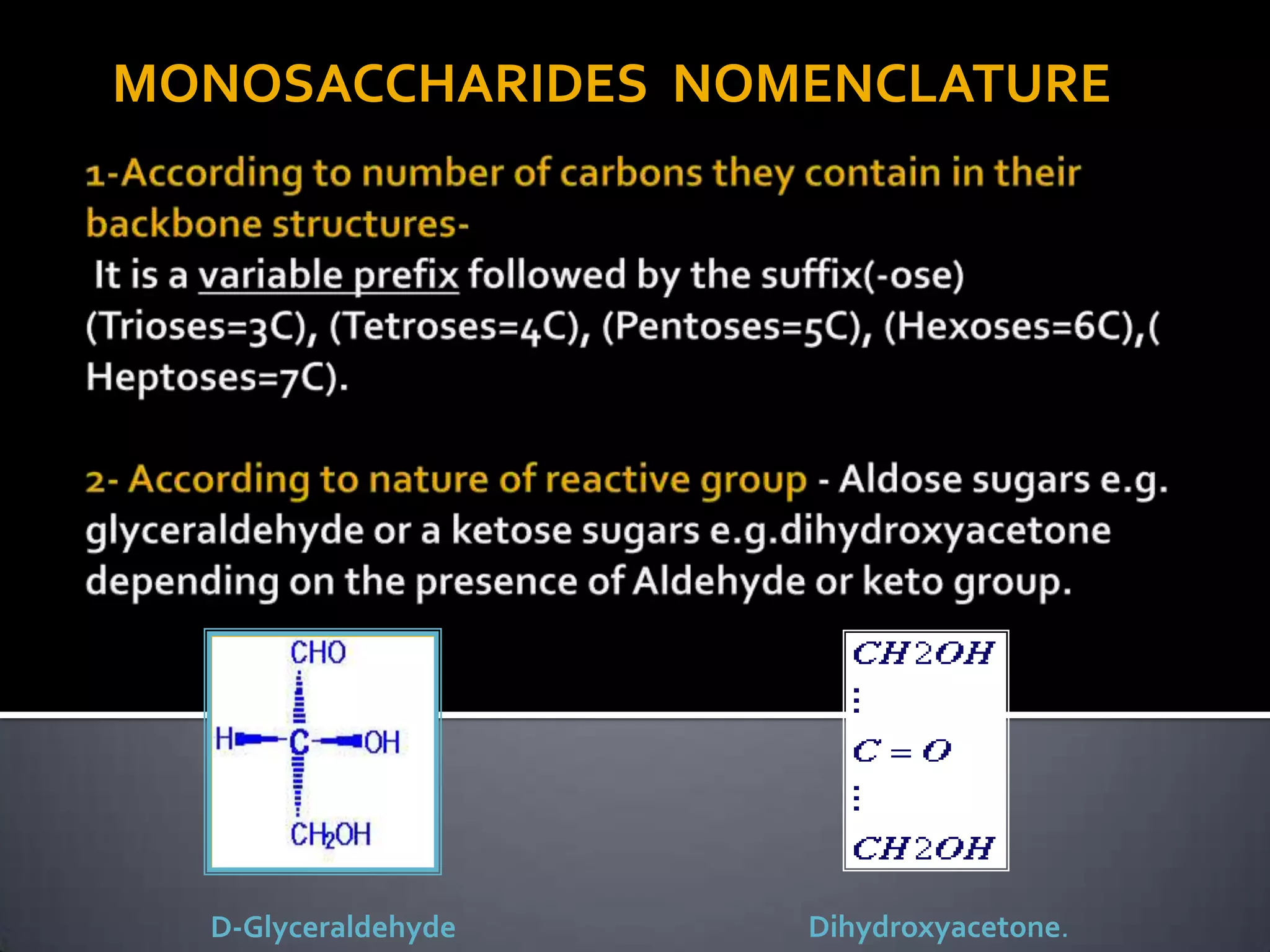
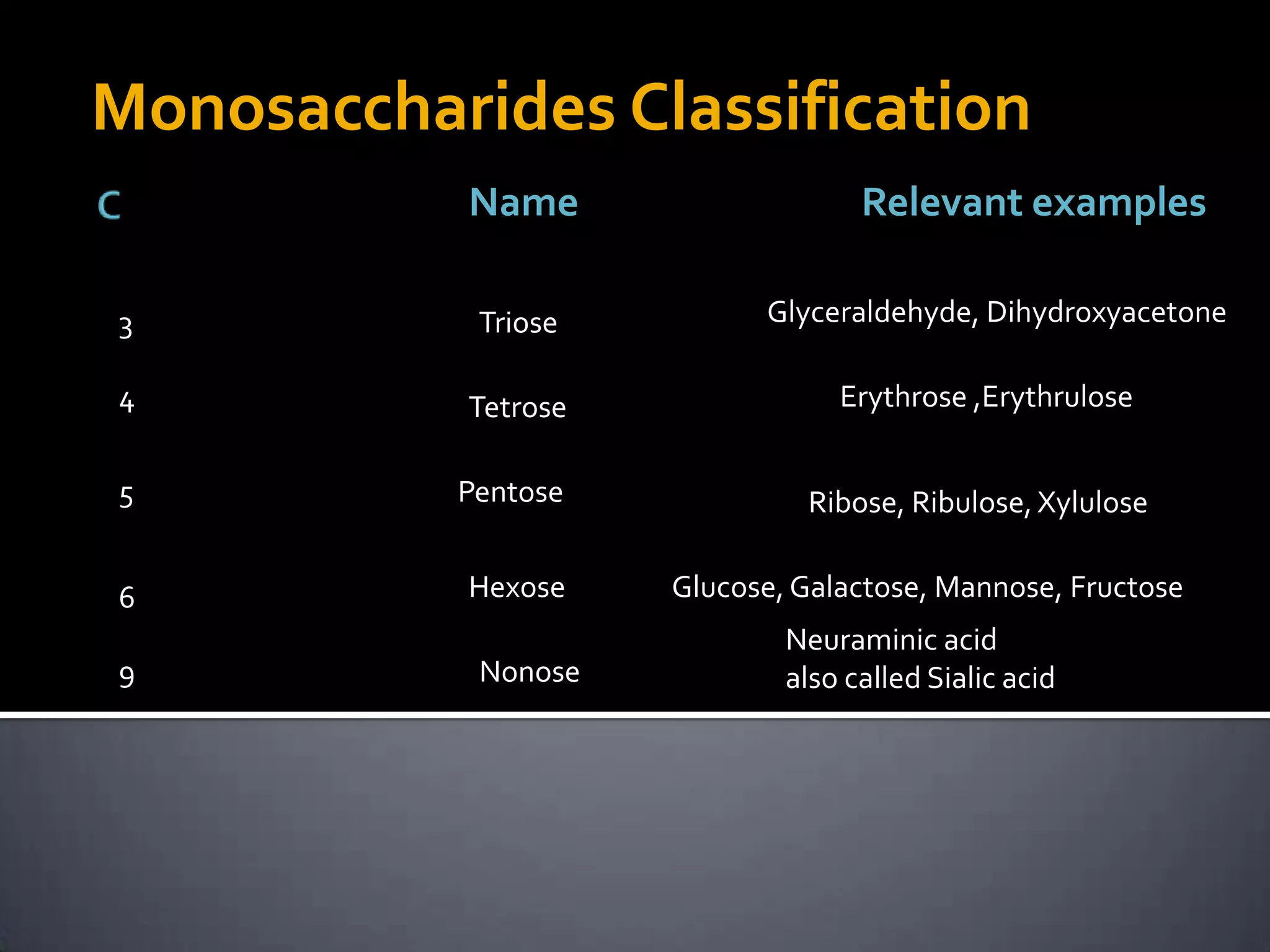
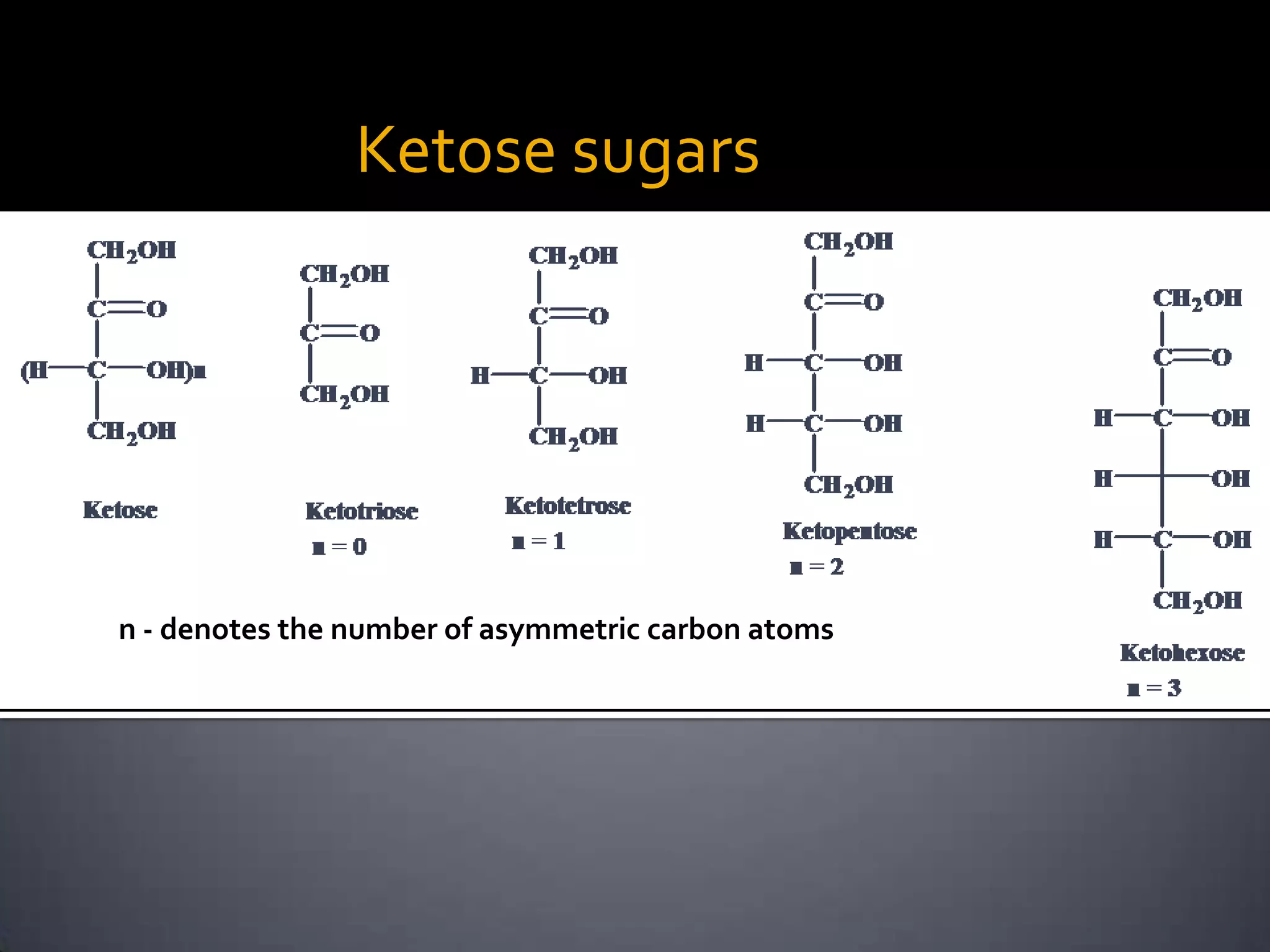
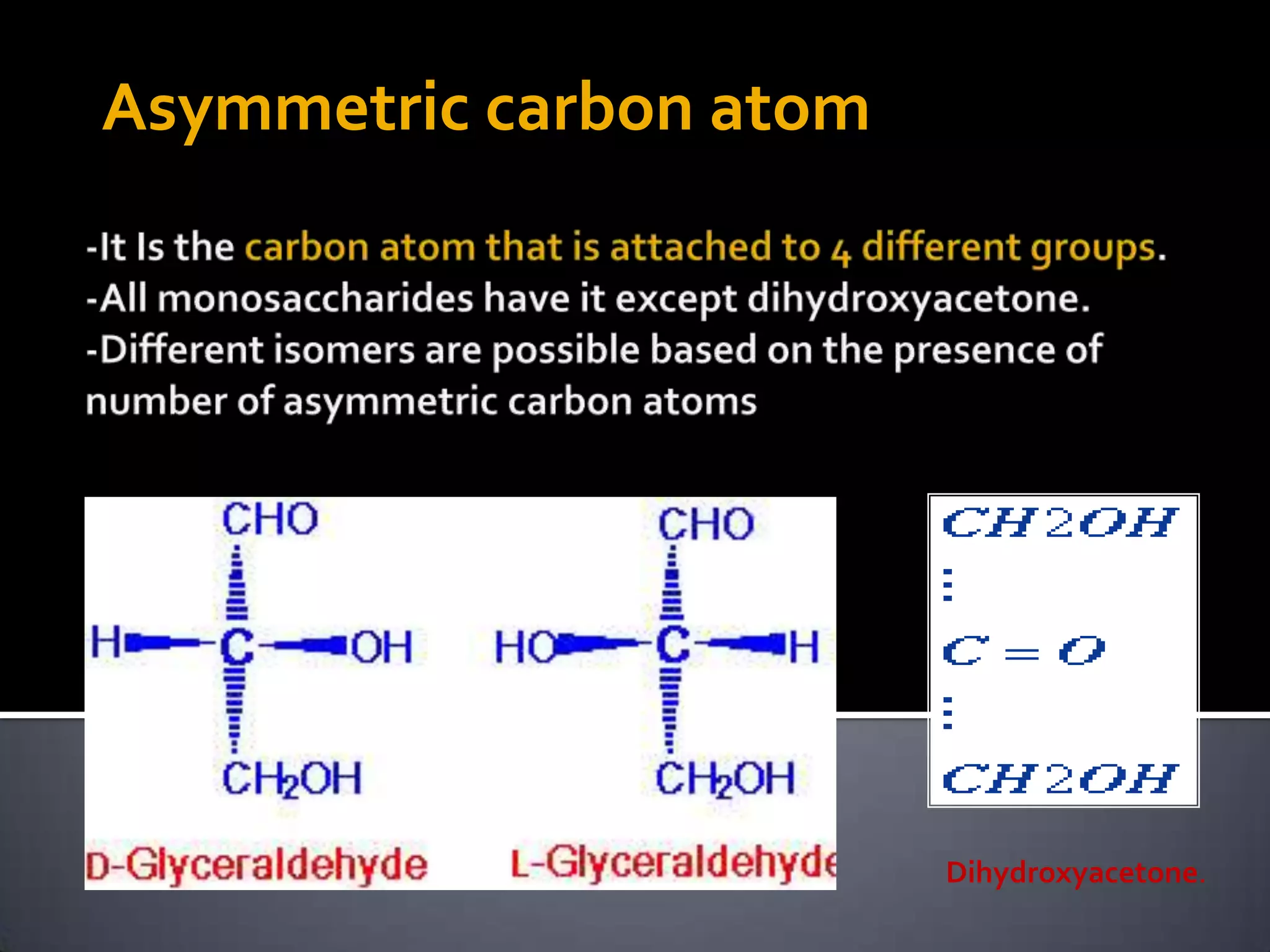
