1. There are three main types of learning: classical conditioning, operant conditioning, and observational learning.
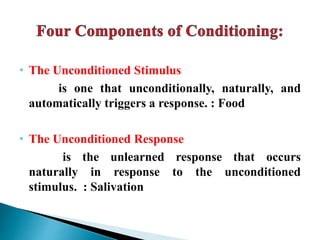
2. Classical conditioning involves forming an association between a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus to elicit a conditioned response, as discovered by Ivan Pavlov in his experiments with dogs.
3. Operant conditioning is a type of learning where behaviors are modified by reinforcement or punishment to increase or decrease the likelihood of those behaviors reoccurring, as proposed by B.F. Skinner.