Embed presentation
Downloaded 466 times

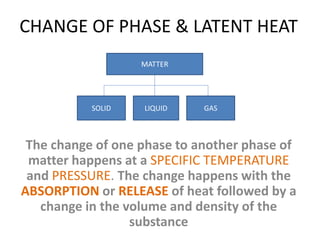

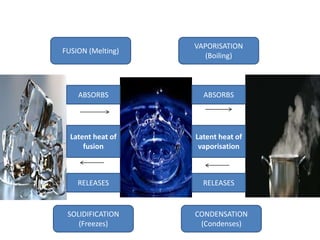
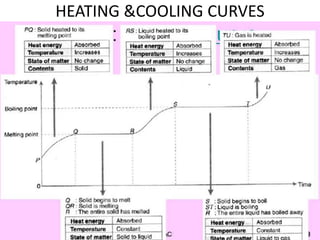
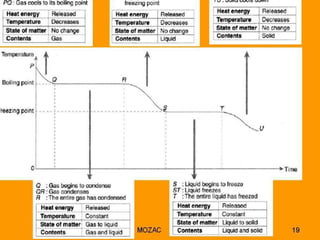

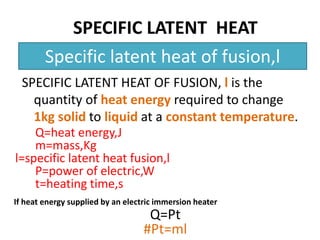

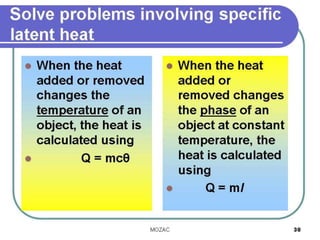












This document discusses latent heat and specific latent heat during phase changes of matter. It explains that phase changes from solid to liquid or liquid to gas occur at specific temperatures and pressures, absorbing or releasing heat. Latent heat refers to the total energy absorbed or released during a full phase change at constant temperature, such as the latent heat of fusion during melting or the latent heat of vaporization during boiling. Specific latent heat is defined as the quantity of heat energy required to change 1 kg of a substance during a phase change, such as the specific latent heat of fusion to change solid to liquid. Equations are provided to calculate heat energy involved in phase changes.




