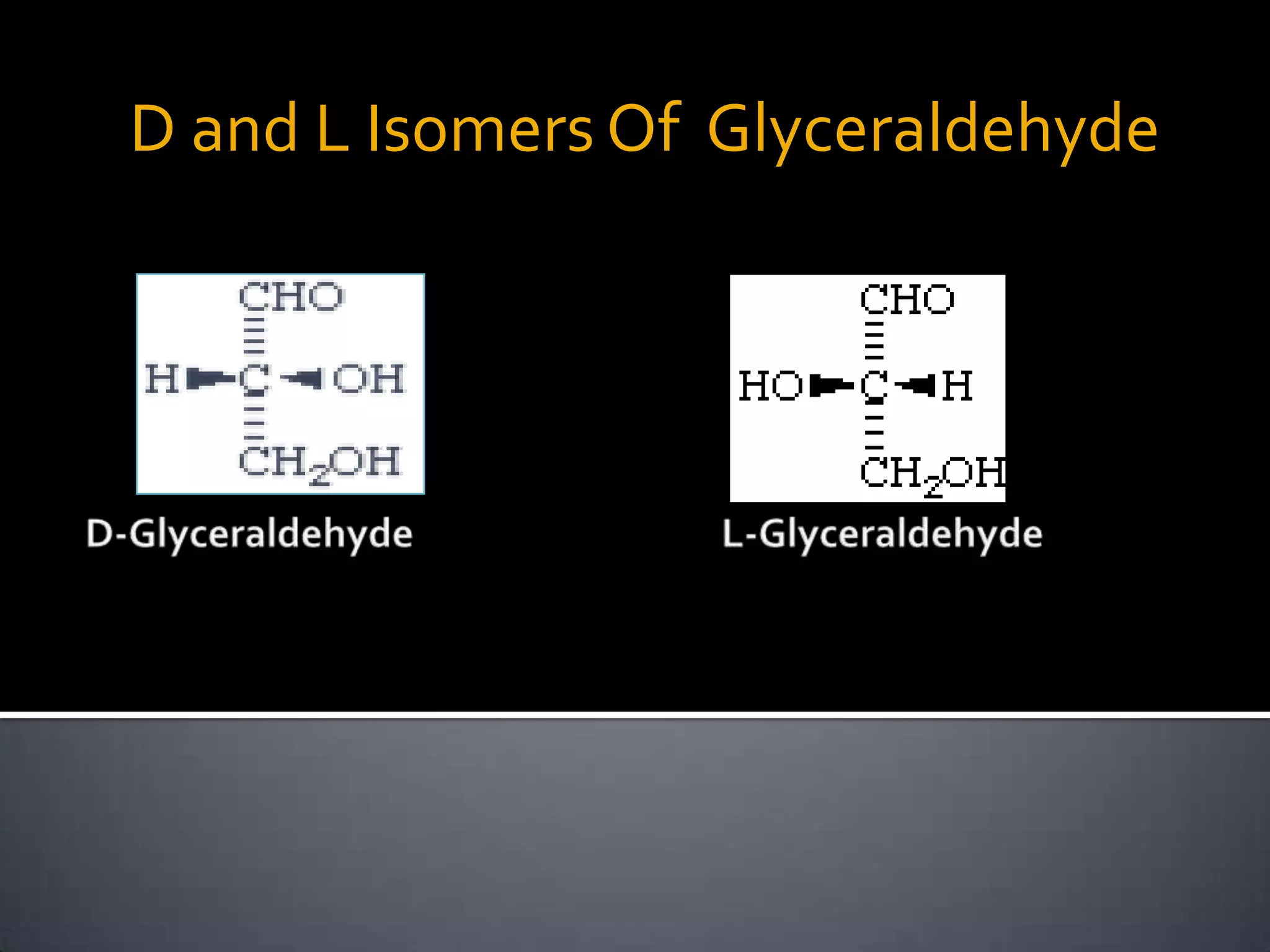
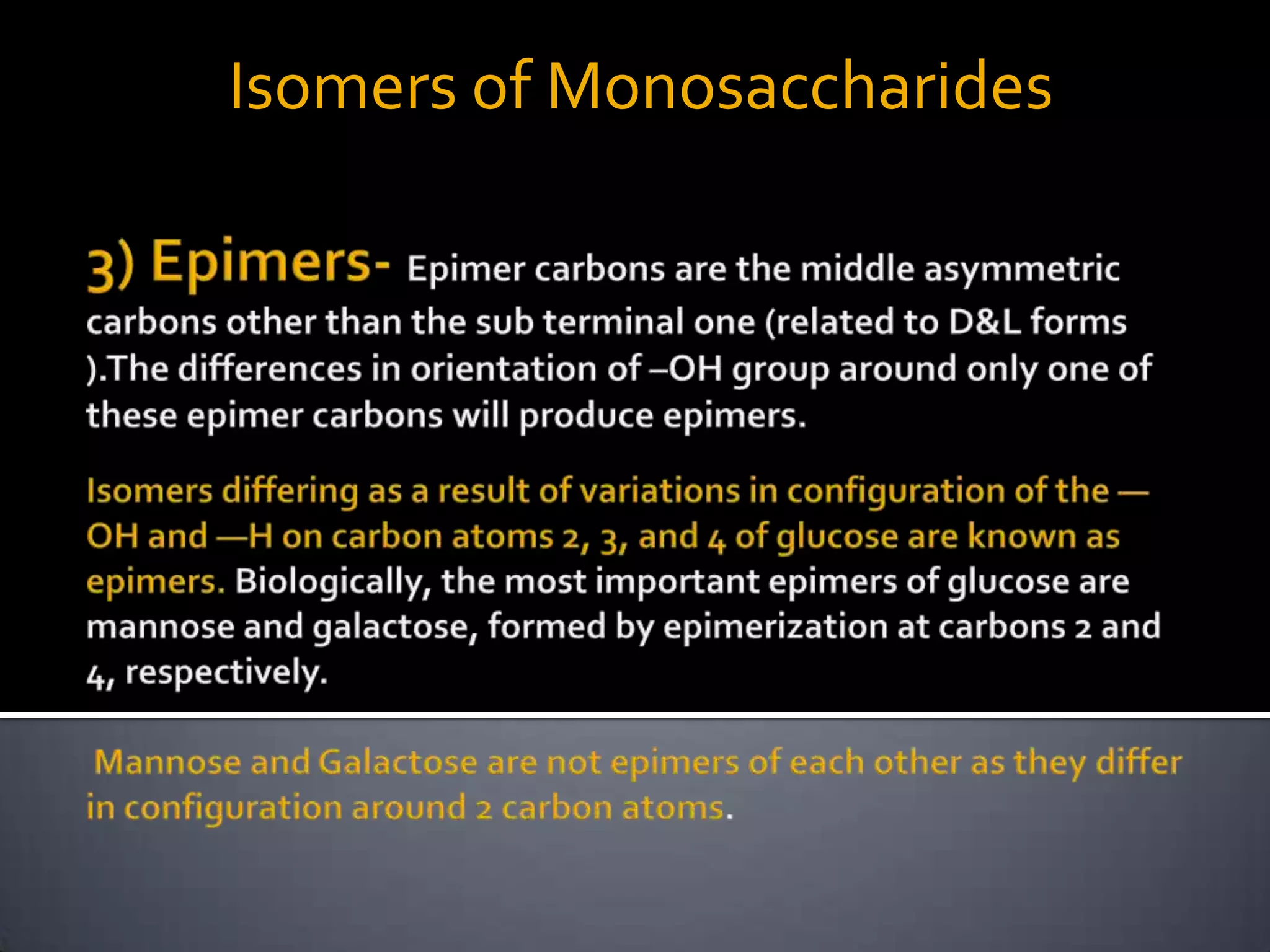
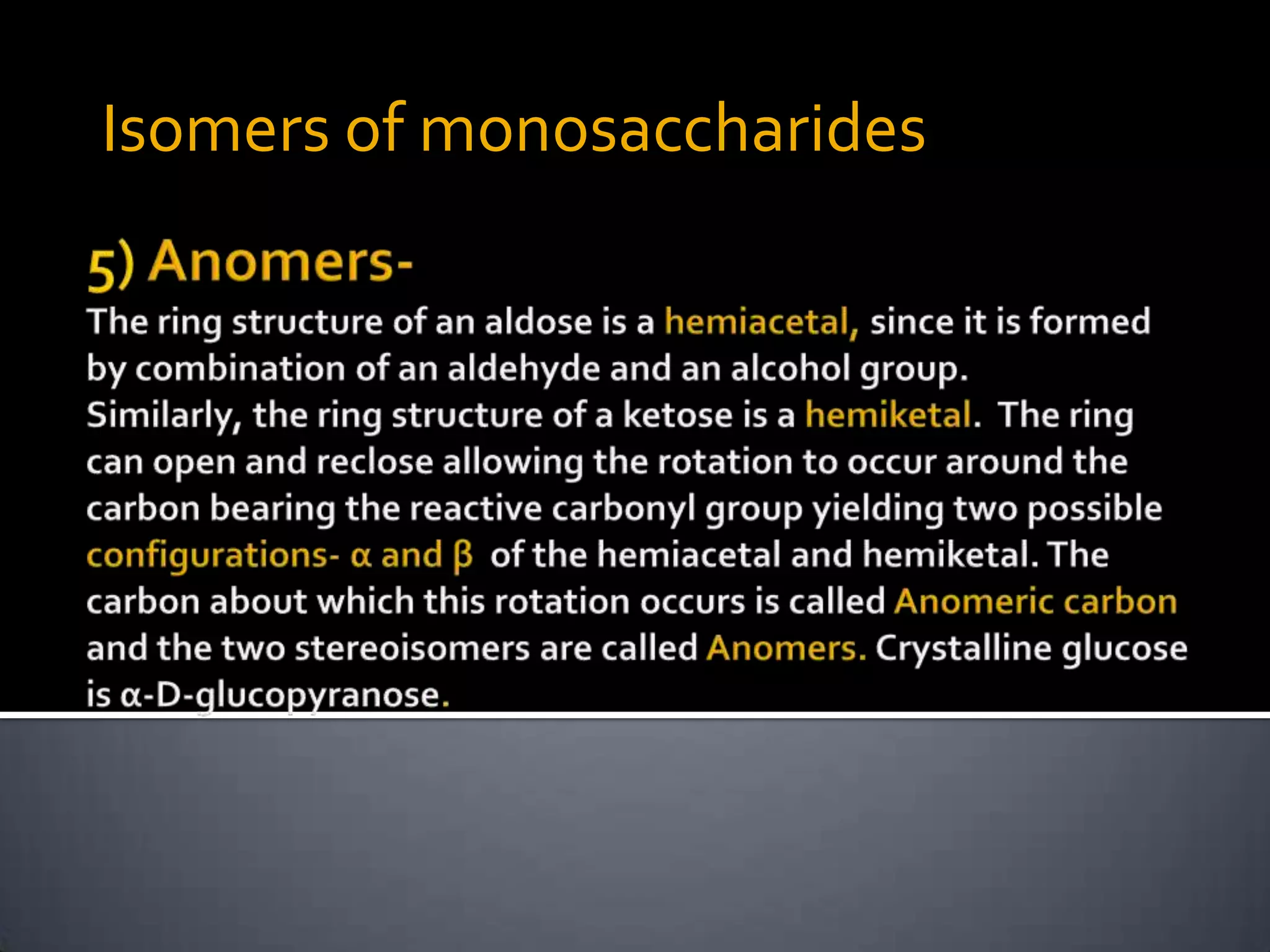
