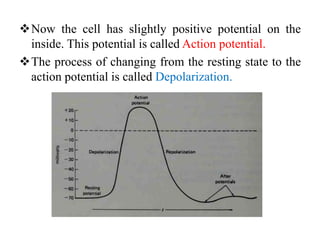
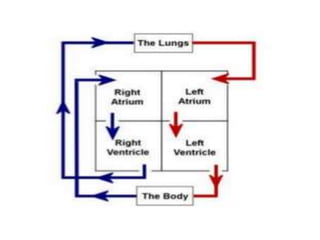
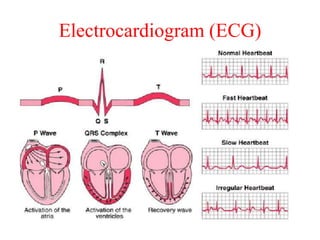
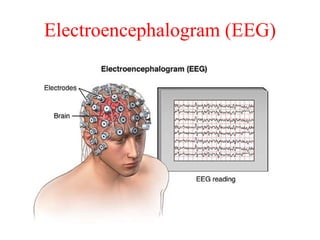
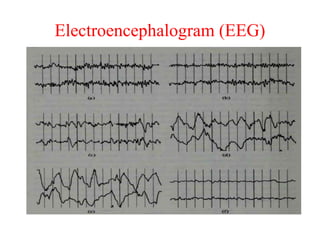
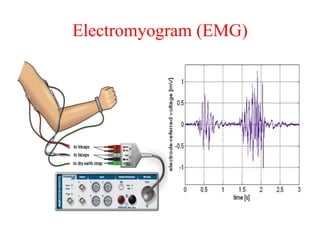
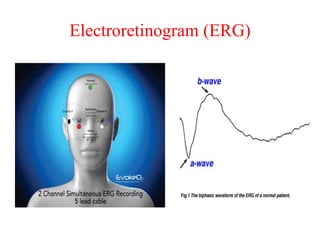
Biopotentials are ionic voltages produced by electrochemical activity in cells. Certain cells like nerve and muscle cells are encased in a semi-permeable membrane that allows some substances to pass through while keeping others out. These membranes maintain a resting potential of -60 to -100 mV by allowing potassium and chloride ions into the cell while blocking sodium ions. When the membrane allows sodium ions to pass through, the cell's potential becomes slightly positive in what is called an action potential, changing the cell from its resting state. Transducers are used to convert these ionic potentials into electrical signals that can be measured and analyzed.