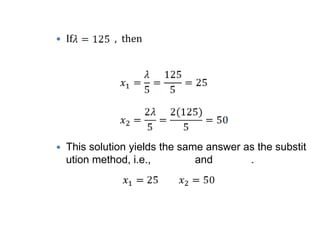Embed presentation
Downloaded 73 times

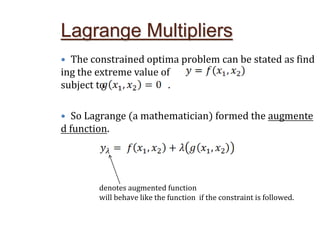
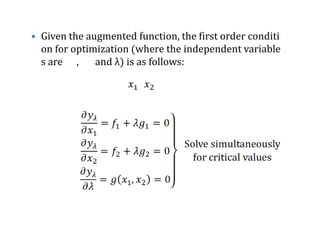
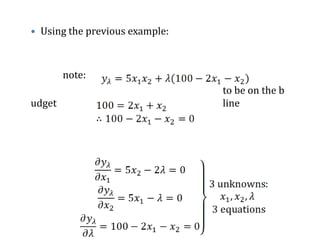
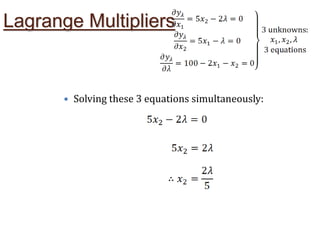

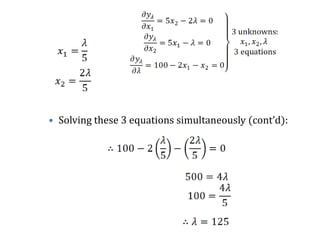
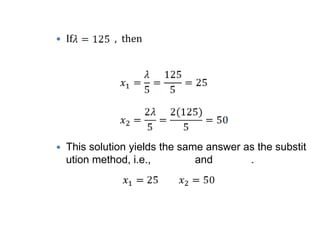

Lagrange's method solves constrained optimization problems by forming an augmented function that combines the objective function and constraints, using Lagrange multipliers (λ) as weighting factors. The method finds extrema by taking partial derivatives of the augmented function with respect to the objective variables and λ, setting the results equal to zero. This produces a system of equations that can be solved simultaneously to identify values that satisfy the constraint and optimize the original objective function.