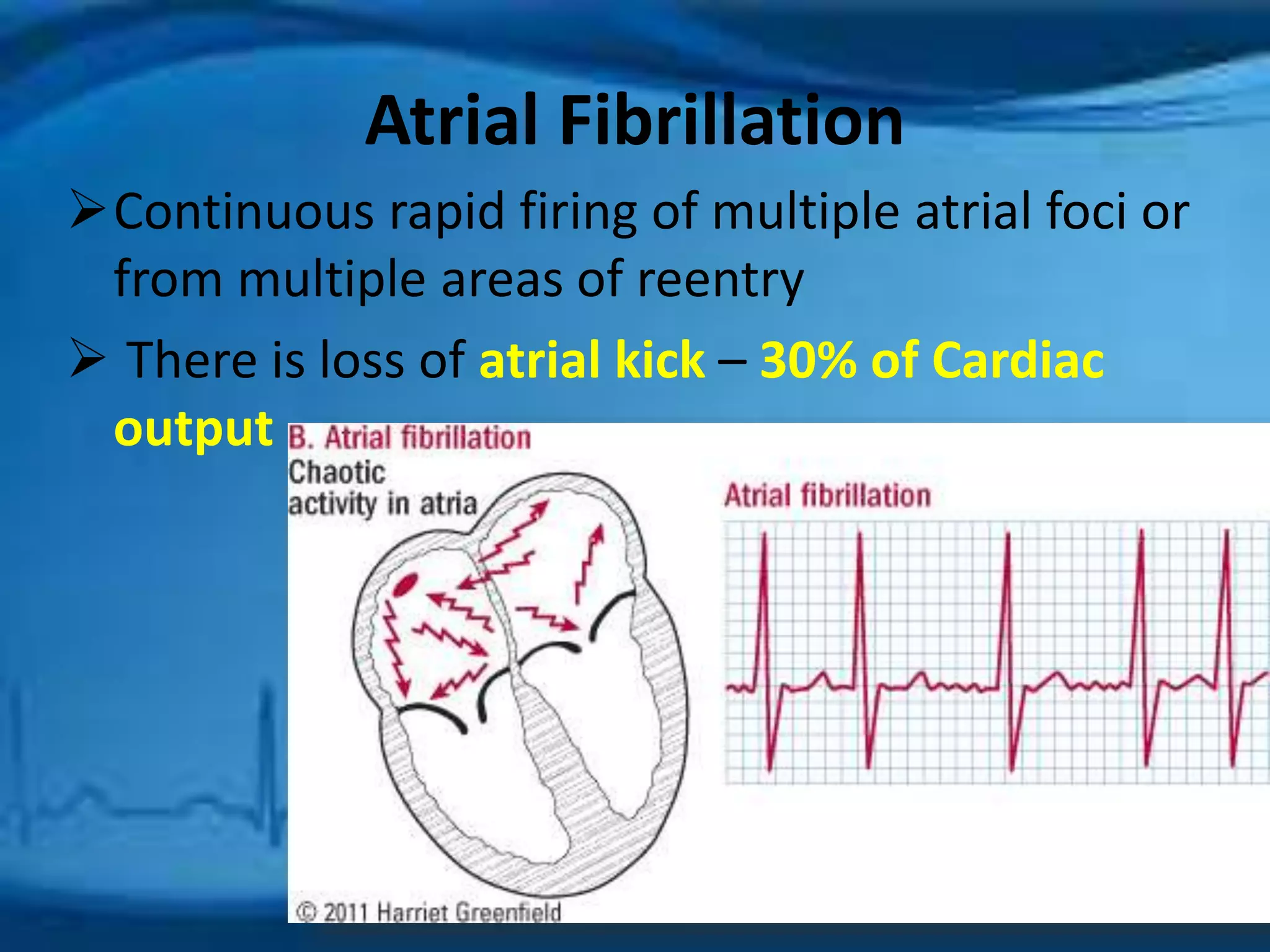
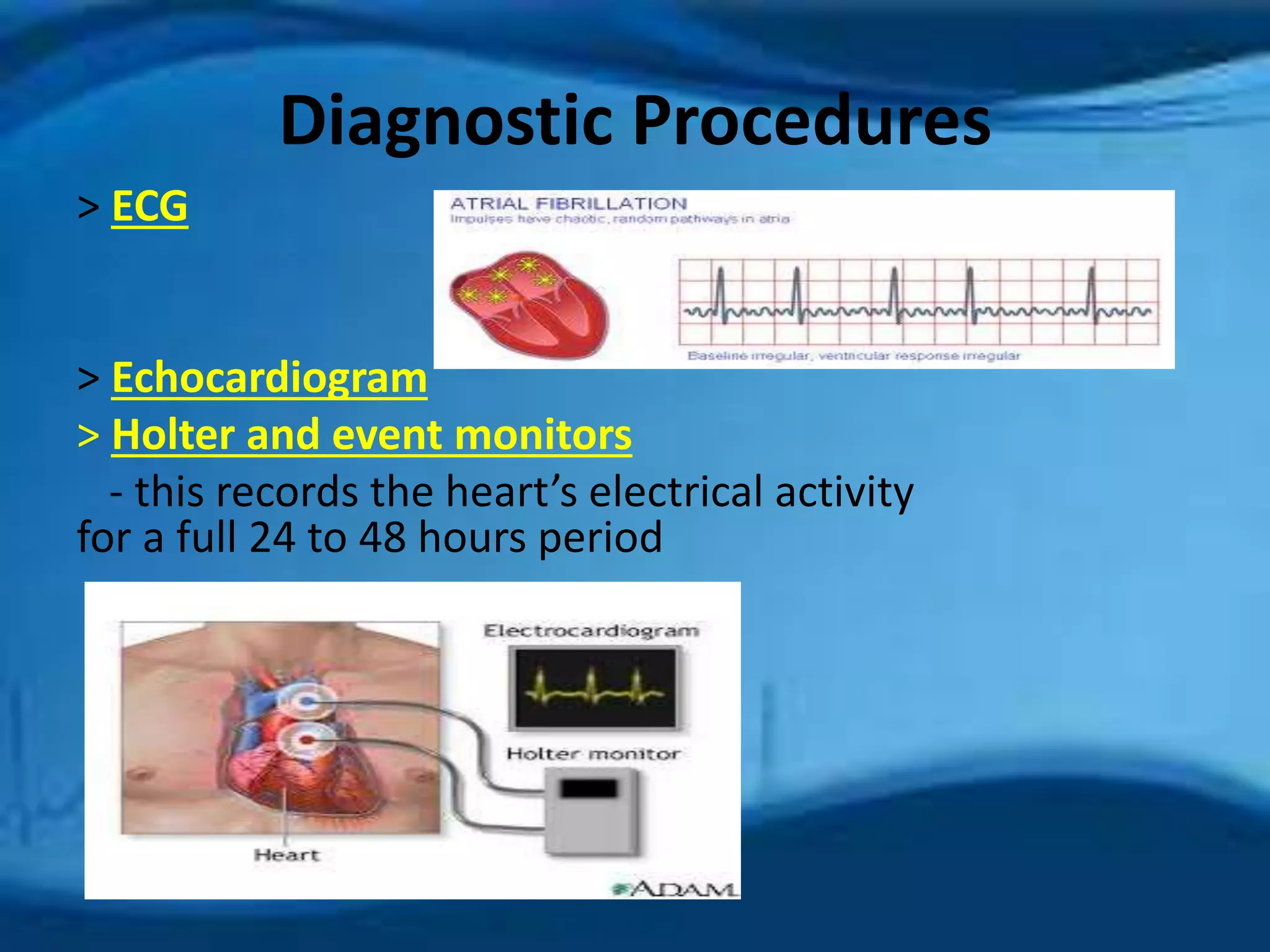
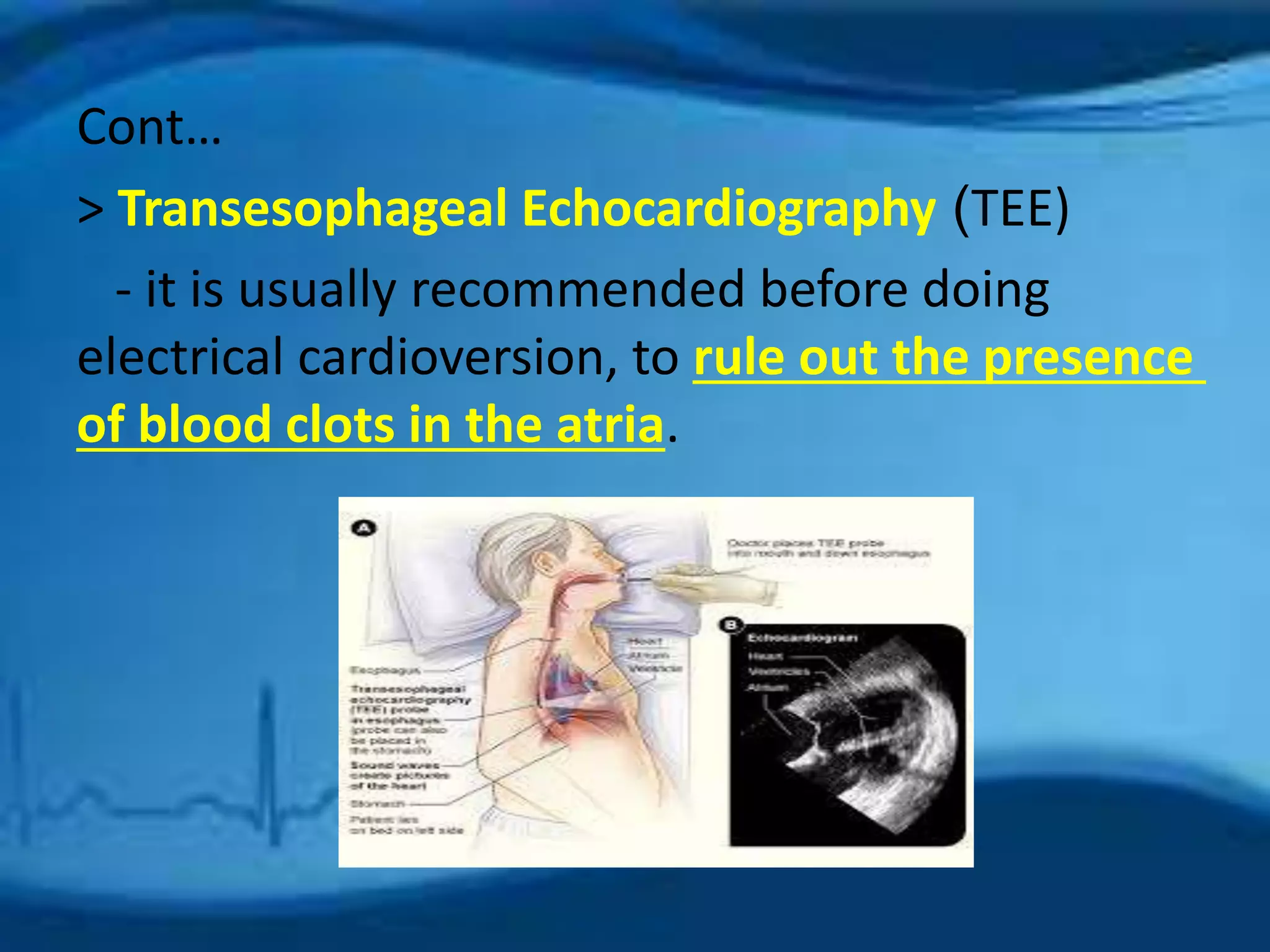
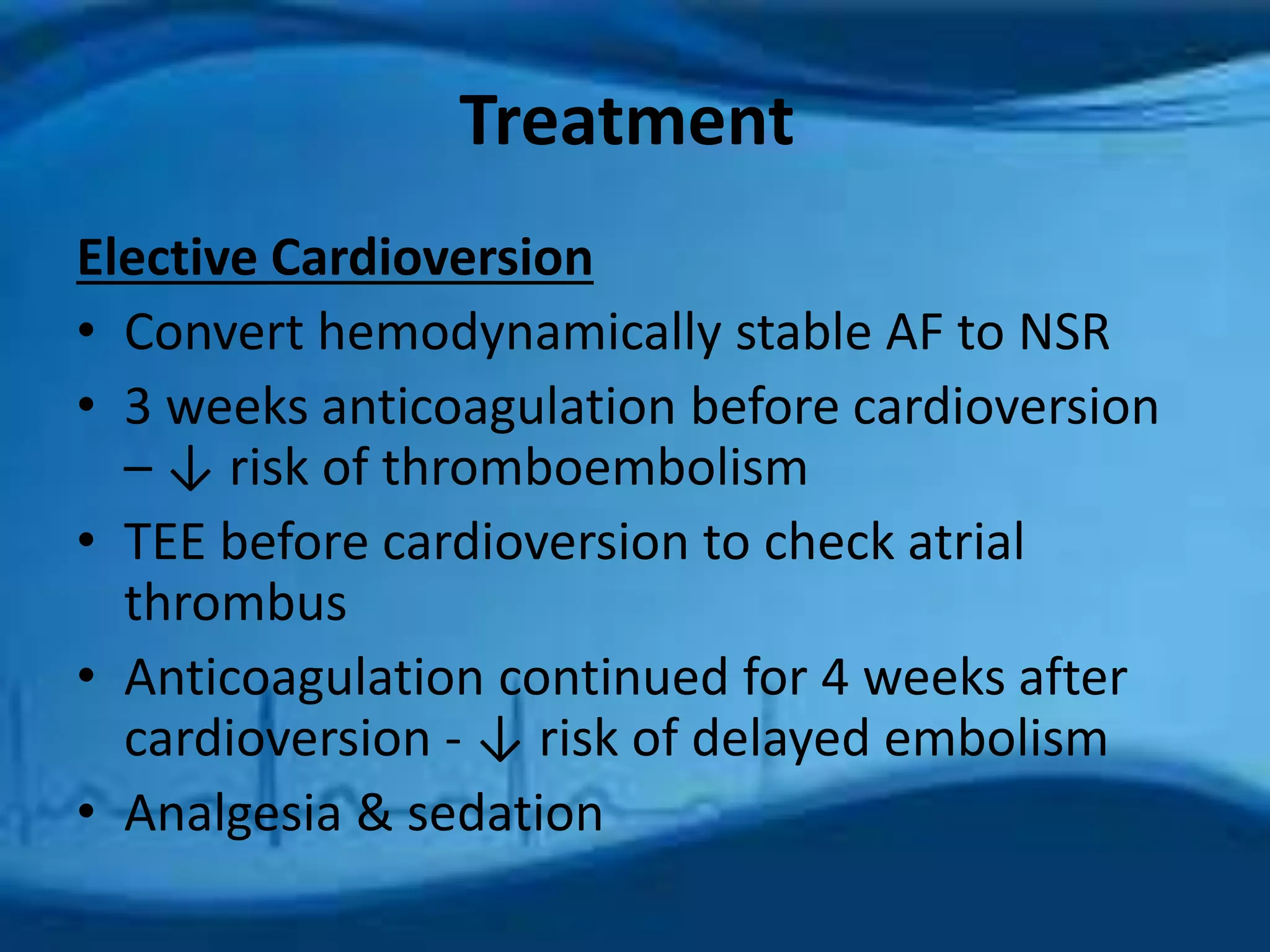