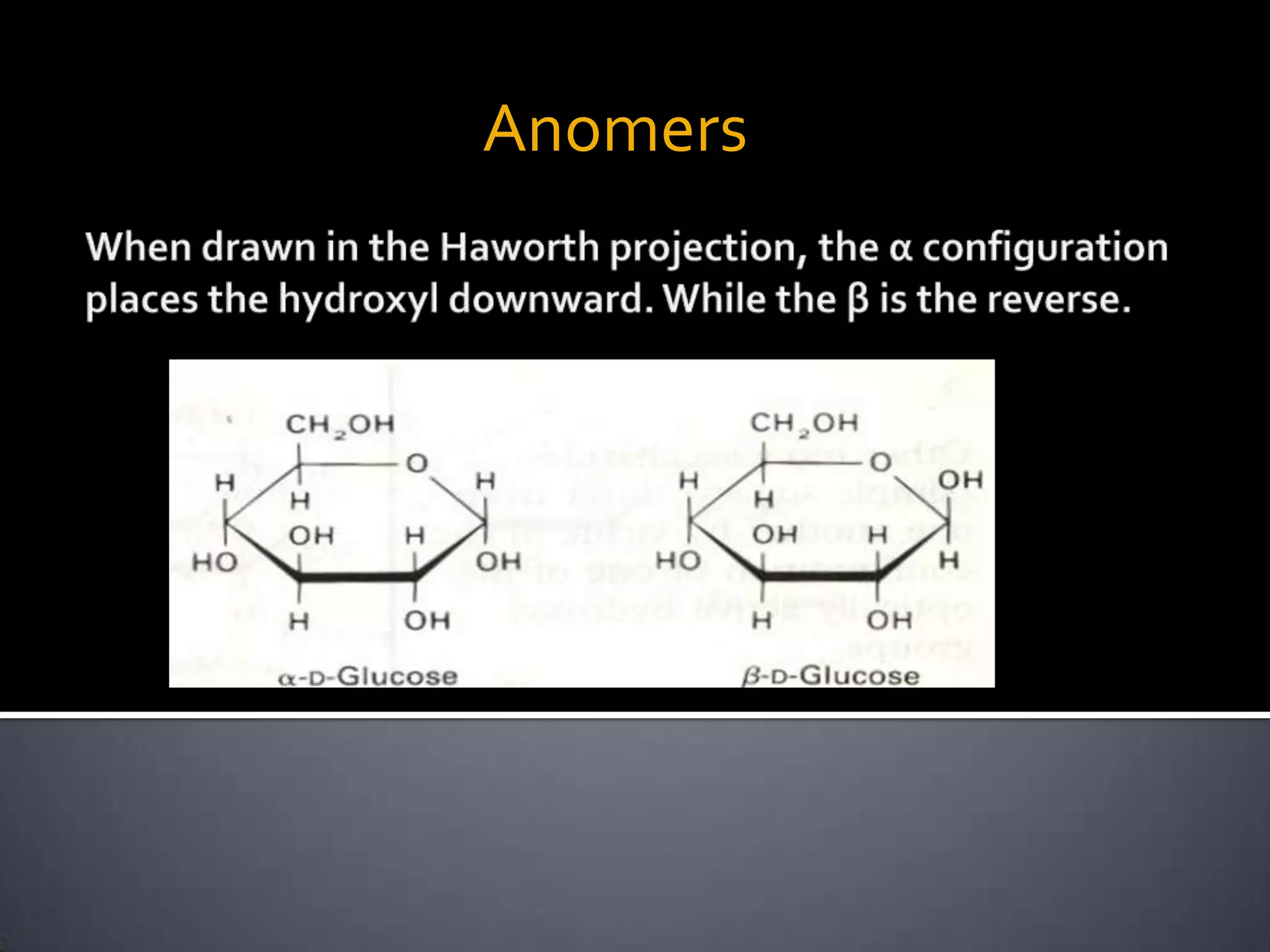
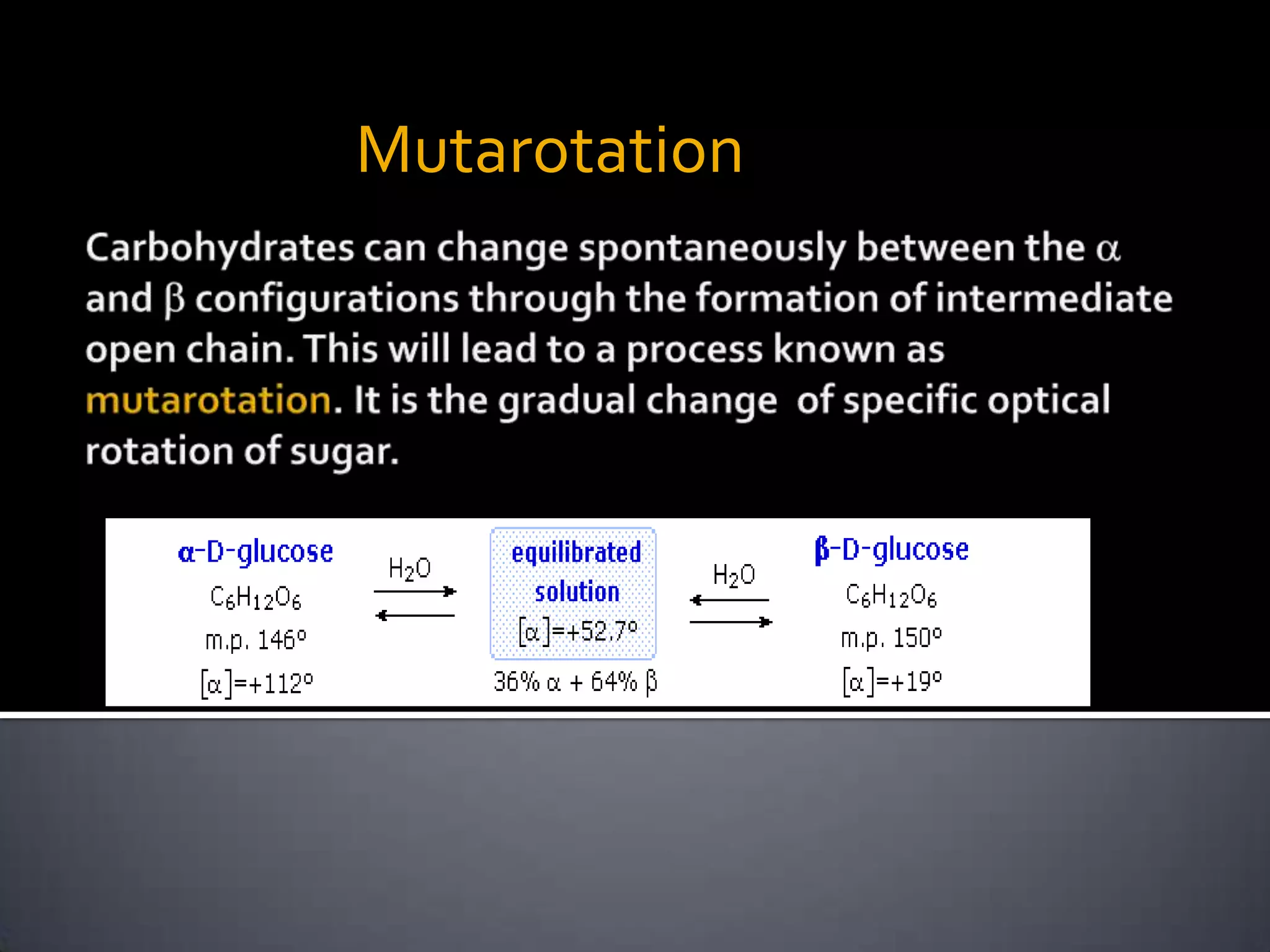
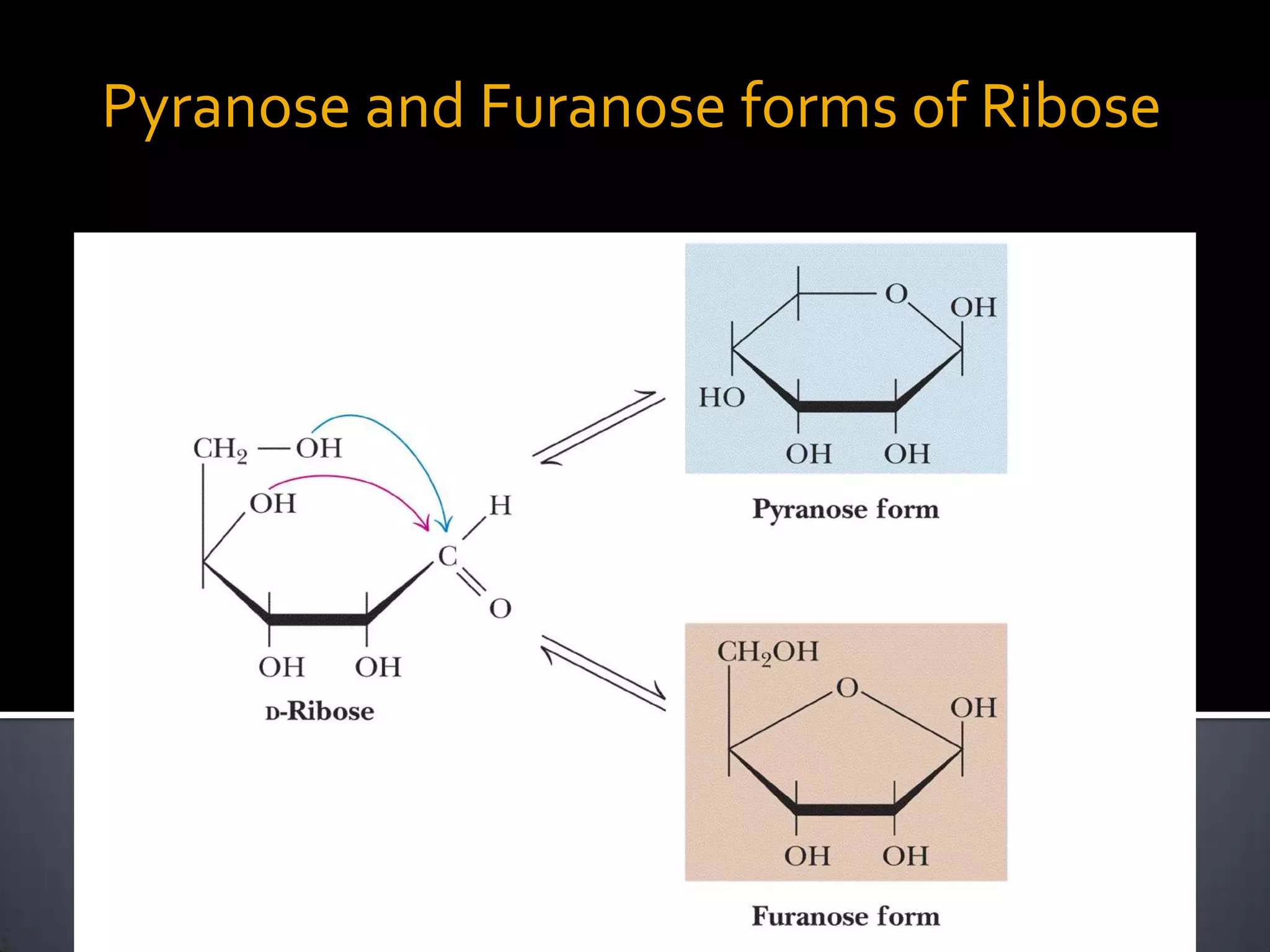
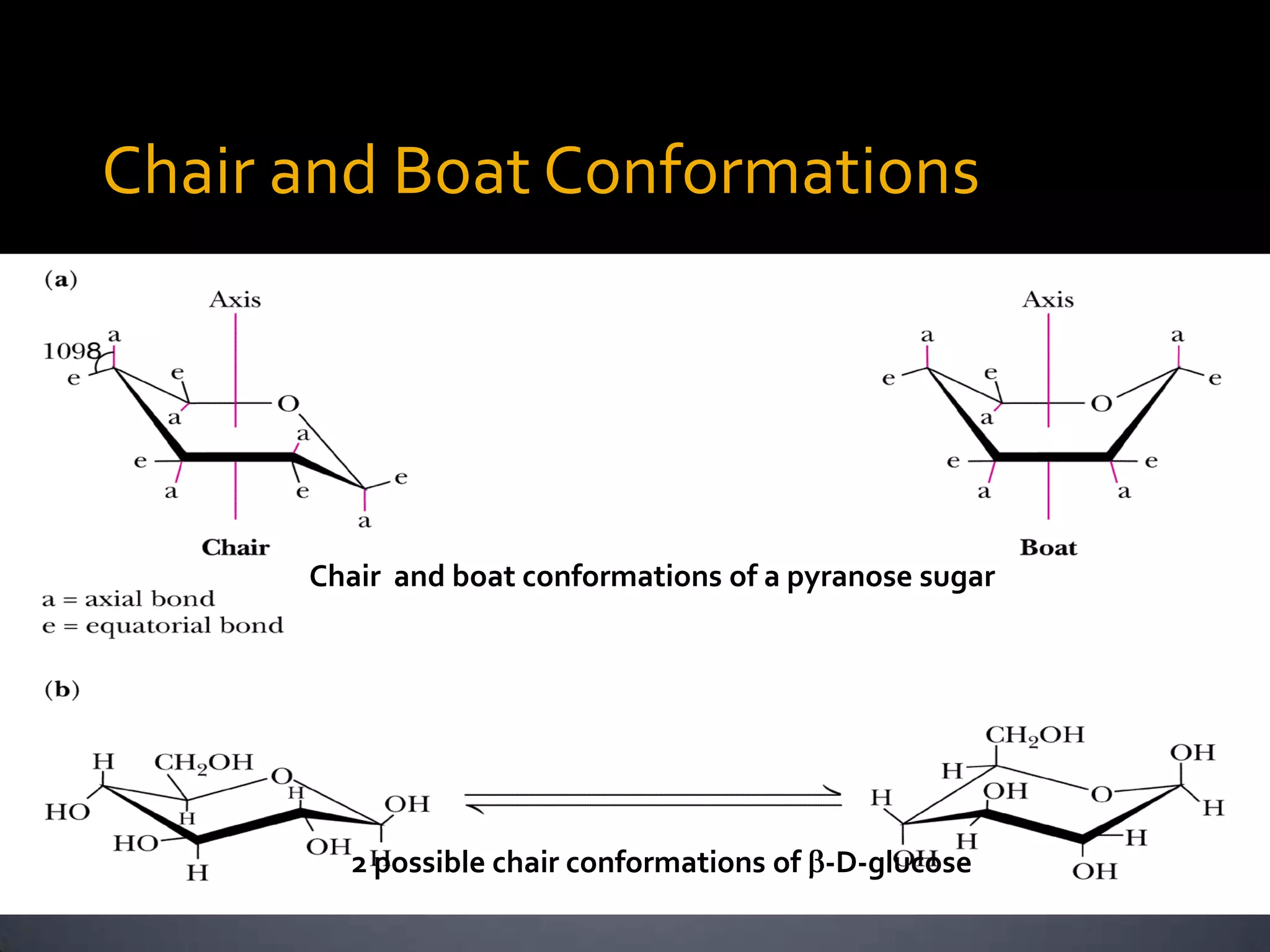
