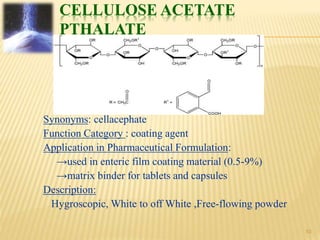
This document provides information on various cellulose derivatives used in pharmaceutical formulations. It begins with an introduction to cellulose derivatives and how they are obtained from cellulose. It then discusses the history and classification of various derivatives such as hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose and carboxymethyl cellulose. The document outlines the properties, applications, and advantages of derivatives like microcrystalline cellulose, cellulose acetate phthalate, and hydroxyethyl cellulose. It concludes by discussing the various uses of cellulose and providing references.