This document provides an overview of ischaemic stroke, including its definition, risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis and management. Key points include:
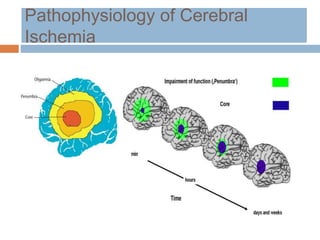
- Ischaemic stroke accounts for 80% of strokes and results from focal brain infarction due to obstruction of cerebral blood flow.
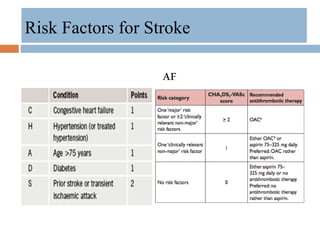
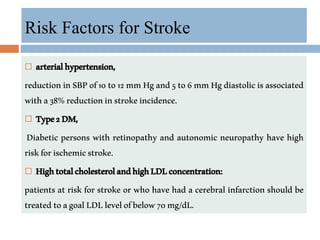
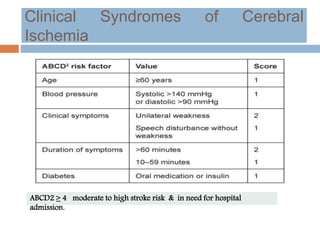
- Major risk factors include hypertension, atrial fibrillation, diabetes, hyperlipidemia and previous stroke or TIA.
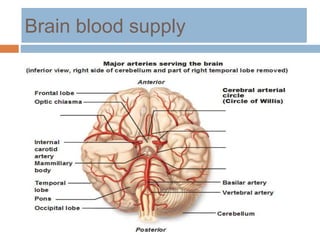
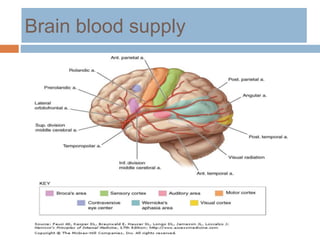
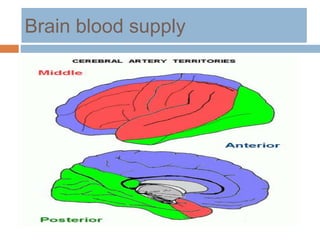
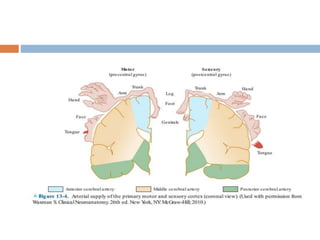
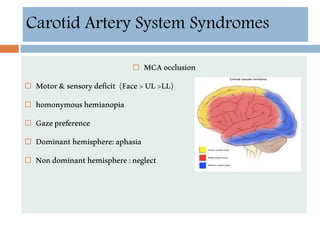
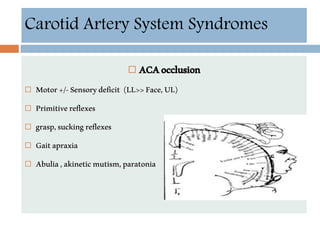
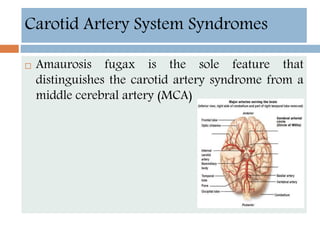
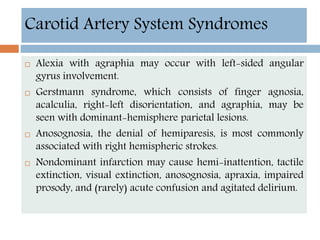
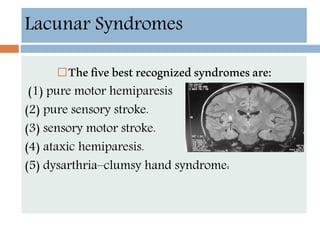
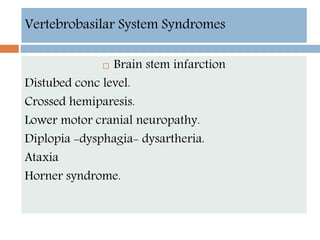
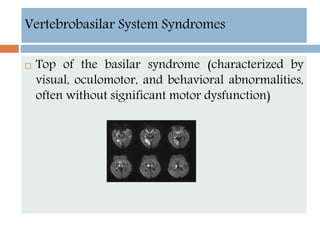
- Clinical syndromes depend on the location of brain infarction and can include motor/sensory deficits, aphasia and visual field cuts.
