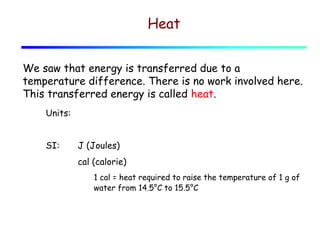
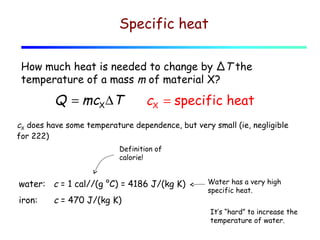
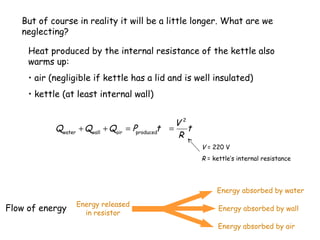
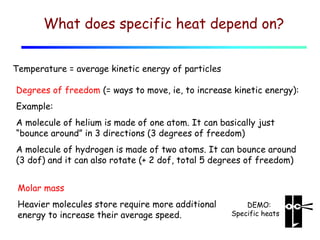
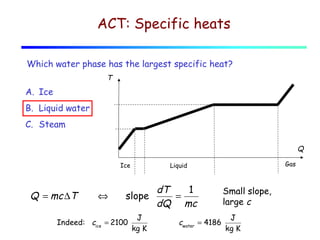
1) Heat is energy transferred due to a temperature difference without work. Specific heat is the amount of heat needed to change the temperature of a mass by a certain amount. Water has a very high specific heat.
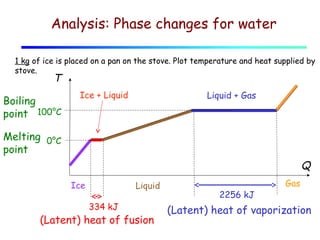
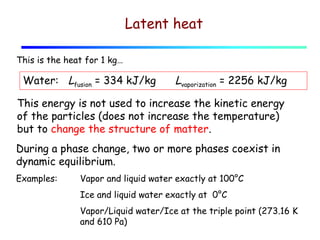
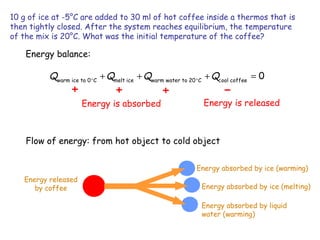
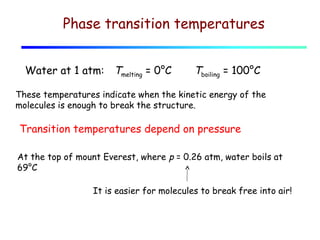
2) Matter exists in solid, liquid, and gas phases. Phase changes involve a structural change of matter and absorb or release latent heat without changing temperature.
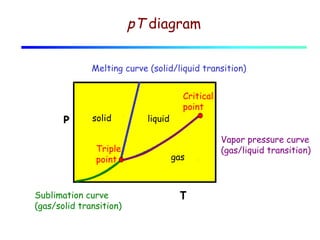
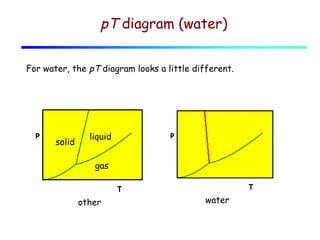
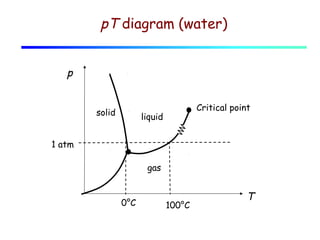
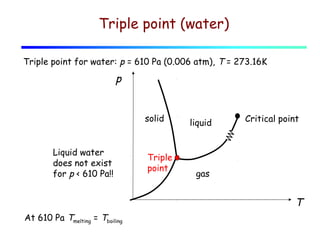
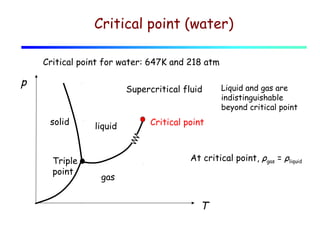
3) A phase diagram shows the relationships between pressure, temperature, and phases of a substance. The triple point is where solid, liquid, and gas phases coexist in equilibrium.