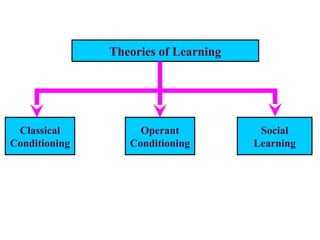
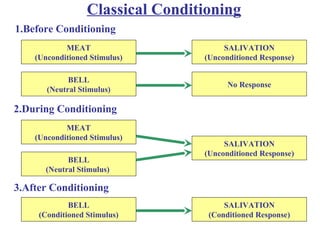
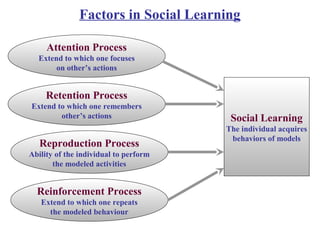
Learning involves relatively permanent changes in behavior due to experience. There are three main theories of learning: classical conditioning, operant conditioning, and social learning. Classical conditioning involves associating a neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus to elicit a conditioned response. Pavlov's dog experiment demonstrated this. Operant conditioning involves reinforcing behaviors with consequences to increase their likelihood. Skinner showed this using a Skinner box. Social learning involves observing and imitating others' behaviors and their consequences. Reinforcement strengthens behaviors through rewards or avoidance of punishment.