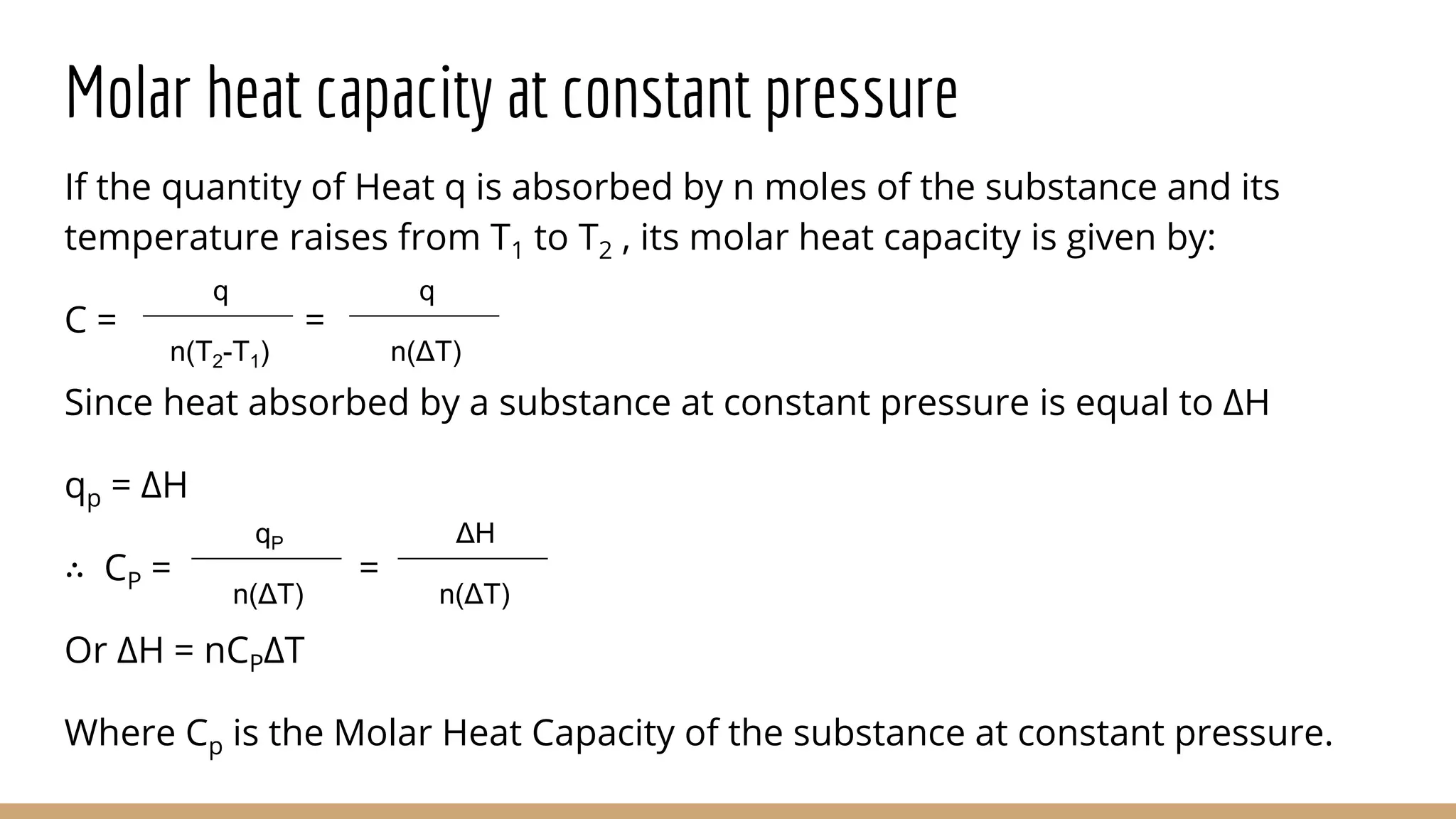
The document discusses heat capacity, which is the amount of heat required to change a substance's temperature by 1 degree Kelvin. There are three types of heat capacity: heat capacity, specific heat capacity (per gram), and molar heat capacity (per mole). Molar heat capacity at constant pressure (Cp) and constant volume (Cv) are also discussed. Calorimetry, the measurement of heat flow, can be used to calculate heat and enthalpy changes through temperature change measurements. Bomb calorimetry under constant volume is given as an example to determine the energy available from combusting foods like glucose.