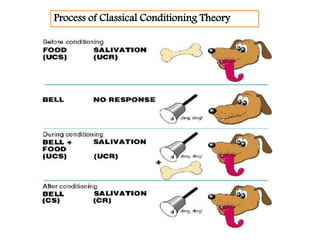
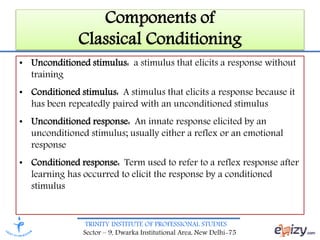
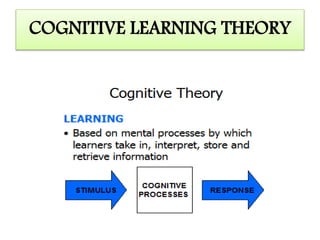
This document discusses learning and various theories of learning. It begins with definitions of learning as involving changes in behavior due to experience. It then discusses the nature of learning, including that changes must be relatively permanent and based on practice or experience. It outlines components and factors that affect learning. Four main theories of learning are described: classical conditioning, operant conditioning, cognitive learning theory, and social learning theory. Classical conditioning involves acquiring new responses to stimuli through repeated associations. Operant conditioning examines how consequences influence voluntary behaviors. Cognitive learning theory views learning as gaining understanding through absorbing information. Social learning theory posits that people learn from observing and imitating others.