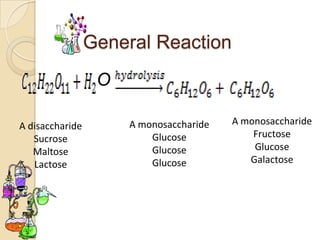
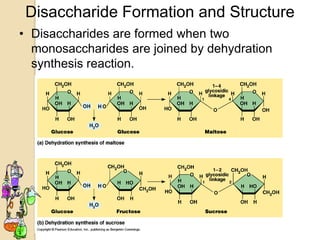
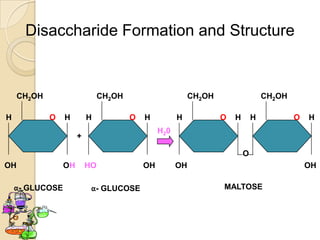
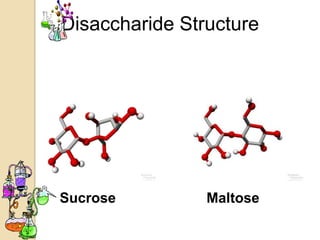
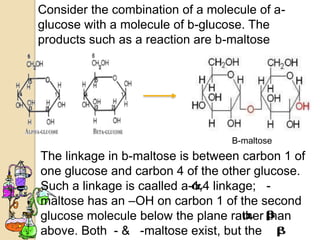
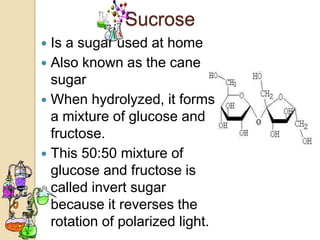
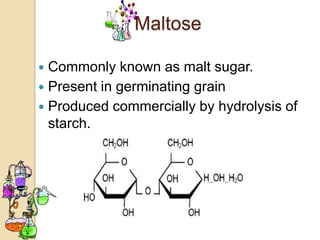
Disaccharides are double sugars that yield two simple sugars called monosaccharides upon hydrolysis. The three main disaccharides are sucrose, maltose, and lactose. They differ in their solubility, with sucrose being very soluble, maltose fairly soluble, and lactose only slightly soluble. Disaccharides are formed through a dehydration synthesis reaction combining two monosaccharides. Their structures depend on the type of glycosidic linkage between the monosaccharides. This determines their properties such as whether they are reducing sugars or able to undergo fermentation.