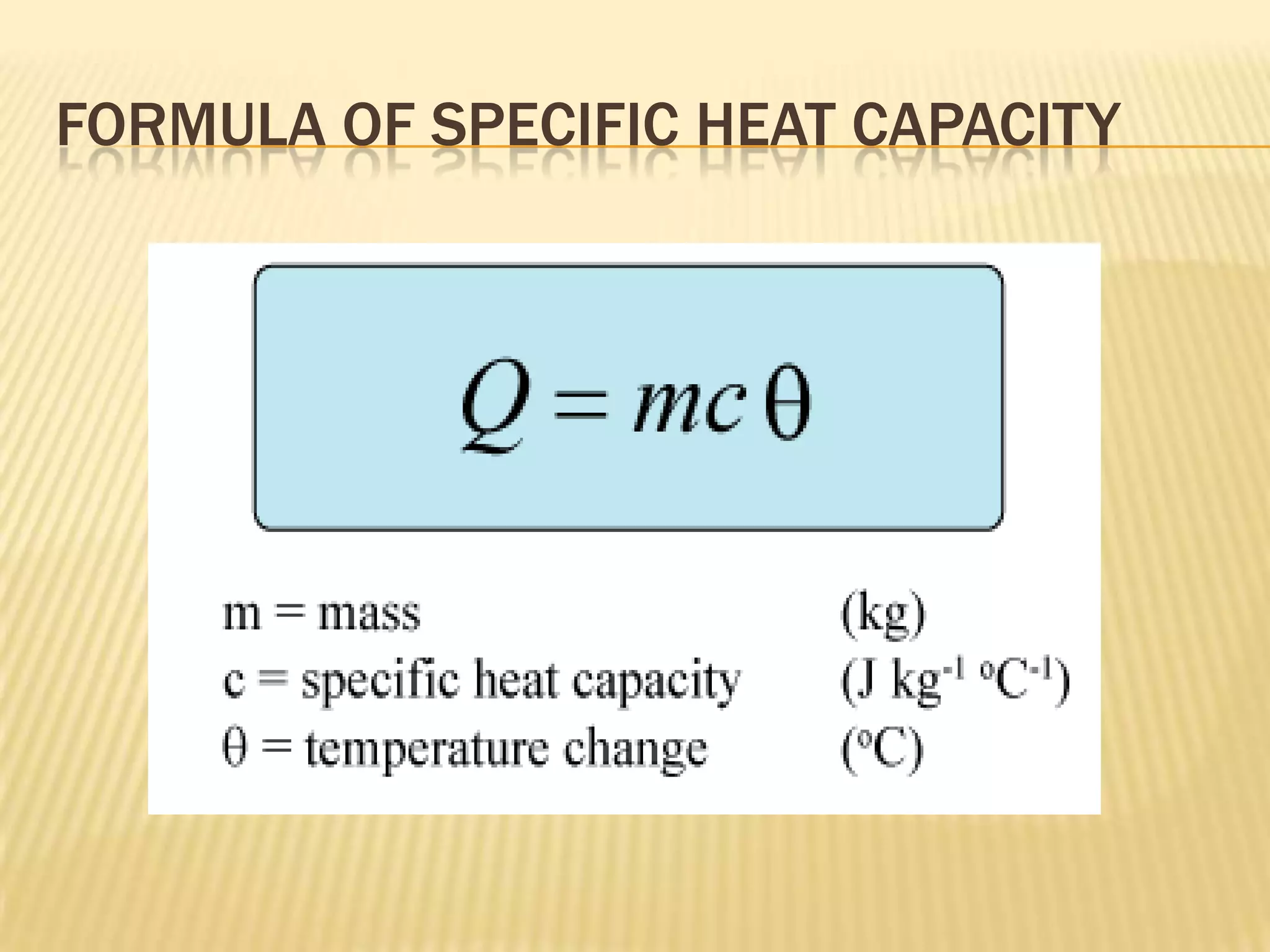
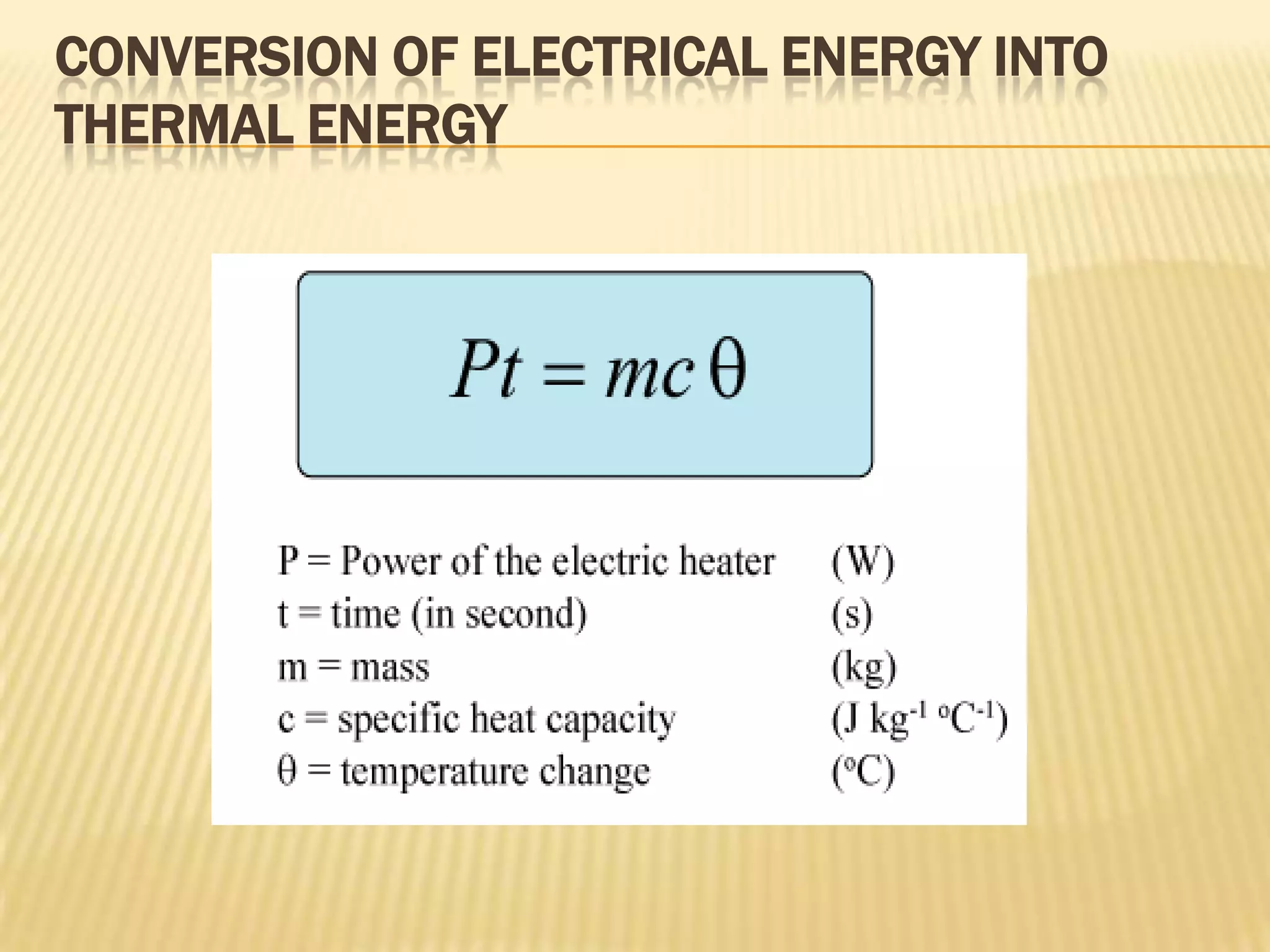
The document defines heat capacity and different types of heat capacity including molar heat capacity and specific heat capacity. It provides formulas for calculating specific heat capacity and examples of using heat capacity to calculate the thermal energy required to change an object's temperature through various processes like mixing liquids and converting potential, kinetic, and electrical energy to thermal energy. Specific examples are worked out showing how to apply the concepts and formulas for heat capacity.



