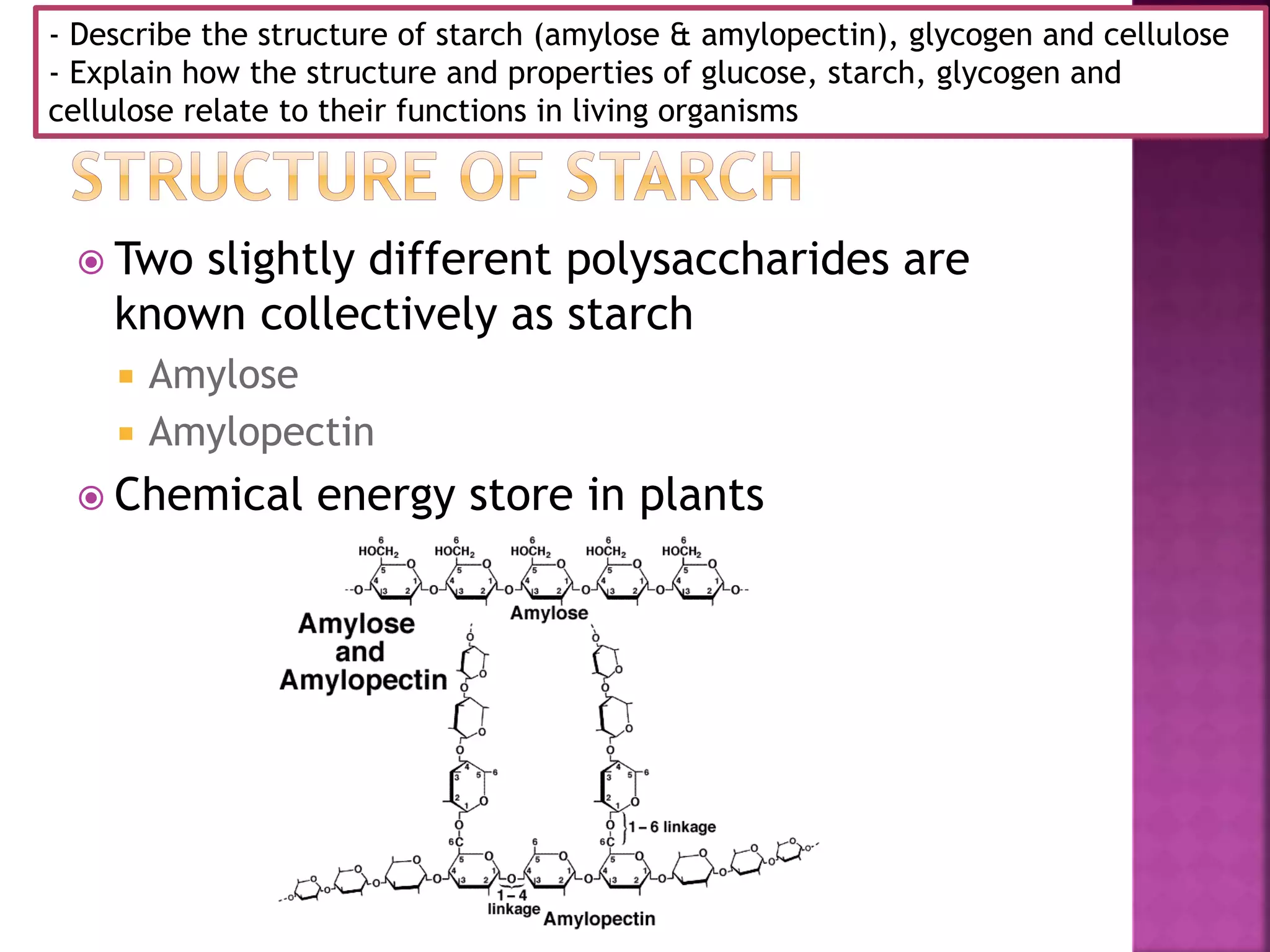
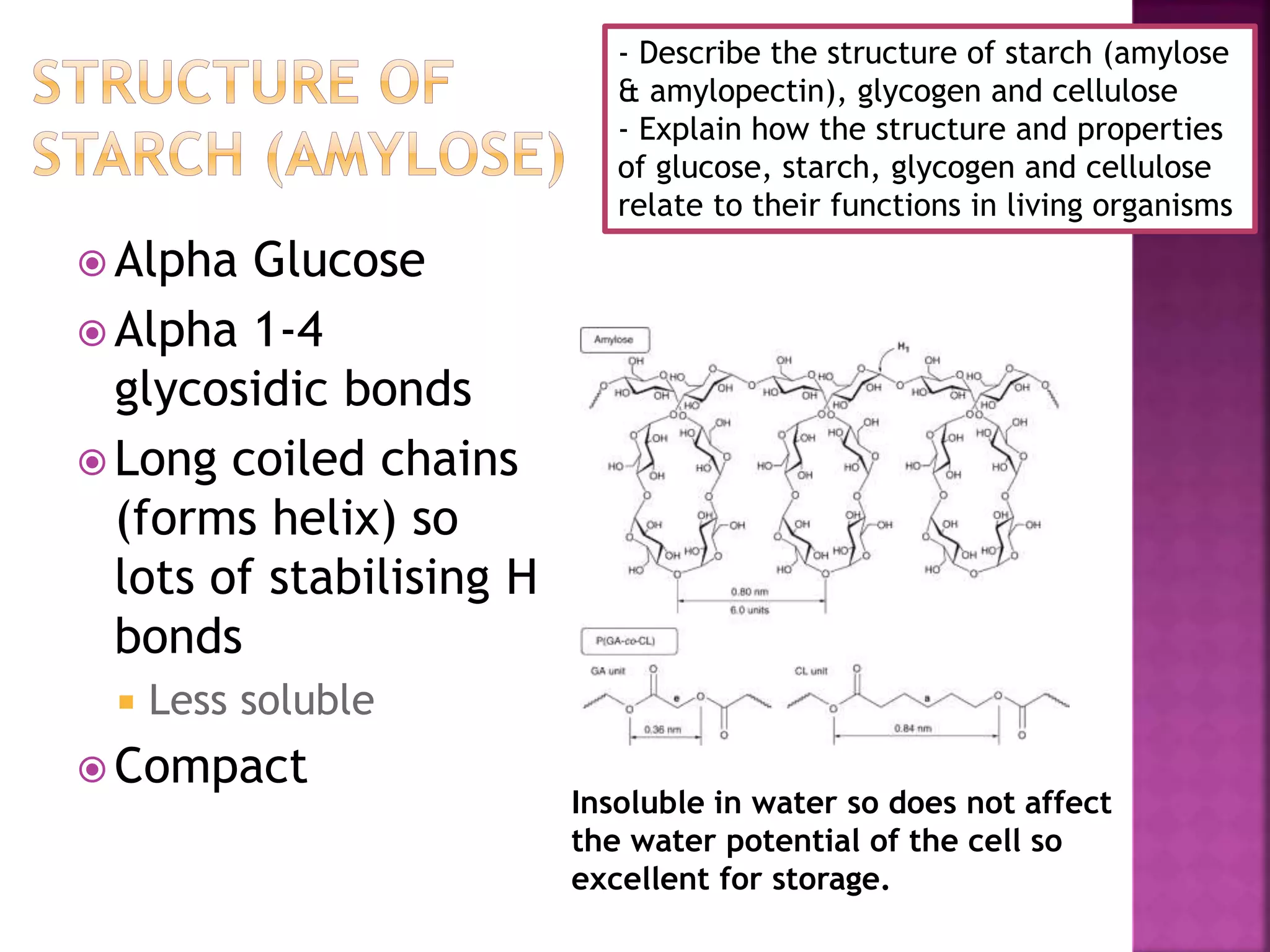
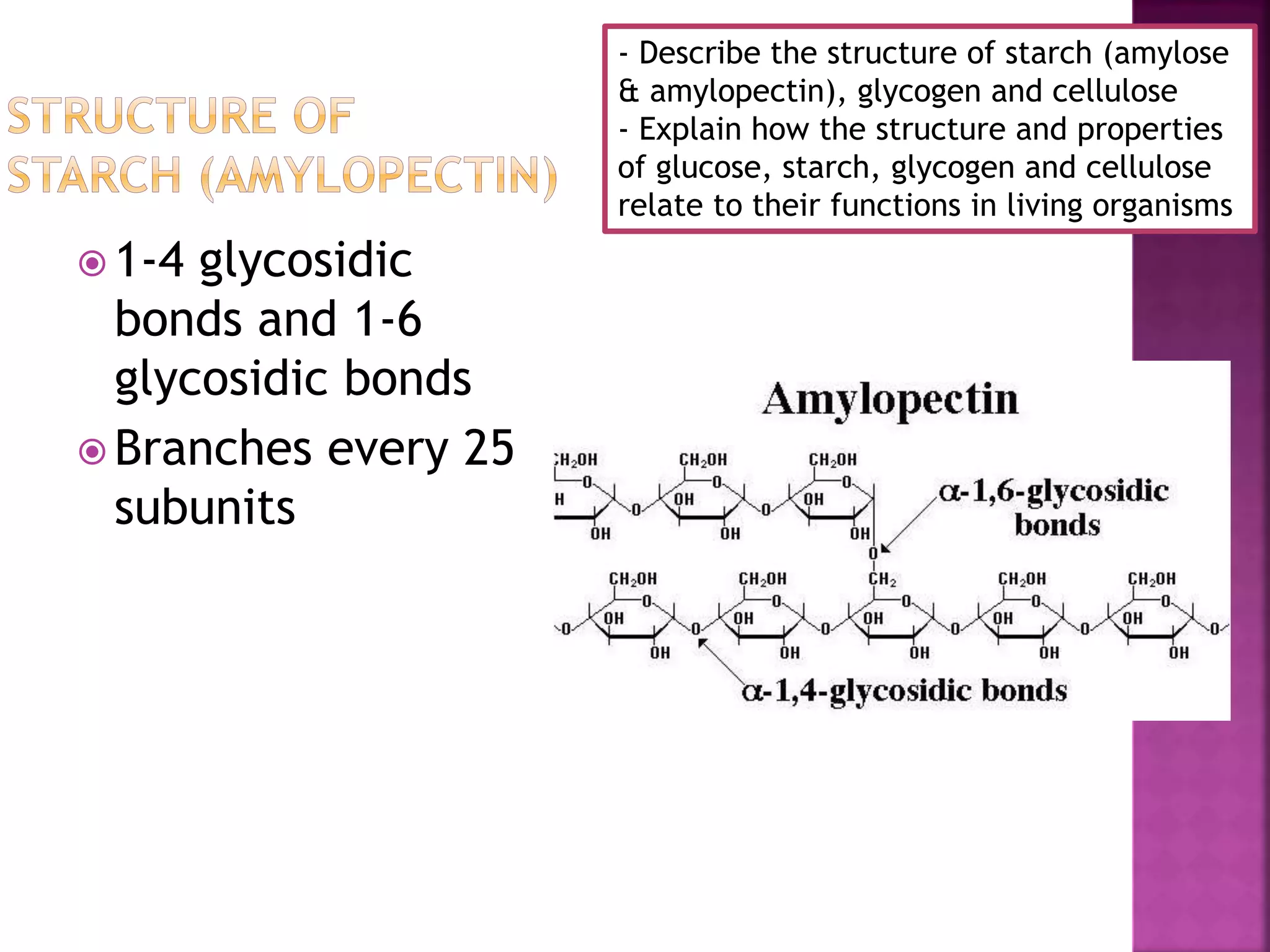
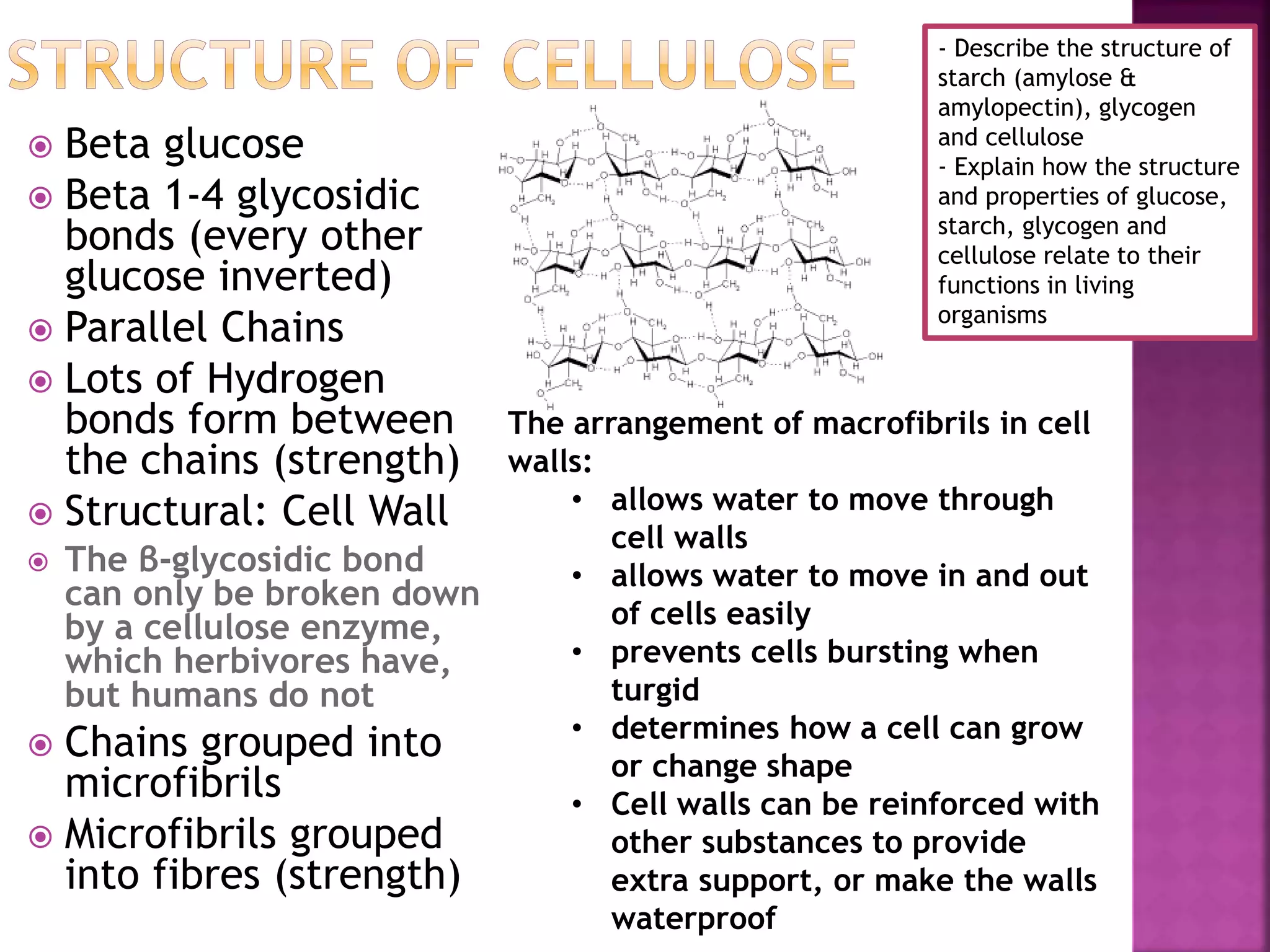
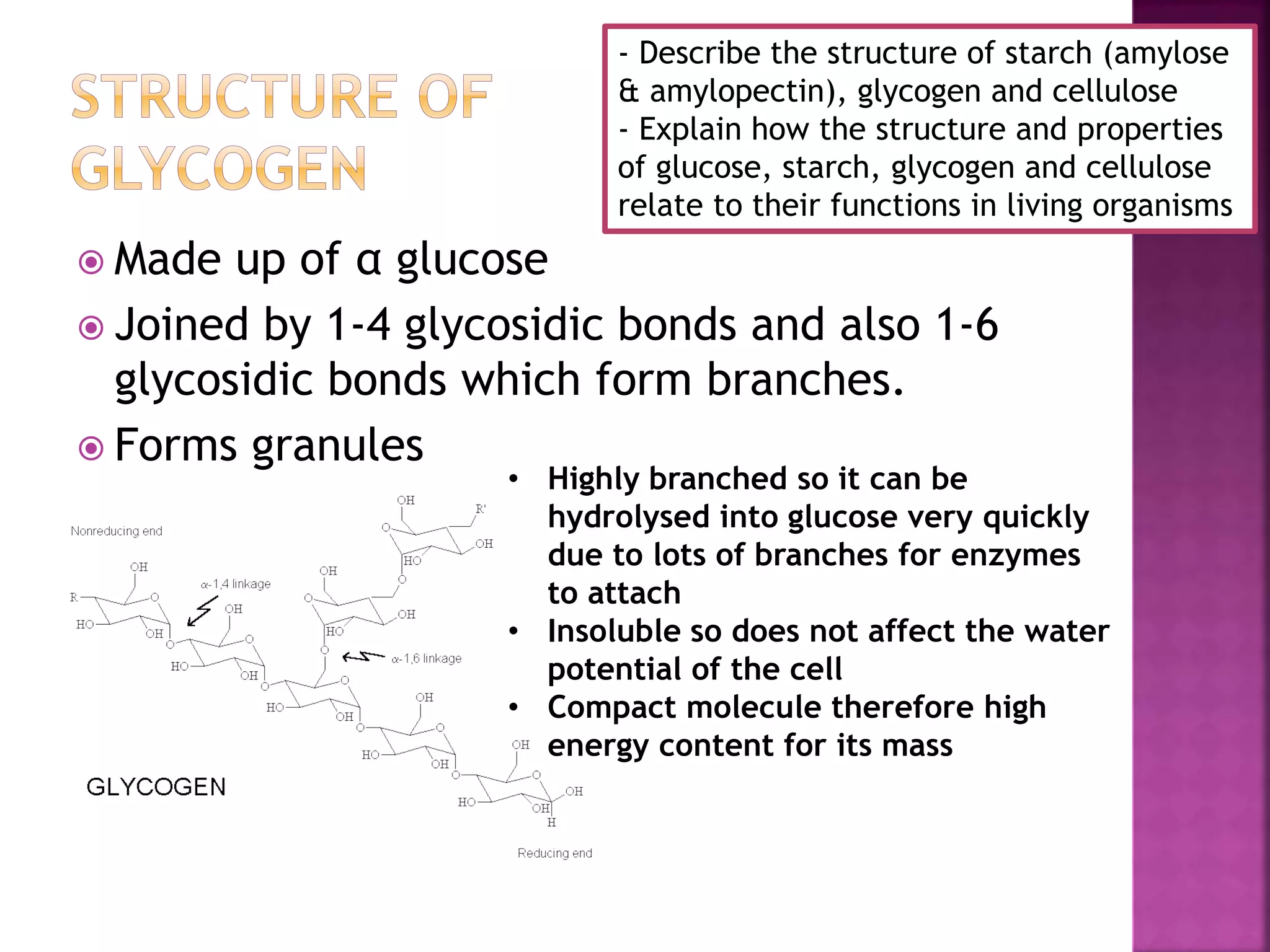
This document discusses the structures and functions of carbohydrates including glucose, starch, glycogen, and cellulose. It describes starch as being made up of amylose and amylopectin, with amylose forming long coiled chains and amylopectin having branches every 25 subunits. Glycogen is also described as being highly branched with 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds, allowing it to be quickly broken down into glucose. Cellulose is explained to have parallel beta glucose chains with 1-4 bonds that form microfibrils and macrofibrils, giving plant cells strength and allowing water movement through cell walls. The document relates these carbohydrate structures to their roles in energy storage and