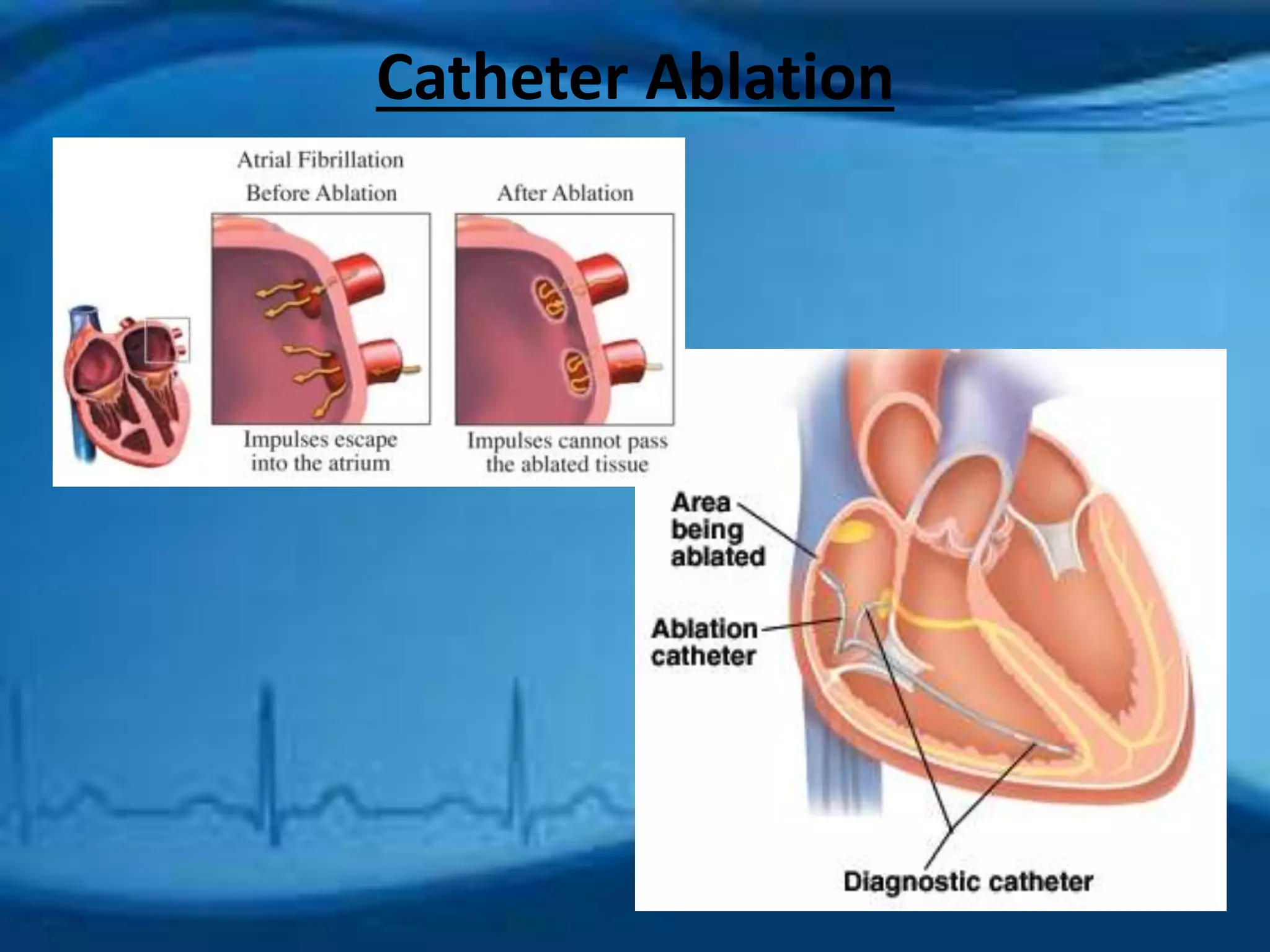
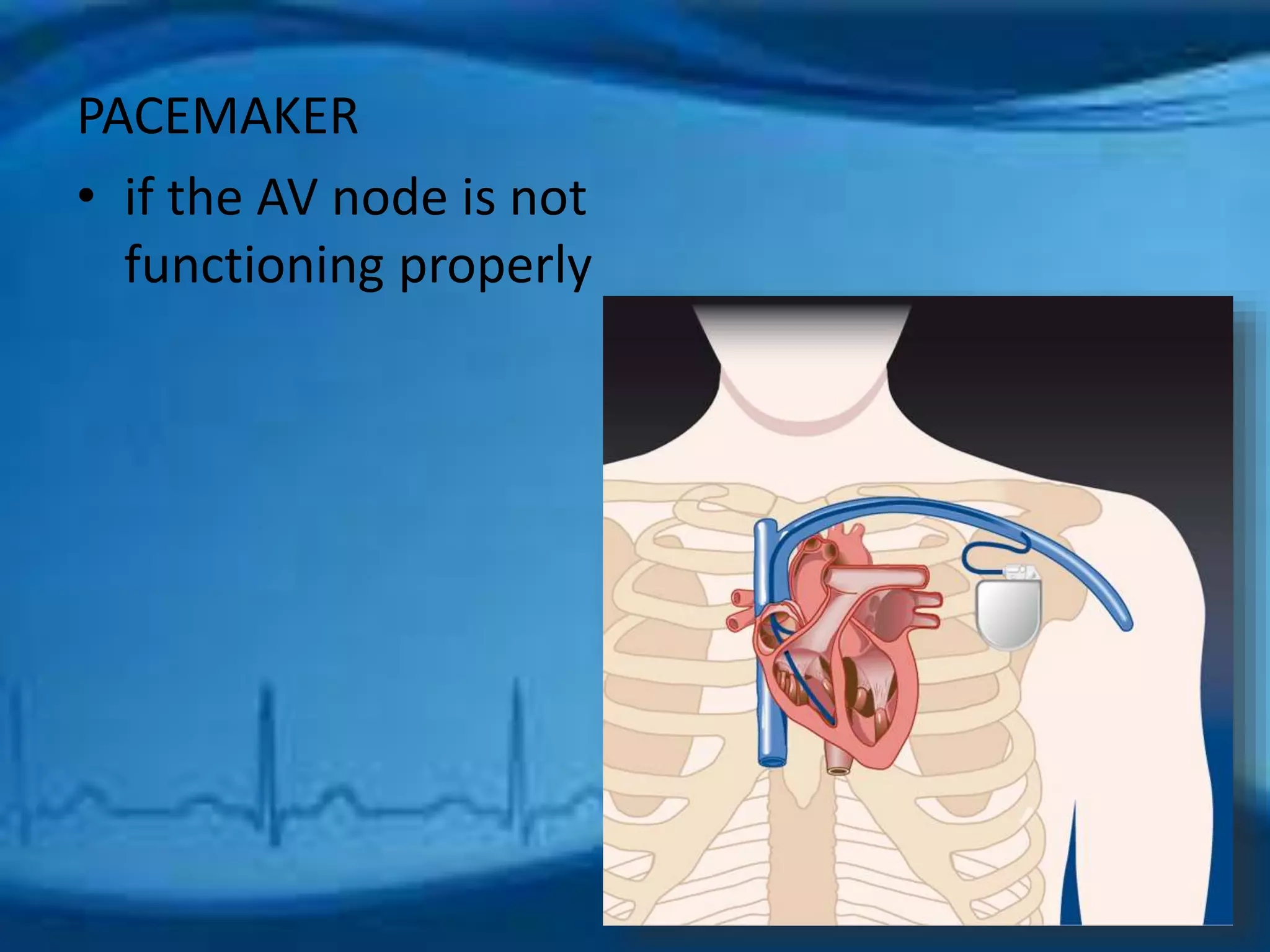
Atrial fibrillation is an irregular heartbeat caused by rapid and chaotic electrical activity in the atria. There are three main types - paroxysmal which comes and goes for less than 2 days, persistent for over 7 days and likely to recur, and permanent which cannot be reverted. Causes include hypertension, obesity, heart disease, alcohol, smoking, and other chronic conditions. Symptoms include fatigue, palpitations, dizziness, and chest pain. Diagnosis involves ECG, echocardiogram, Holter monitor and other tests. Treatment options include rate control with medications, rhythm control with antiarrhythmics like amiodarone, cardioversion, catheter ablation, or a pacemaker. A