![EXAMPLE
How much thermal energy is required to raise the temperature of a 2
kg aluminium block from 25 C to 30 C? [The specific heat
capacity of aluminium is 900 Jkg-1 oC-1]
Answer:
Mass, m = 2kg
Specific heat capacity, c = 900 Jkg-1 oC-1
Temperature change, θ = 30 - 25 = 5 oC
Thermal energy required,
Q = mcθ = (2)(900)(5) = 9000J.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-120224082351-phpapp02/75/specific-heat-capacity-5-2048.jpg)
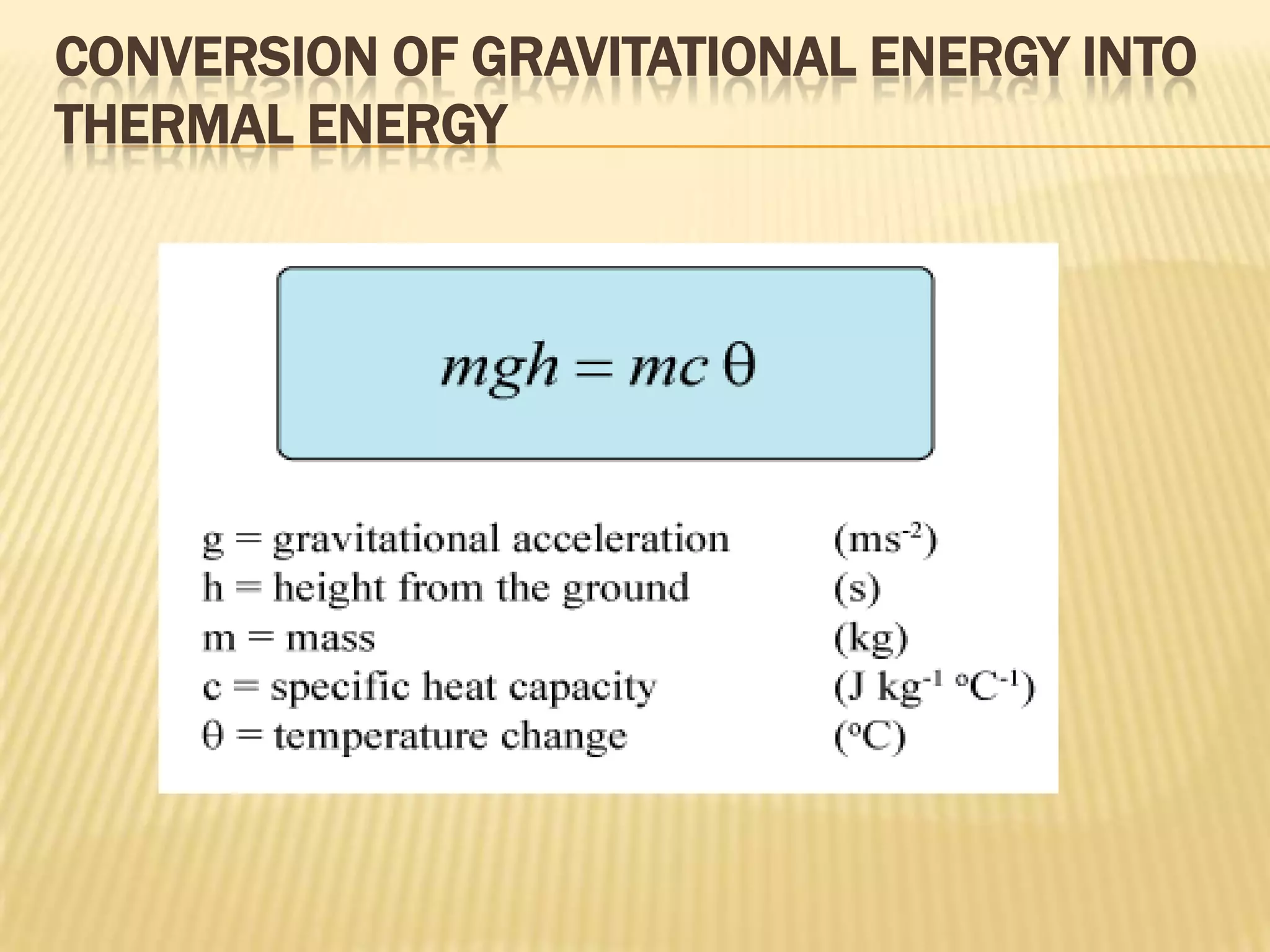
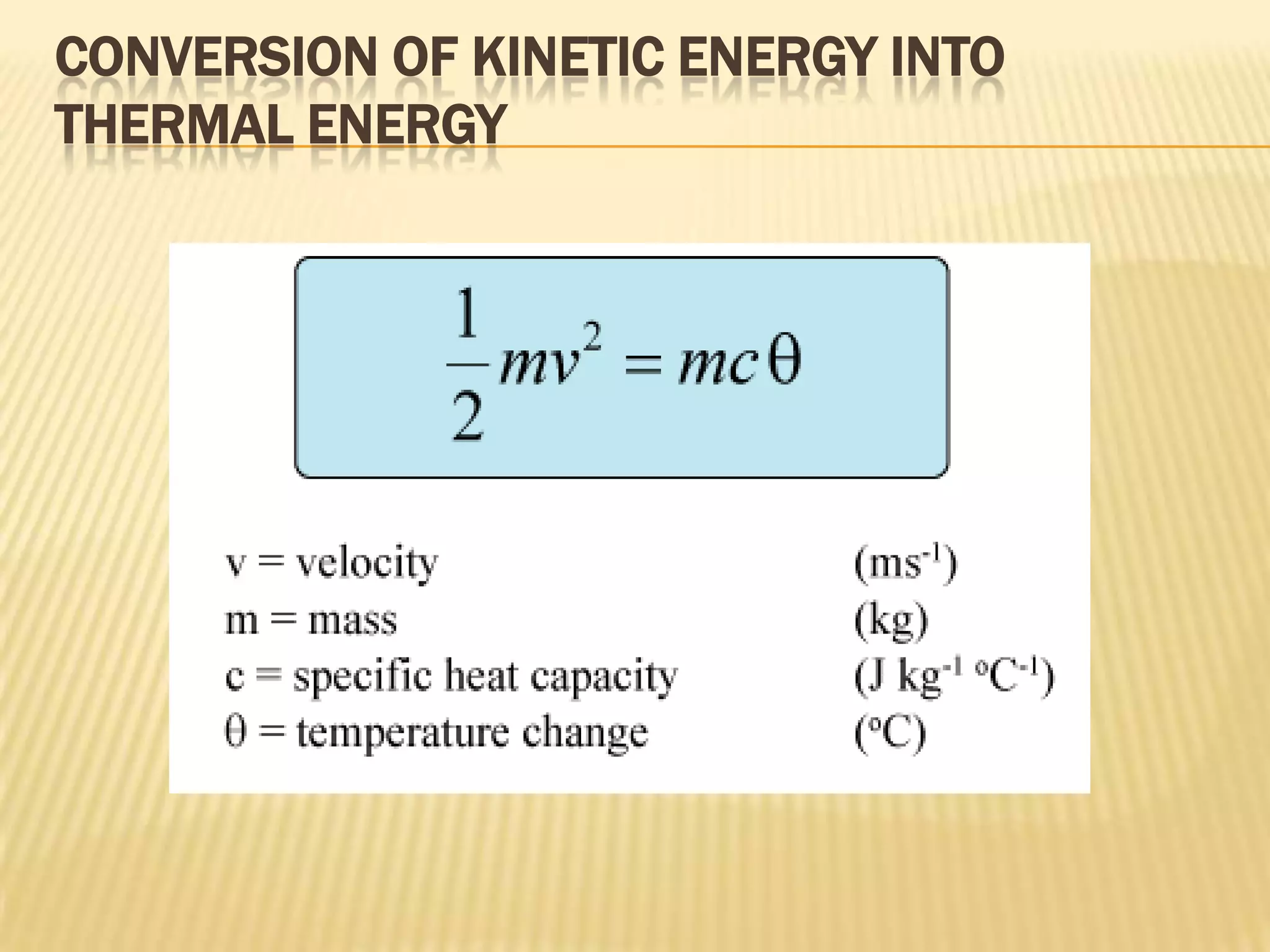
![EXAMPLE
A lead shot of mass 5g is placed at the bottom of a vertical cylinder that
is 1m long and closed at both ends. The cylinder is inverted so that the shot
falls 1 m. By how much will the temperature of the shot increase if this
process is repeated 100 times? [The specific heat capacity of lead is
130Jkg-1K-1]
Answer:
m = 5g
h = 1m × 100 = 100m
g = 10 ms-2
c = 130Jkg-1K-1
θ=?
In this case, the energy conversion is from potential energy to heat
energy. We assume that all potential energy is converted into heat energy.
Therefore
mgh = mcθ
gh = cθ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-120224082351-phpapp02/75/specific-heat-capacity-7-2048.jpg)

![EXAMPLE
Example 4
What will be the final temperature if 500 cm3 of water at 0 �C is added to
200cm3 of water at 90 �C? [Density of water = 1gcm-3]
Answer:
The density of water is 1g/cm3, which means the mass of 1 cm3 of water is
equal to 1g.
Let the final temperature = θ
m1 = 500g = 0.5kg
c1 = c
θ1 = θ - 0 = θ
m2 = 200g = 0.2kg
c2 = c
θ2 = 90 - θ
m1c1θ1 = m2c2θ2
(0.5) c ( θ ) = (0.2) c ( 90 - θ )
0.5 θ = 18 - 0.2 θ
0.5 θ + 0.2 θ = 18
0.7 θ = 18
θ = 25.71 oC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-120224082351-phpapp02/75/specific-heat-capacity-11-2048.jpg)
