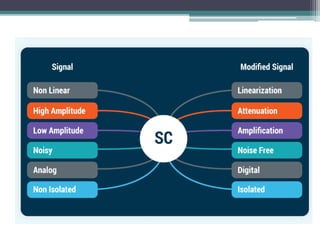
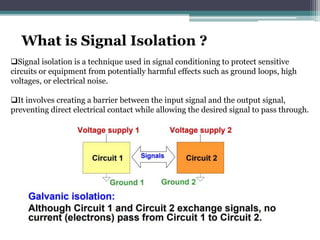
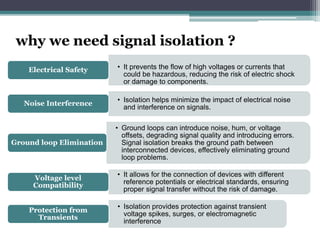
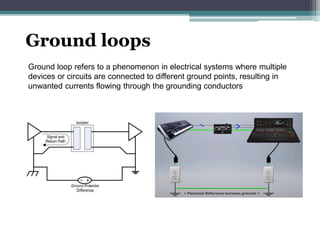
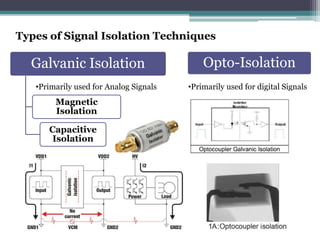
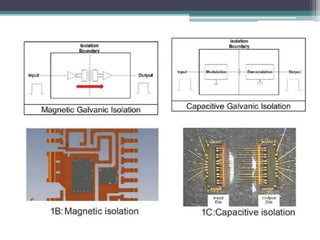
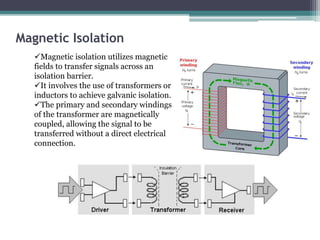
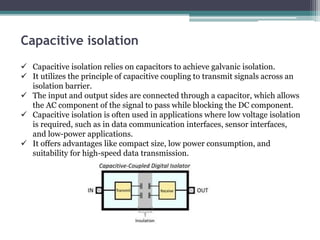
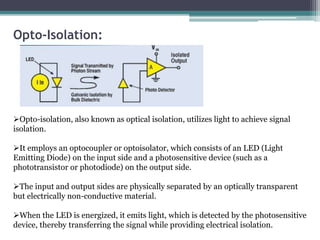
Signal isolation is a technique used in signal conditioning to protect sensitive circuits from harmful effects like ground loops, high voltages, and electrical noise. It creates a barrier between input and output signals to allow the desired signal to pass through while preventing direct electrical contact. Common isolation techniques include magnetic isolation using transformers, capacitive isolation using capacitors, and opto-isolation using optocouplers consisting of an LED and photodetector.