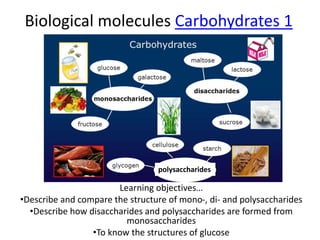
This document discusses carbohydrates and their structure and function. It defines monomers and polymers and lists monosaccharides, amino acids and nucleotides as examples of monomers. Monosaccharides can combine through condensation reactions to form disaccharides and polysaccharides. Common disaccharides formed from specific monosaccharide combinations are described, such as maltose being formed from two glucose monomers. Polysaccharides have many monomer units and include starch, glycogen and cellulose, which serve important energy storage and structural roles in plants and animals.