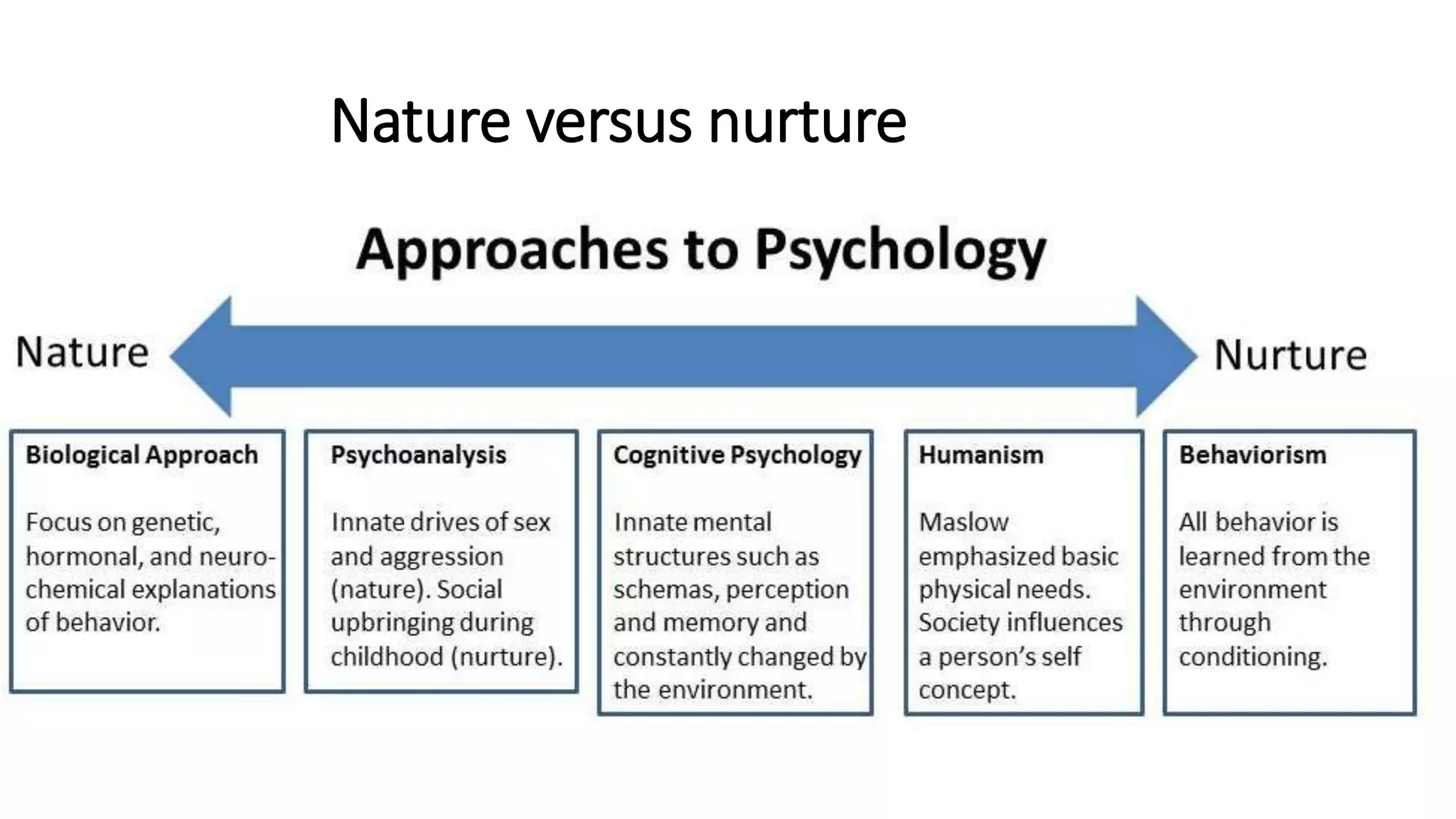
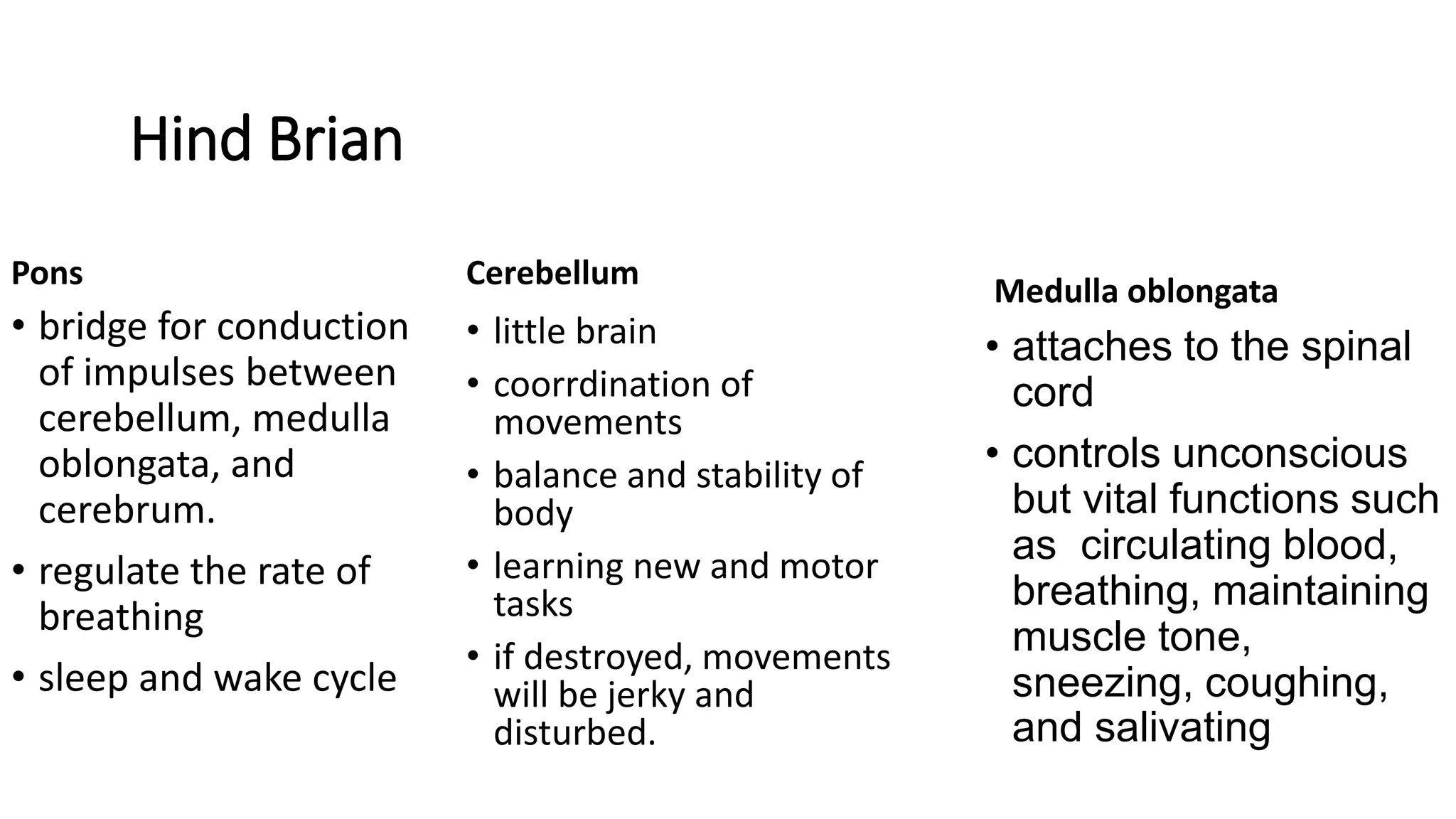
The biological perspective views behavior and mental processes as ultimately resulting from biological influences, particularly evolutionary processes and genetic factors. Historically, philosophers and scientists have explored the relationship between the physical body and mental processes. In the 18th-19th centuries, thinkers like Descartes, James, and Dunlap contributed to understanding the biological underpinnings of psychology. The biological perspective examines behavior through comparative studies, physiology, and inheritance. Major theories like dualism, materialism, heredity, and natural selection helped develop this perspective. Biological psychology analyzes behaviors in relation to genetics, the nervous system, neurotransmitters, and other biological factors.









![Biological Perspective
• Biological Perspective presented by McDougall
• Explained biological functions as the basis of behaviour
• The biological perspective states that all thoughts, feeling & behavior ultimately
have a biological cause.
• Major Areas of Biological perspective
• Genetics
• Immune system
• Human Nervous System[ brain]
• Neuro-transmitters
• Glands](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biologicalperspective-210731031629/75/Biological-perspective-10-2048.jpg)