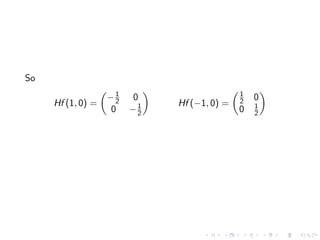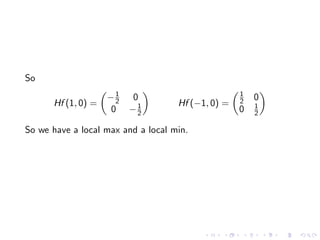Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX







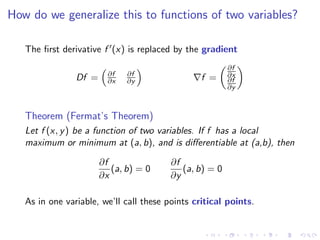







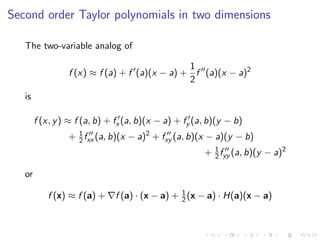




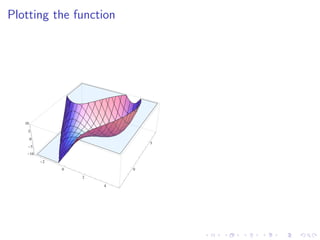
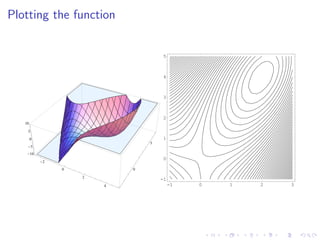






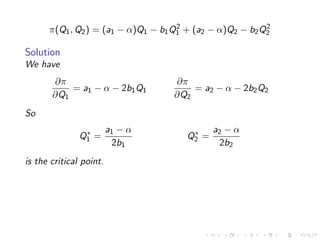
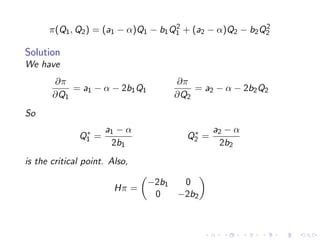
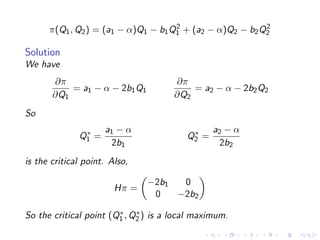

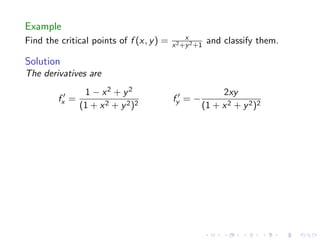

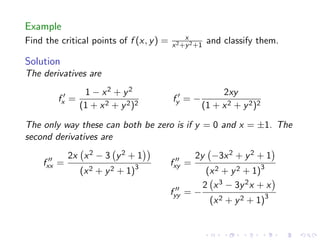
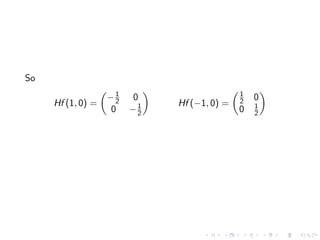
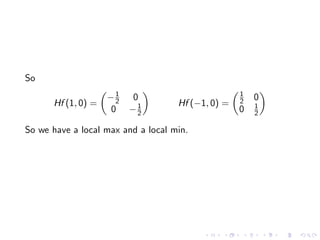
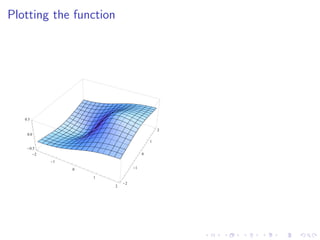
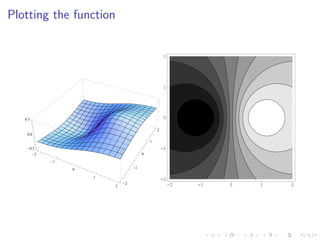

This document summarizes key concepts in unconstrained optimization of functions with two variables, including: 1) Critical points are found by taking the partial derivatives and setting them equal to zero, generalizing the first derivative test for single-variable functions. 2) The Hessian matrix generalizes the second derivative, with its entries being the partial derivatives evaluated at a critical point. 3) The second derivative test classifies critical points as local maxima, minima or saddle points based on the signs of the Hessian matrix's eigenvalues. 4) Taylor polynomial approximations in two variables involve partial derivatives up to second order, analogous to single-variable Taylor series. 5) An example classifies the critical points