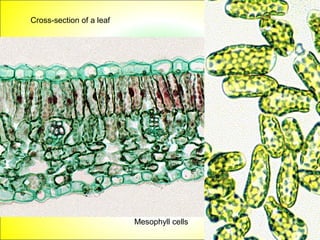
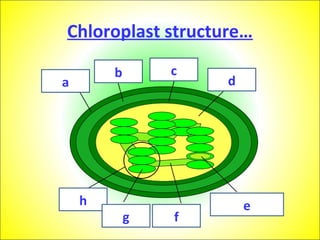
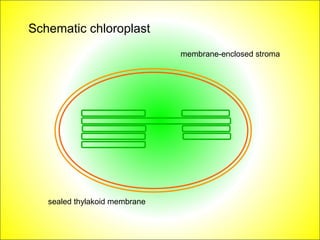
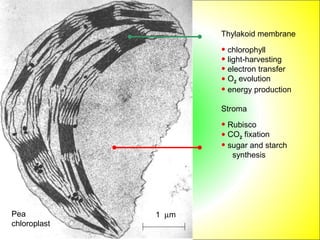
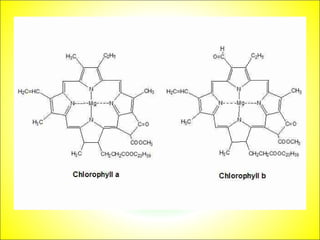
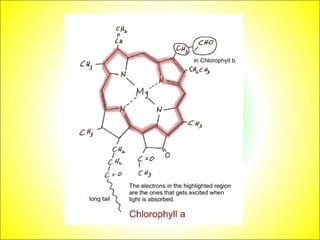
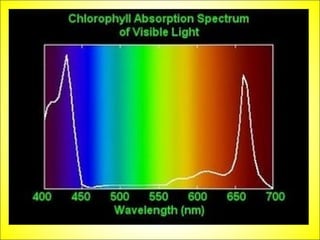
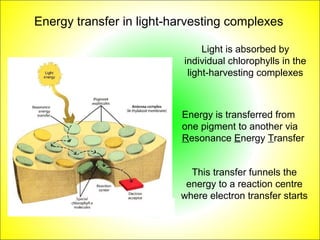
This document discusses photosynthesis and chloroplast structure. It begins by outlining learning objectives about linking leaf structure to photosynthesis efficiency, reviewing chloroplast structure, and describing the role of photosynthetic pigments in light harvesting. It then provides an overview of photosynthesis as a two-stage process that takes place in chloroplasts, and explains chloroplast structure through diagrams and electron micrographs. Specifically, it notes that chloroplasts contain thylakoids which harbor chlorophyll and other pigments for light absorption and energy transfer during the light reactions of photosynthesis.