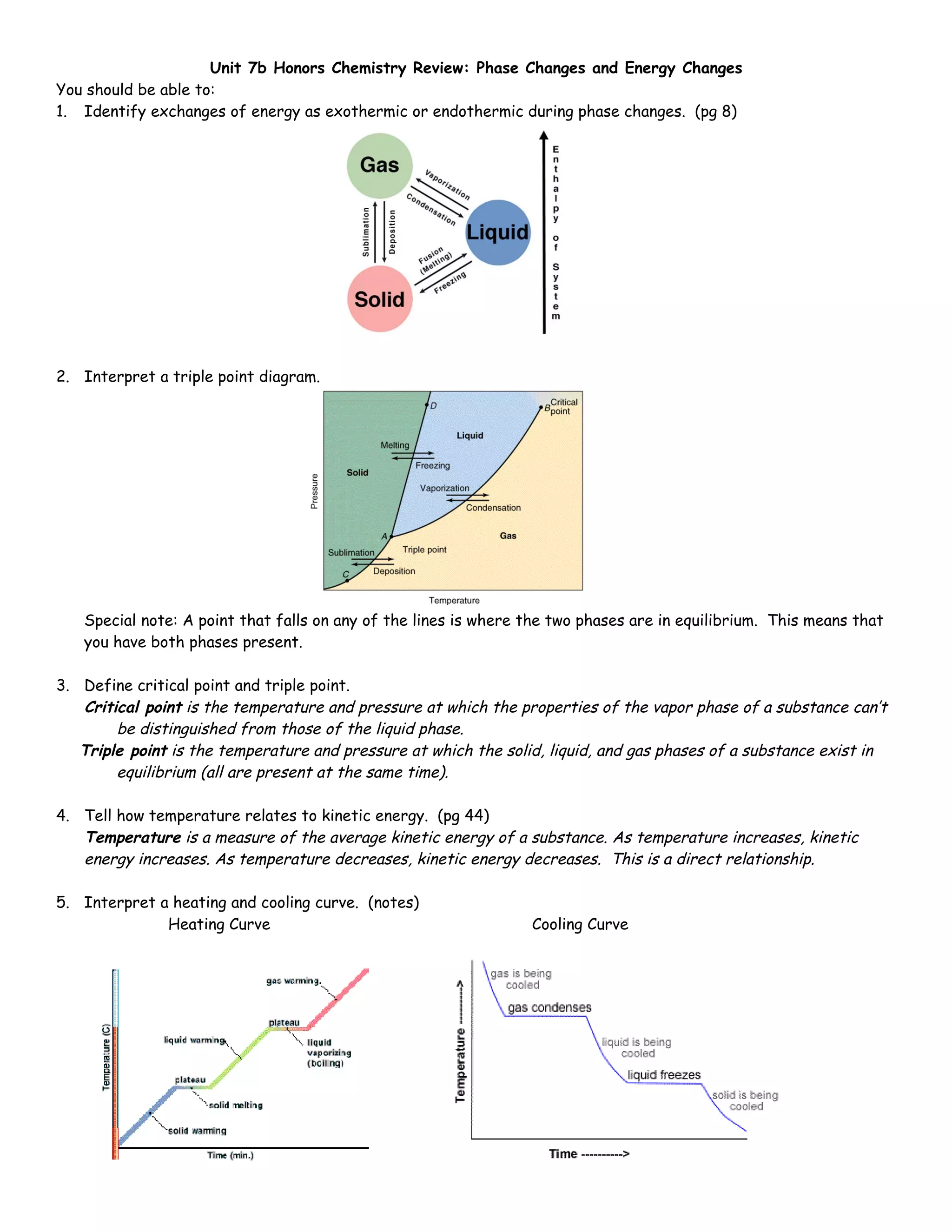
The document summarizes key concepts about phase changes and energy changes, including:
1) Phase changes can be exothermic or endothermic.
2) Heating and cooling curves illustrate changes in kinetic and potential energy that occur during temperature and phase changes.
3) The specific heat capacity of a substance determines how much its temperature changes with added or removed energy.