Embed presentation
Downloaded 30 times

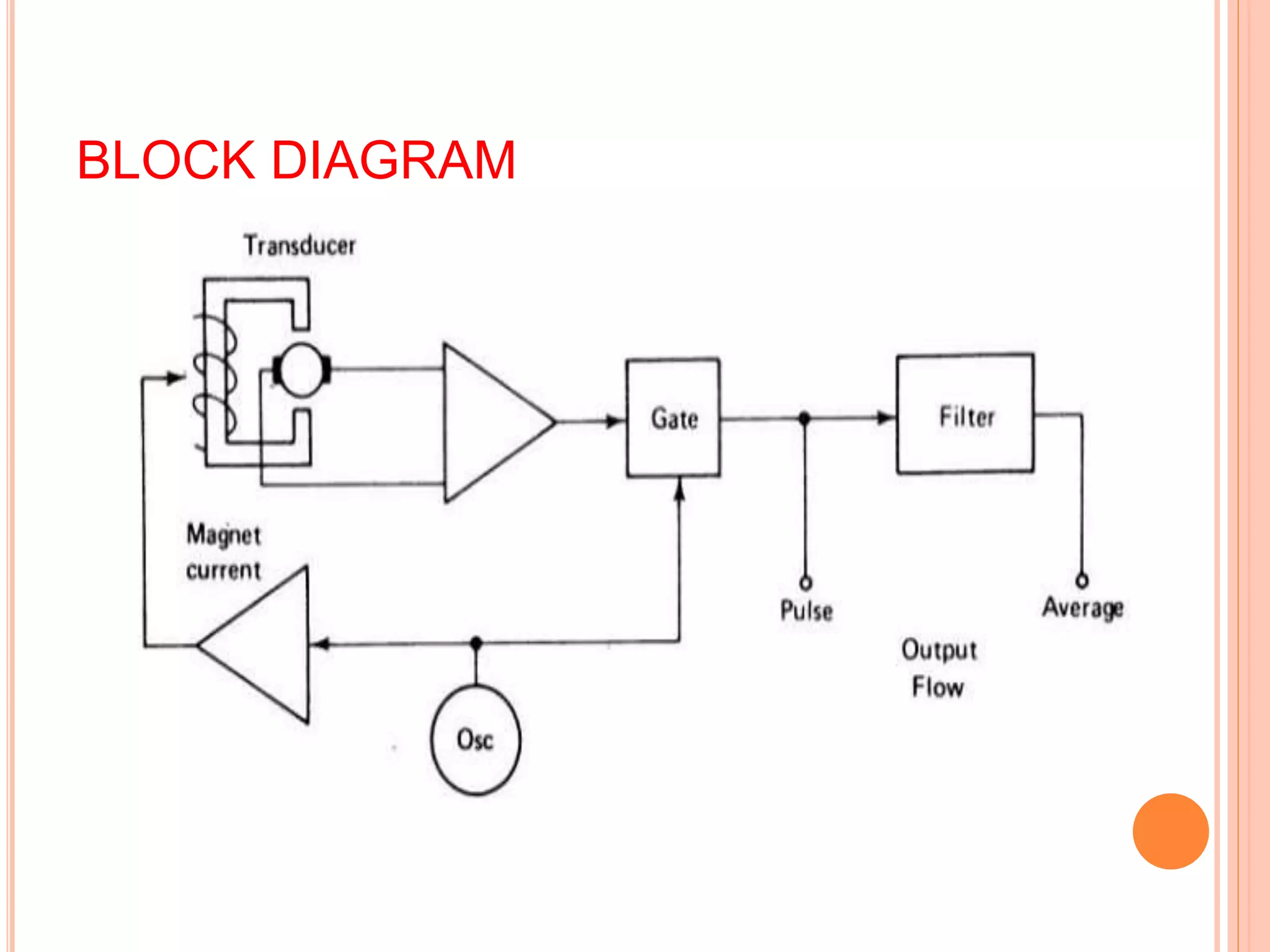
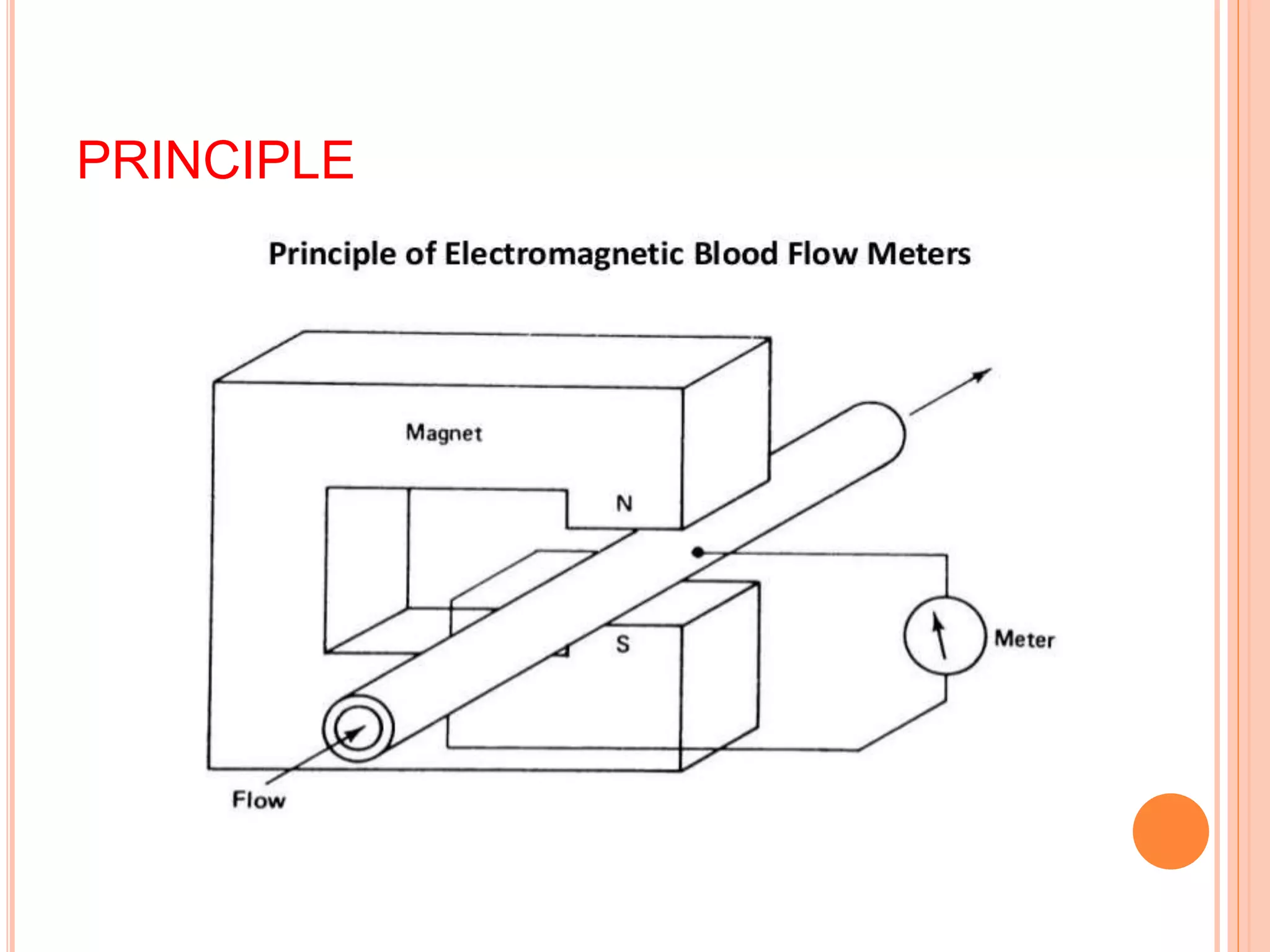


The document discusses an electromagnetic blood flow meter. It operates based on electromagnetic induction principles, inducing an EMF in blood flowing through a vessel perpendicular to a magnetic field. Electrodes placed across the vessel measure this induced EMF, which is proportional to blood velocity. The small EMF signal is amplified for measurement and low pass filtered to determine average blood flow rate. Advantages include a linear dynamic range and no mechanical limitations for measuring high and low blood flows.






