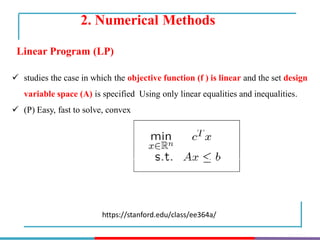
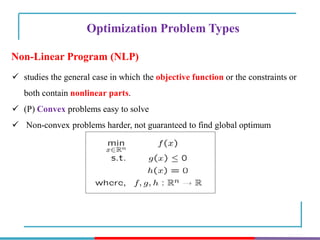
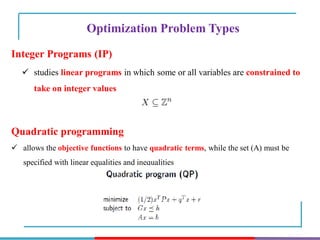
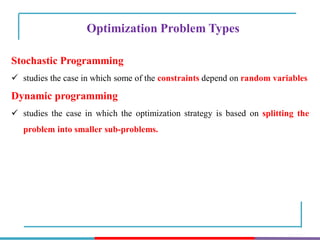
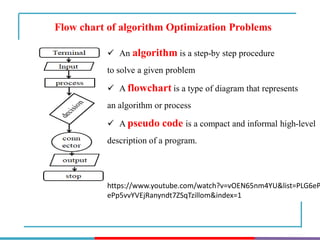
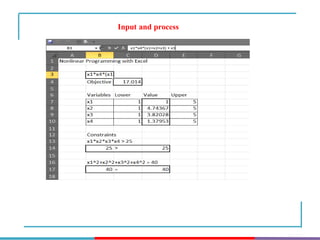
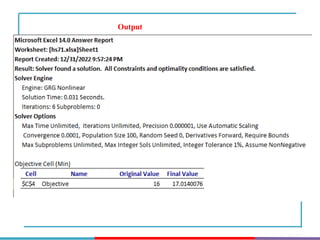
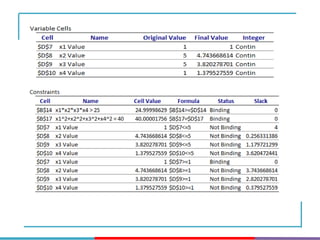
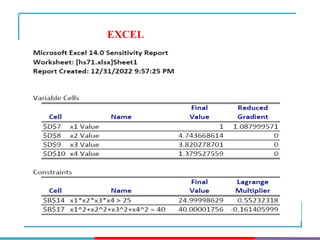
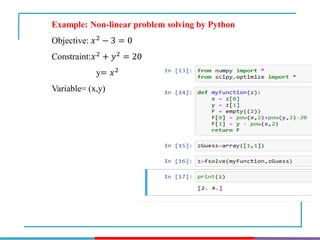
The document discusses different types and methods of optimization problems. It defines optimization as finding the maximum or minimum value of a quantity given certain limits. It provides examples of problems that can be modeled by optimization like scheduling, network design, and inventory management. The document then covers classical optimization techniques using calculus, numerical methods like linear programming, and advanced methods such as swarm intelligence algorithms. It also discusses different software that can be used to solve optimization problems including Excel, Python, and MATLAB.