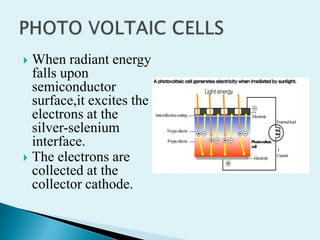
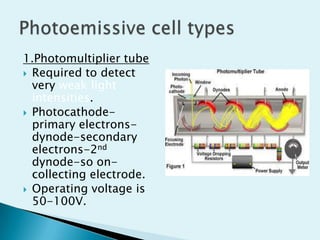
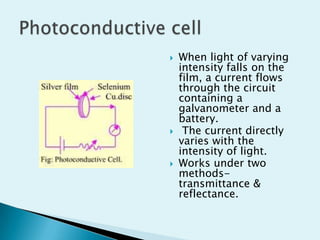
The document discusses various types of photosensitive devices that can convert light energy into electrical energy. It describes passive transducers like photoemissive, photoconductive cells and active photovoltaic transducers. Selenium cells are introduced as early photovoltaic devices that use the photovoltaic effect to generate voltage and current. Other active transducers discussed include photomultiplier tubes, photodiodes, and light dependent resistors. Various biomedical applications of photosensitive devices are also mentioned like pulse pickup, respiration monitoring, and blood oxygen detection.