Embed presentation
Download to read offline

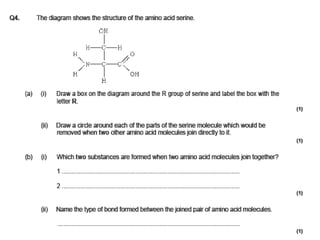

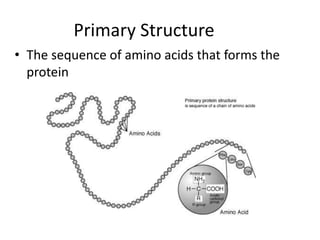
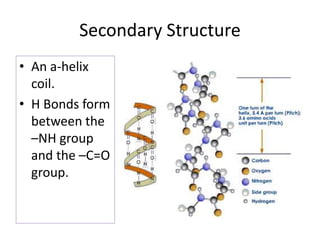
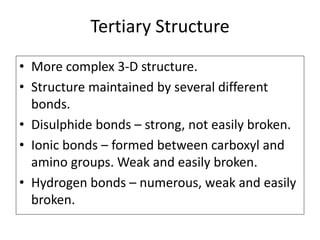
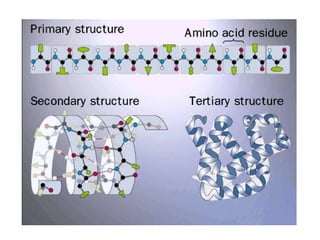

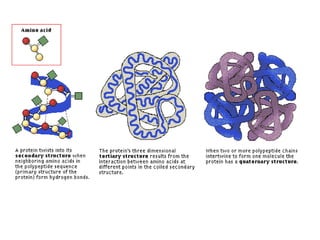


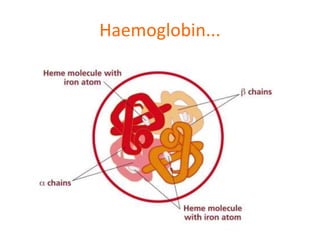

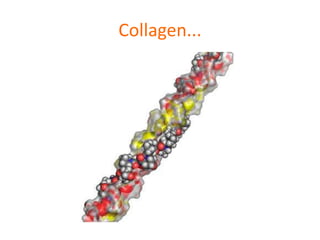

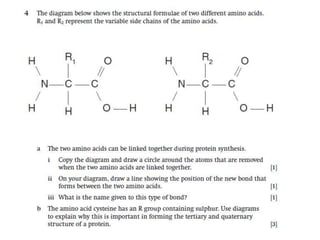
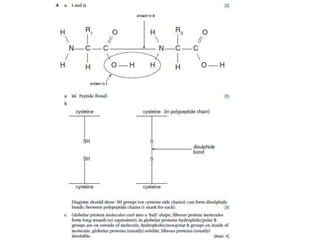
This document discusses protein structure and function. It begins by stating the aim is to understand how proteins fold into their correct shape. It then lists several important functions of proteins, including serving as enzymes, transporting molecules, storage, movement, structure, and mediating responses and immunity. The document goes on to explain the four levels of protein structure: primary structure is the amino acid sequence; secondary structure involves hydrogen bonds forming alpha helices and beta sheets; tertiary structure is the complex 3D shape formed by additional bonds; and quaternary structure refers to large proteins made of multiple polypeptide chains. Examples of hemoglobin and collagen are provided.


















