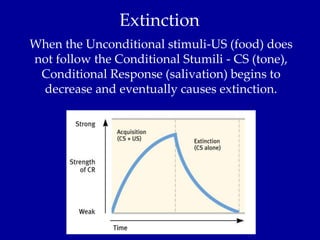
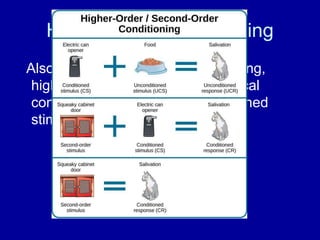
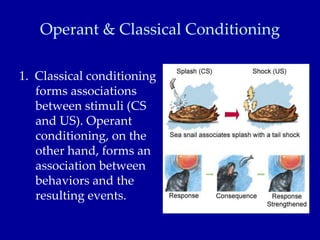
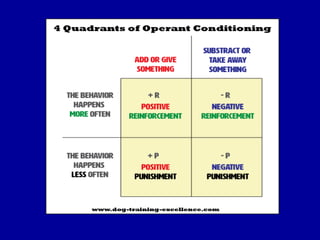
Learning is defined as a relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience. Classical conditioning links a neutral stimulus to an unconditioned stimulus that elicits a natural response, forming an association. Ivan Pavlov's famous experiments on dogs demonstrated classical conditioning. Operant conditioning associates responses with consequences, such as reinforcement or punishment, shaping behavior. Both types of associative learning are important ways organisms learn about their environment.