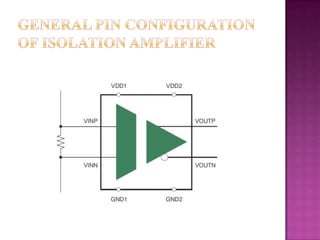
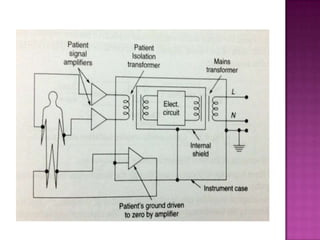
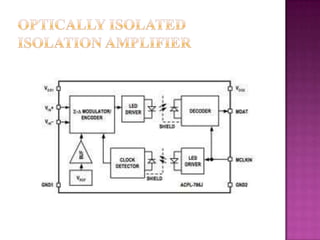
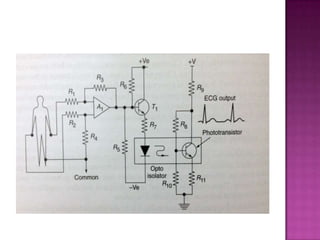
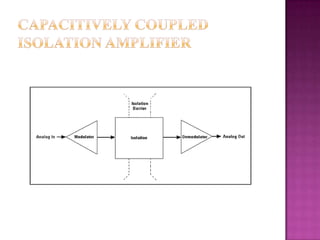
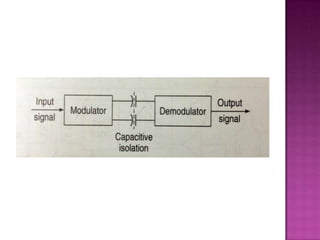
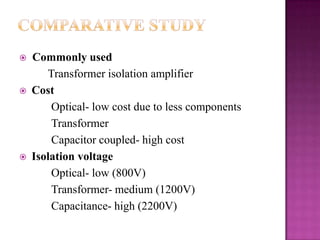
Isolation amplifiers provide electrical isolation and safety barriers between input and output stages. They use transformer, optical, or capacitive isolation methods and isolated power supplies to break continuity while amplifying low-level signals. Common applications include medical equipment, industrial processes, and data acquisition where electrical isolation is needed to protect patients or eliminate noise.