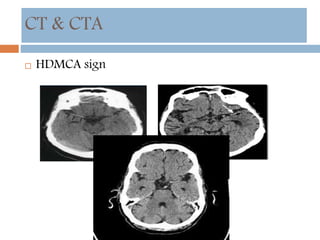
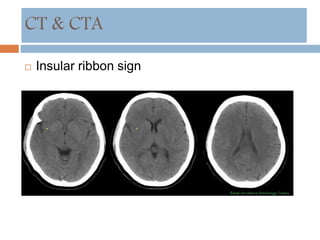
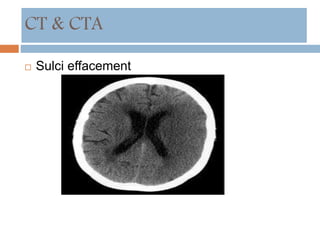
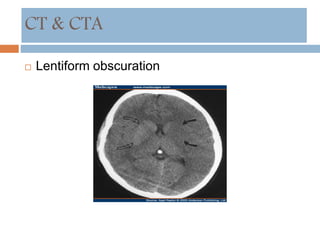
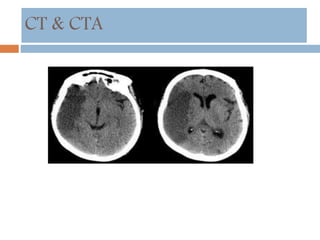
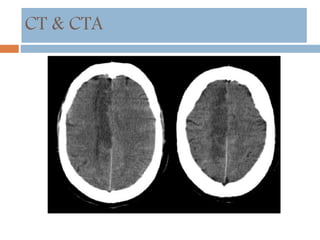
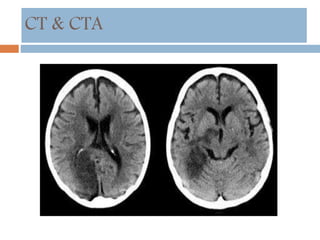
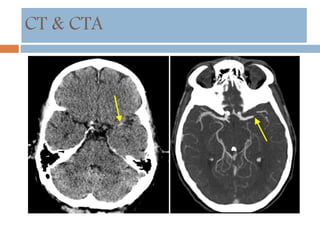
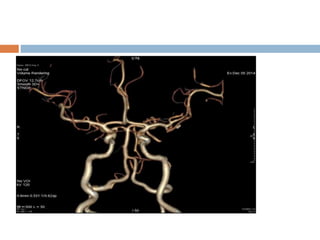
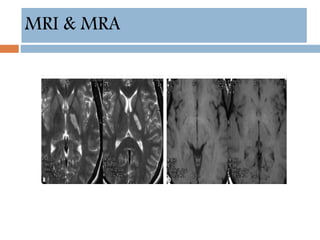
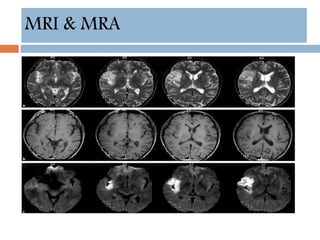
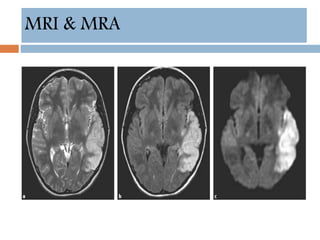
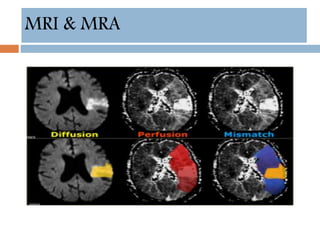
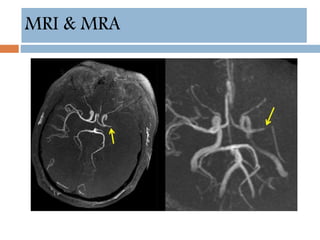
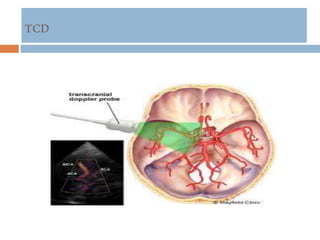
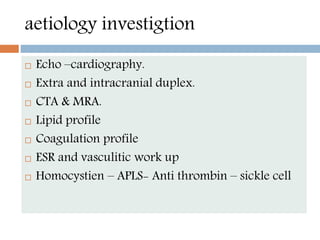
- Diagnosis involves neuroimaging such as CT, MRI and vascular imaging to identify the cause.
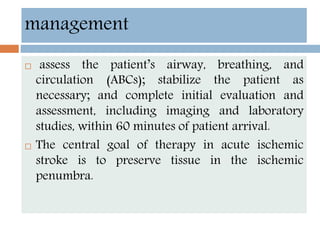
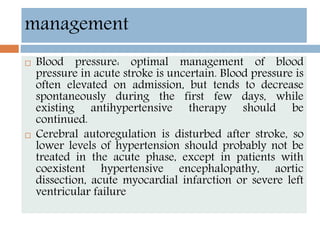
- Acute













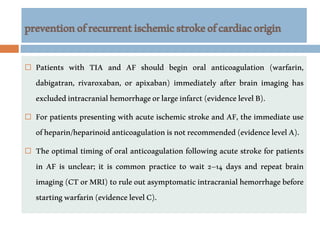
![Neuroprotection
Currently, data are inadequate to justify the
routine use of heparin or other anticoagulants in
the acute management of ischemic stroke.[126]
Patients with embolic stroke who have another
indication for anticoagulation (eg, atrial
fibrillation) may be placed on anticoagulation
therapy nonemergently, with the goal of
preventing further embolic disease; however, the
potential benefits of that intervention must be
weighed against the risk of hemorrhagic
transformation.[1] For more information](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ischaemicstrokeppt-160812010715/85/Ischaemic-stroke-55-320.jpg)