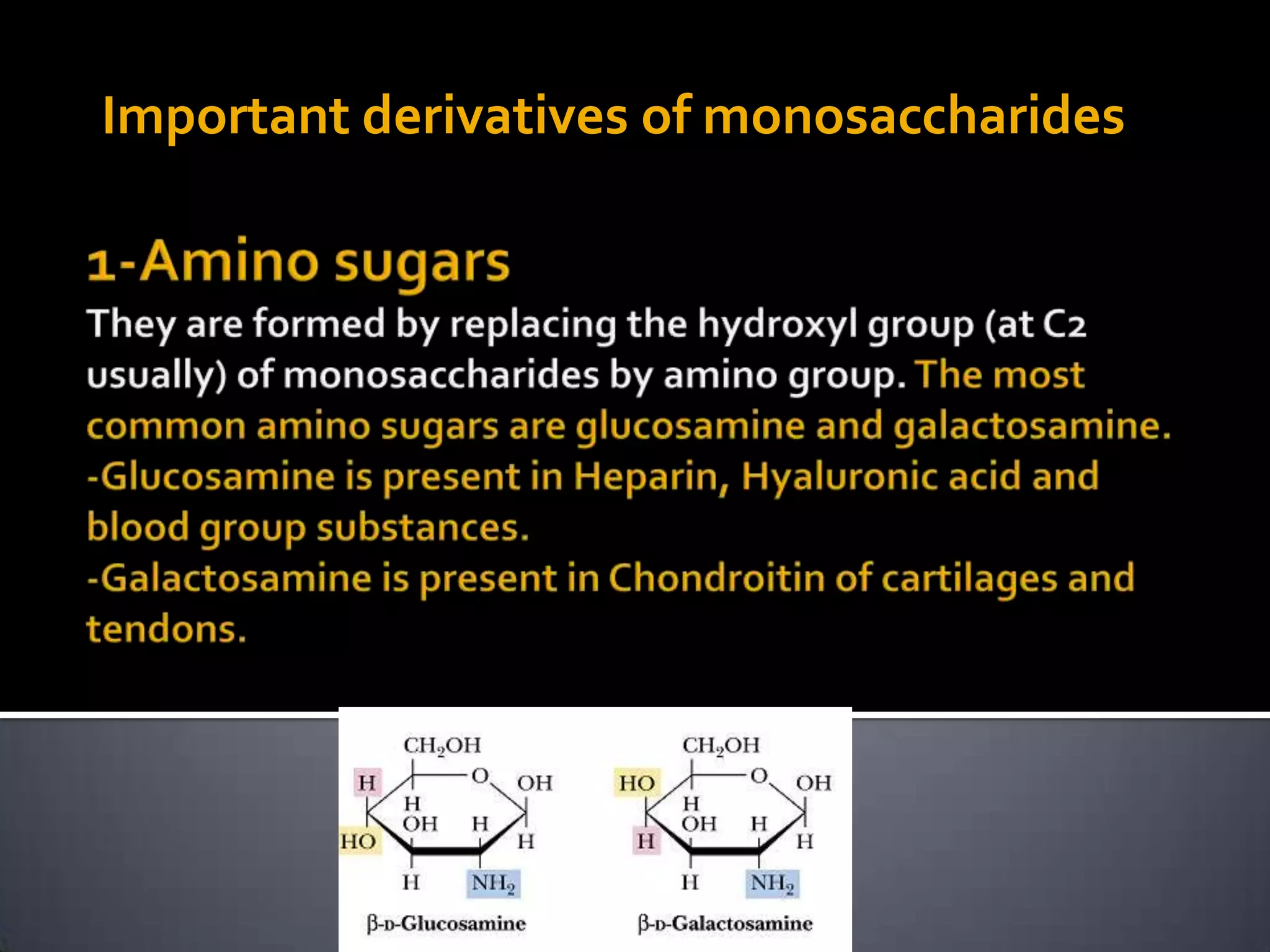
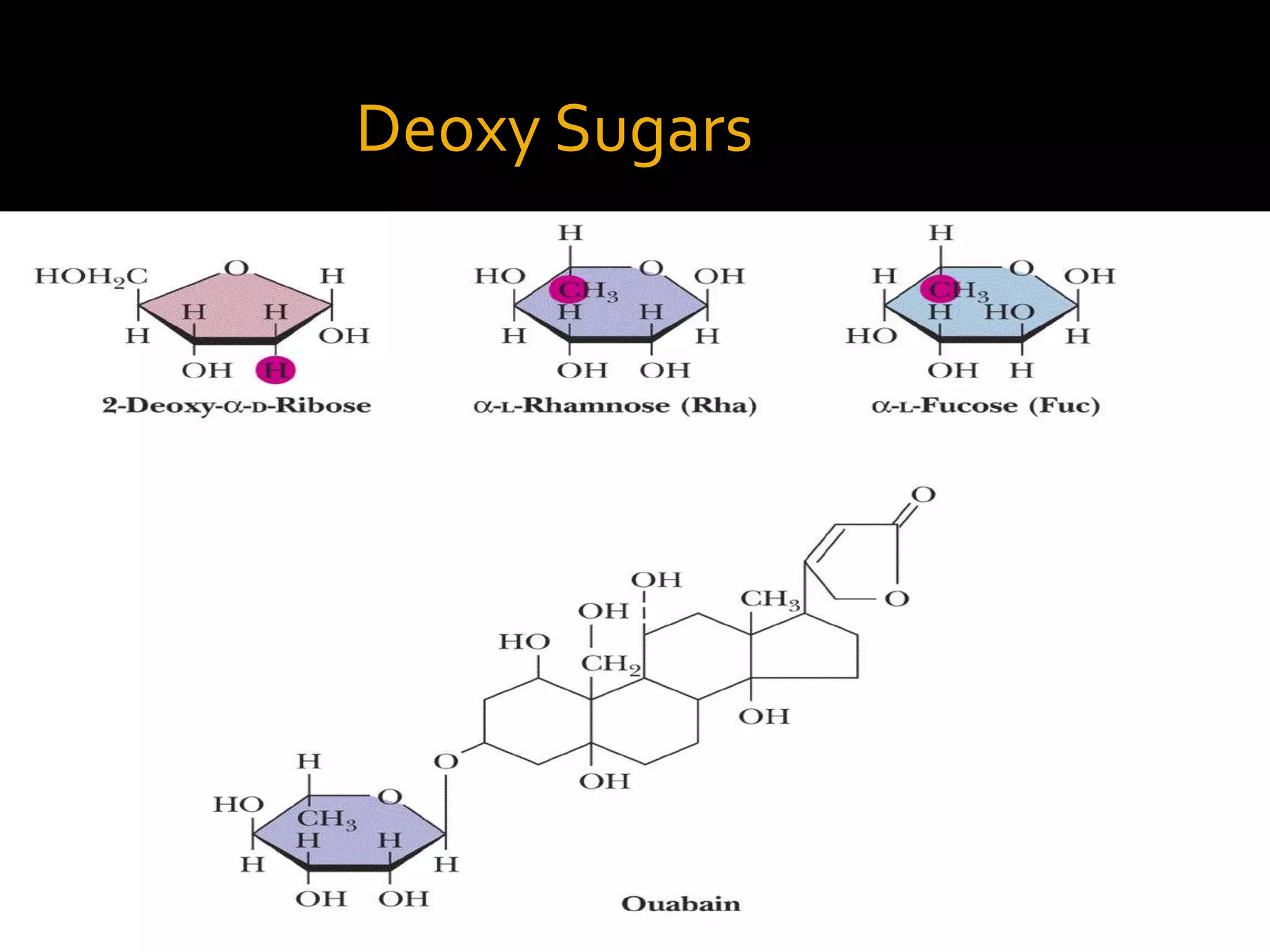
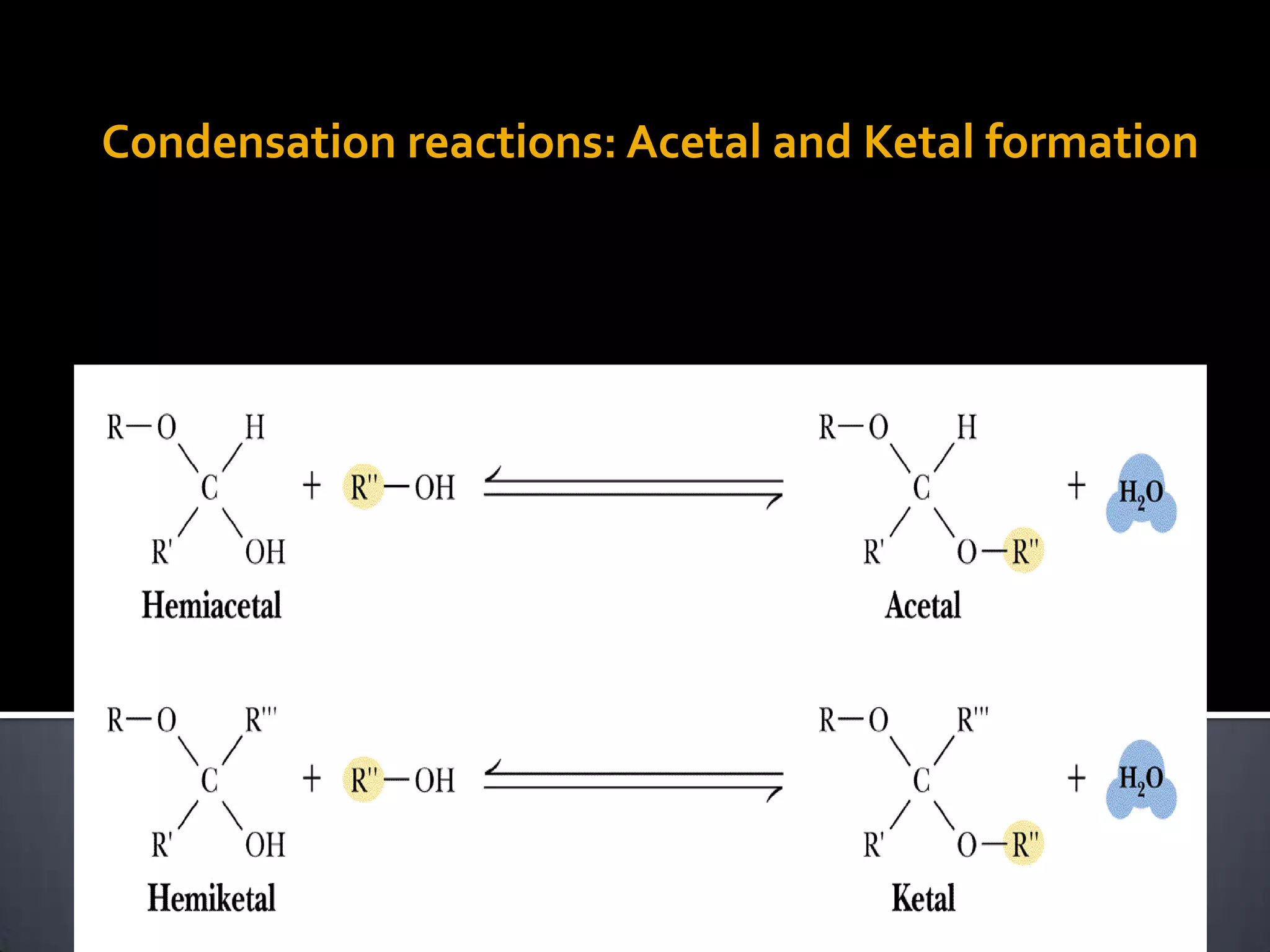
This document discusses carbohydrates and monosaccharides. It defines carbohydrates as compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Monosaccharides are the simplest form of carbohydrates and include trioses, tetroses, pentoses, and hexoses. The document discusses various properties of monosaccharides including isomerism, anomerism, mutarotation, and common chemical reactions like oxidation, reduction, and reactions with acids and bases. It also summarizes important derivatives of monosaccharides such as amino sugars, deoxy sugars, sugar acids, sugar alcohols, esters, and glycosides.