Embed presentation
Downloaded 136 times




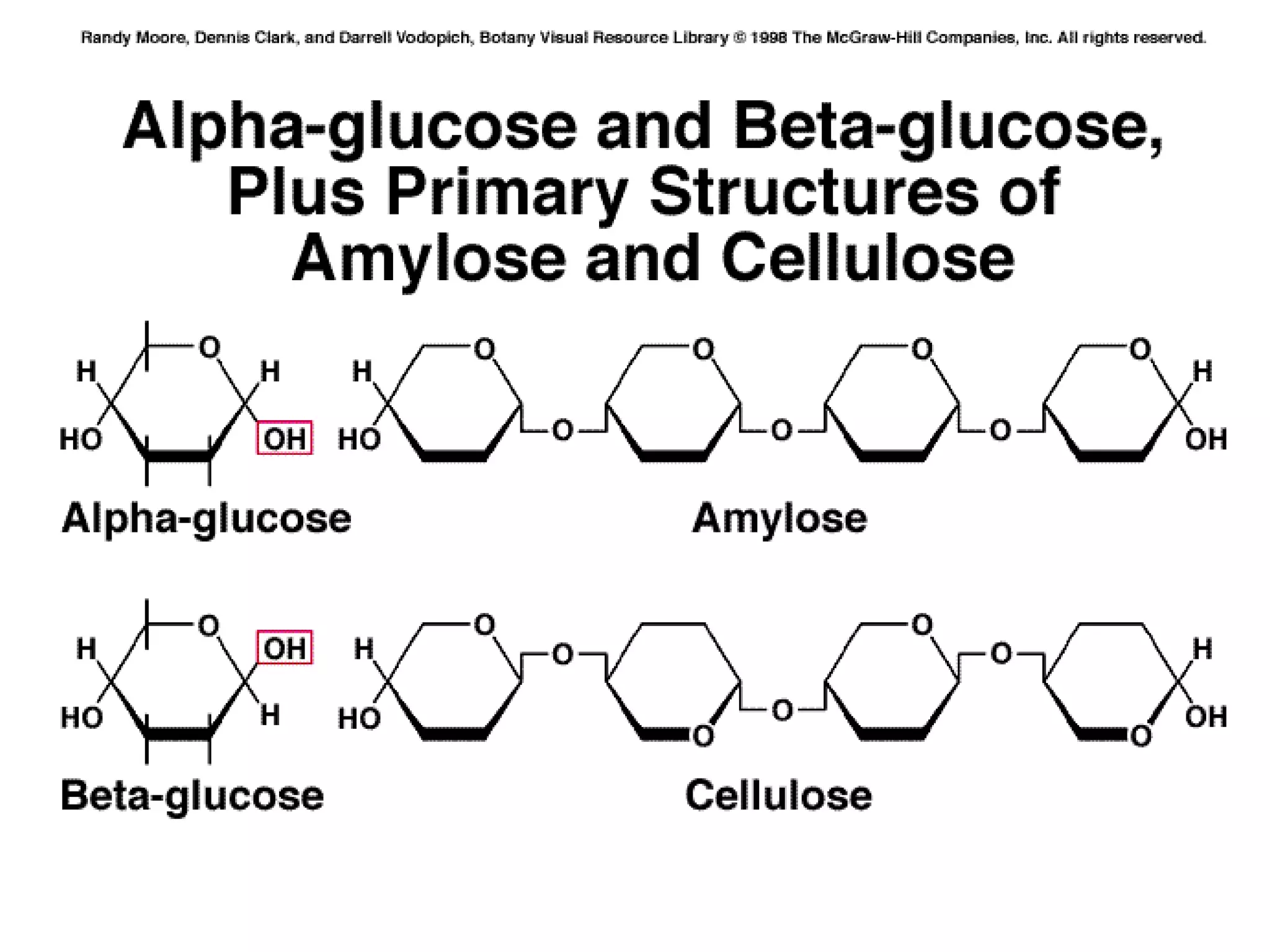
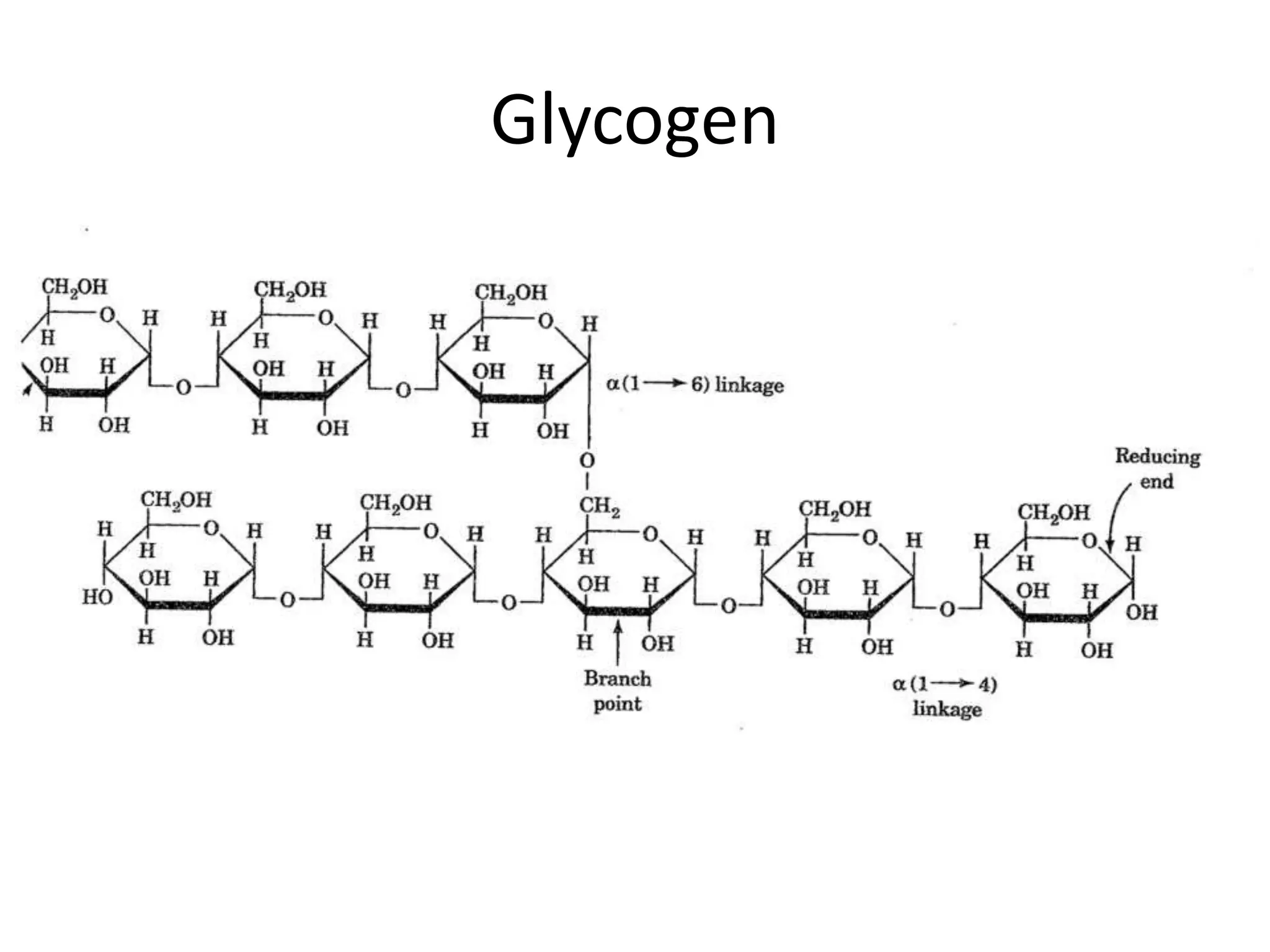

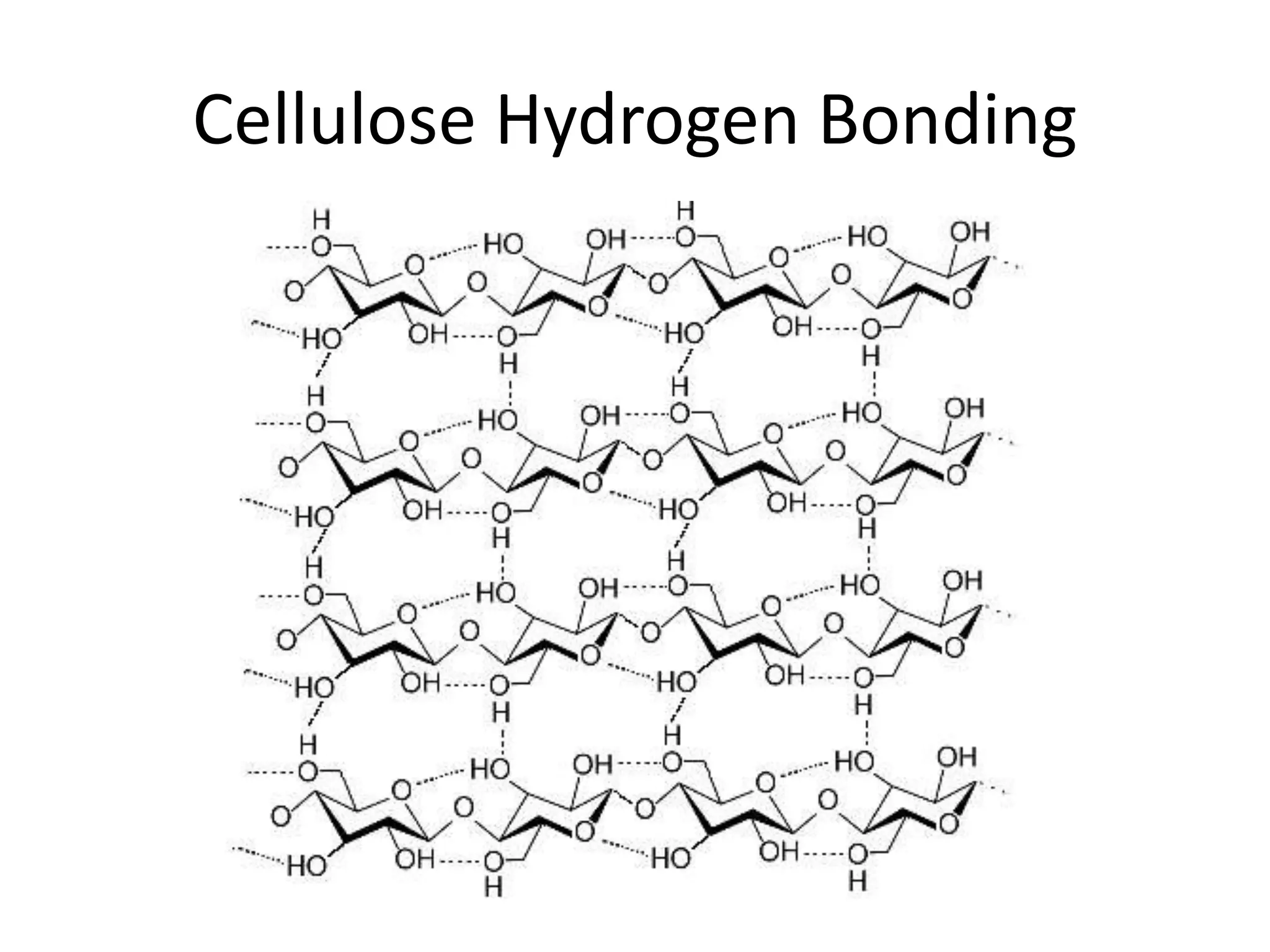





1. Starch, glycogen, and cellulose are polysaccharides made of glucose monomers that differ in their structure and function. 2. Starch has a linear structure that allows for close packing, making it a good energy store that can be easily broken down into glucose. 3. Glycogen branches, allowing several branches to be cut off at once to quickly supply energy. 4. Cellulose has hydroxyl groups that form hydrogen bonds between chains, holding them firmly together into strong microfibrils.













