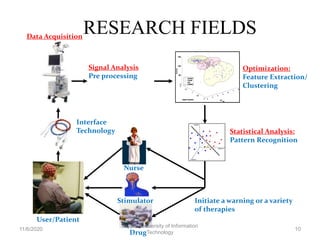
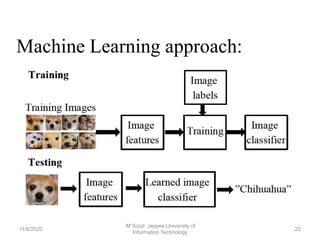
Biomedical signal processing involves applying engineering principles and techniques to medical fields. It combines engineering design skills with medical sciences to improve healthcare diagnosis and treatment. Some key biomedical signals discussed include ECG, EMG, EEG, and others. There are several research gaps and areas discussed such as signal conditioning, feature extraction, optimization techniques, and classification methods. Machine learning and deep learning approaches using techniques like convolutional neural networks show promise for biomedical signal processing applications in areas like medical research.