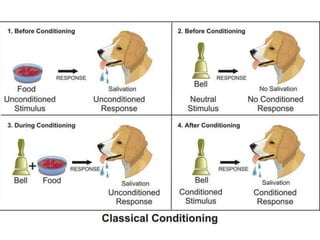
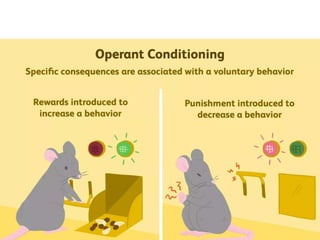
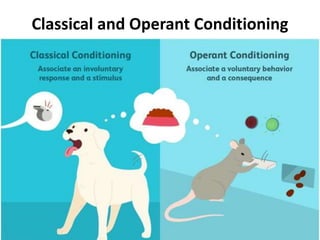
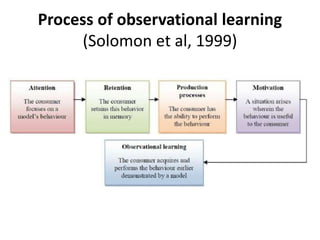
Rustam's lecture outline covered various types of learning. It defined learning as a relative change in behavior or knowledge due to experience. The lecture discussed classical conditioning, where a biologically strong stimulus is paired with a previously neutral stimulus. It also covered operant conditioning, where behaviors are linked to consequences through rewards and punishments. Observational learning was explained as learning by watching others' behaviors. The lecture outlined how both classical and operant conditioning lead to learning through different pairings and explained the processes of observational learning involve imitation.