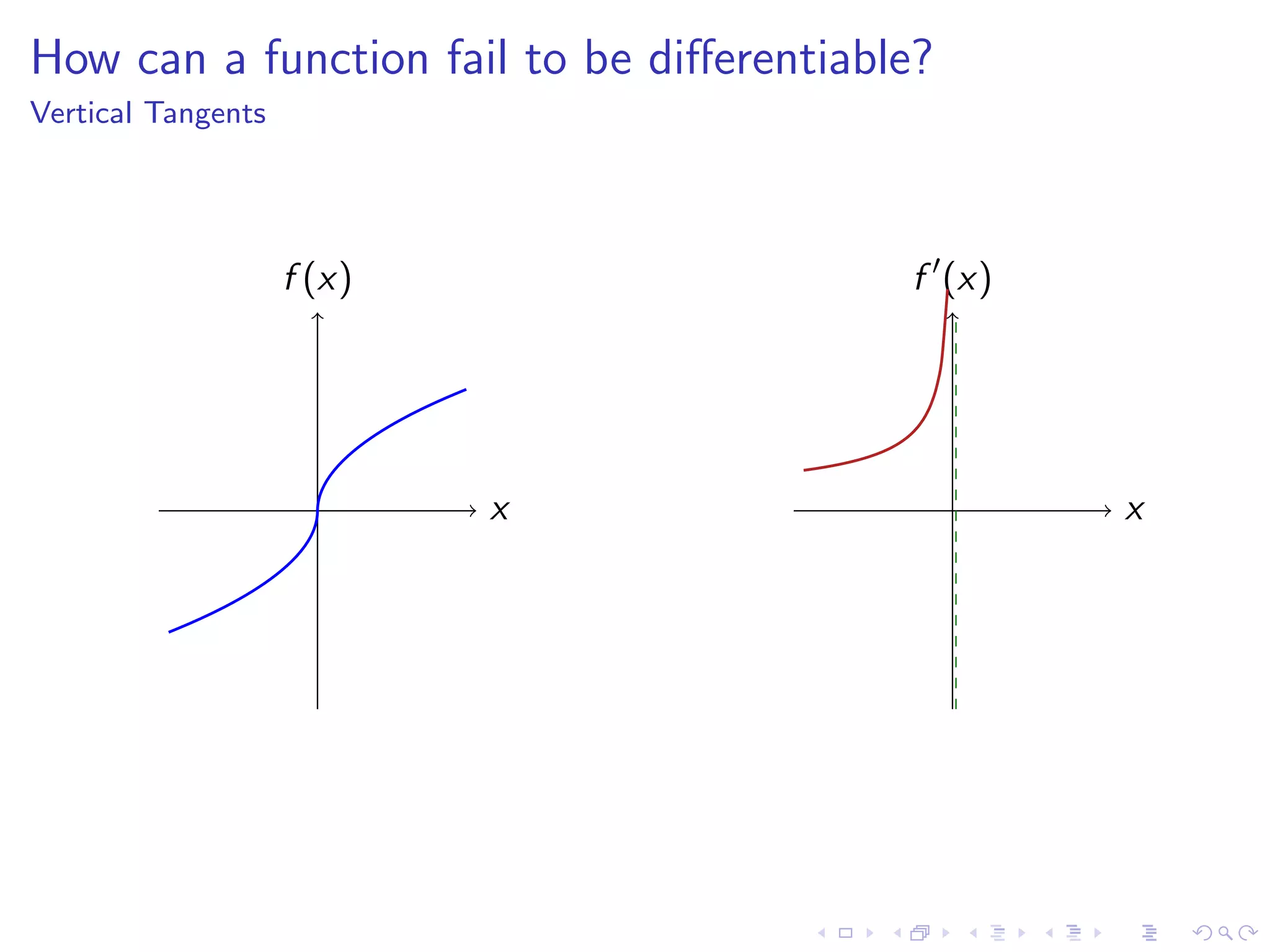
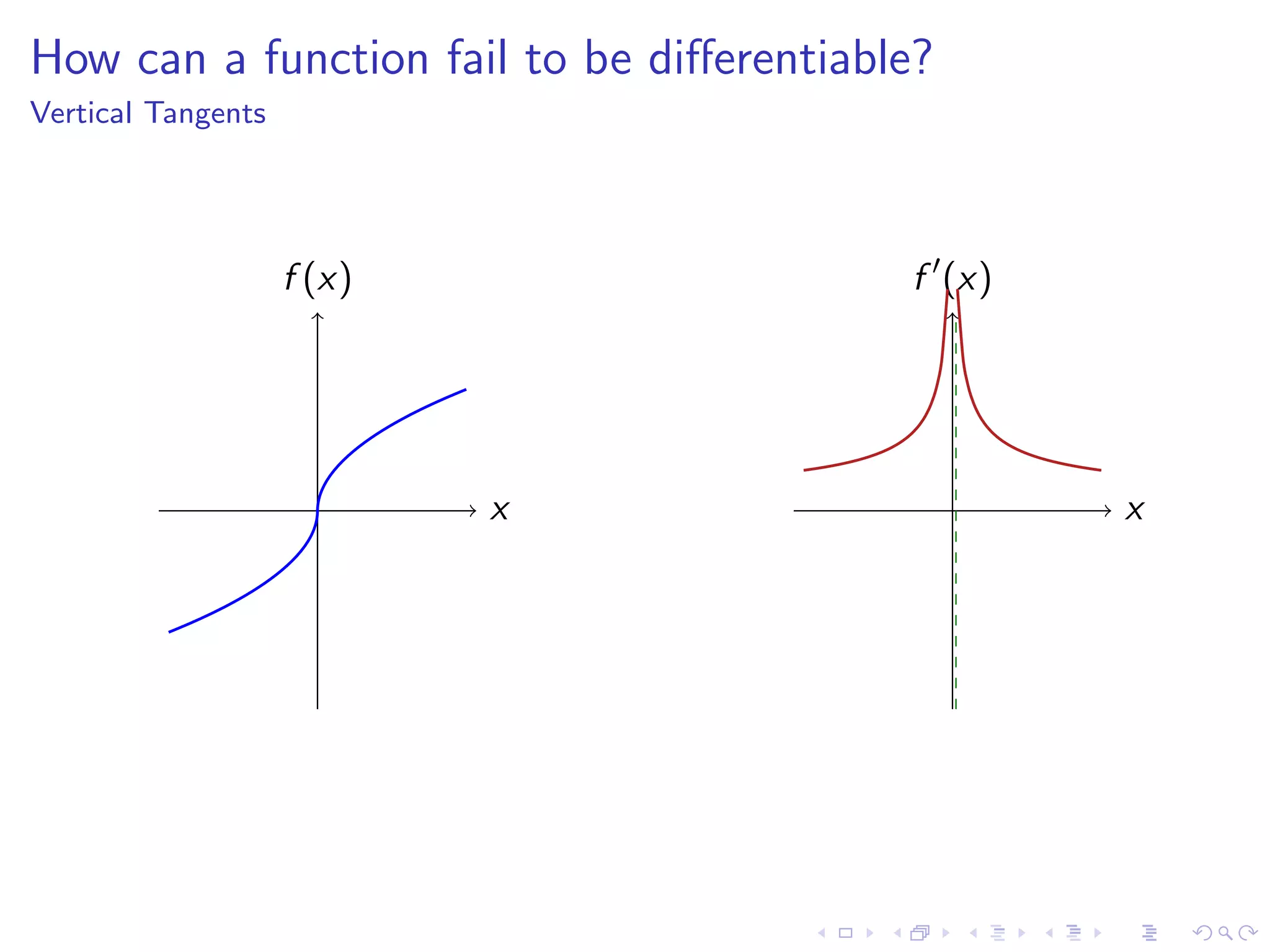
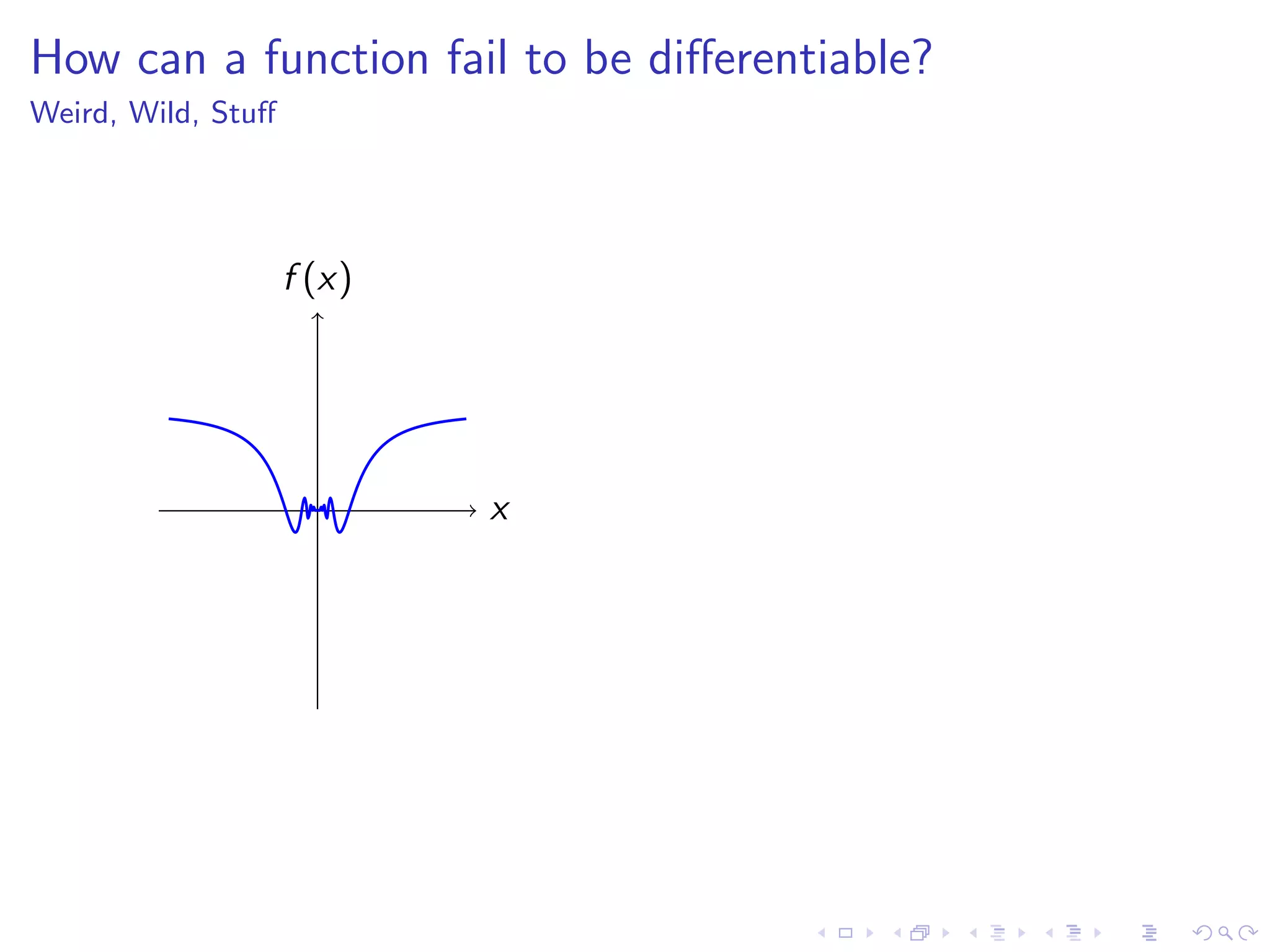
Discusses how functions can fail to be differentiable with examples such as kinks, cusps, vertical tangents, and other irregularities.
Introductory notes on mathematicians Isaac Newton and Gottfried Leibniz, their contributions, and notations for derivatives.
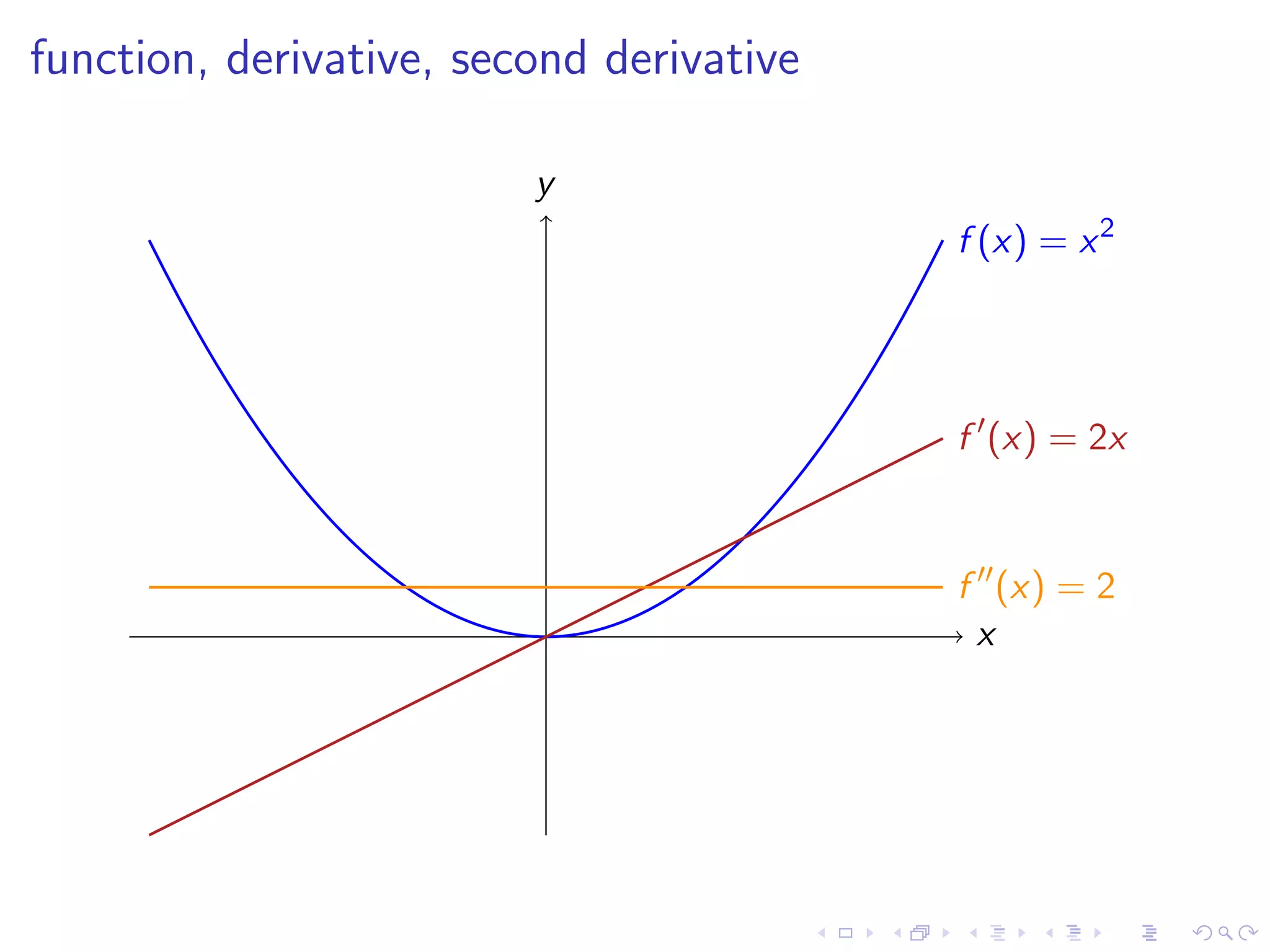
Explains the second derivative, its significance as the rate of change of the rate of change, and its representations.





























































